How to implement an ERP system successfully – Implementing an ERP system successfully is a critical endeavor that can transform your business. This comprehensive guide will provide you with the knowledge and insights you need to navigate the complexities of ERP implementation and achieve optimal outcomes.
Project Planning
Effective ERP implementation hinges on meticulous project planning. Defining clear objectives and scope provides a roadmap for the project, ensuring alignment among stakeholders and reducing the likelihood of deviations. Establishing a realistic timeline and budget helps manage expectations, allocate resources efficiently, and mitigate delays or cost overruns.
Stakeholder Involvement
Involving key stakeholders throughout the planning process is crucial for their buy-in and support. Their insights and perspectives inform decision-making, ensuring the project aligns with organizational goals and meets the needs of end-users. Stakeholder engagement fosters a sense of ownership, promotes collaboration, and enhances the likelihood of successful implementation.
Data Migration
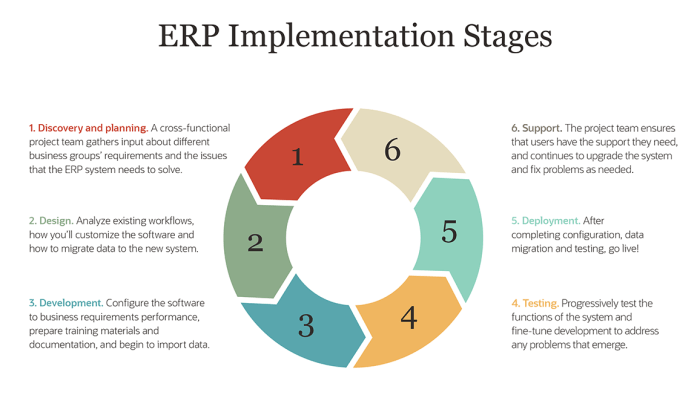
Data migration is a critical phase in any ERP implementation project. It involves the transfer of data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. The challenges associated with data migration include data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. Best practices for data migration include data cleansing, validation, and mapping.
Data cleansing involves removing duplicate data, correcting errors, and filling in missing values. Data validation involves checking the accuracy and completeness of data. Data mapping involves defining the relationships between data elements in the legacy system and the new ERP system.
Methods of Data Migration
There are three main methods of data migration: manual, automated, and hybrid. Manual data migration involves manually entering data into the new ERP system. This method is time-consuming and error-prone. Automated data migration involves using software tools to transfer data from the legacy system to the new ERP system.
This method is faster and more accurate than manual data migration. Hybrid data migration involves a combination of manual and automated data migration.
Change Management
Effective change management is crucial for successful ERP implementation. It involves preparing users for the upcoming changes, managing their expectations, and providing support throughout the transition. Neglecting change management can lead to resistance, low adoption rates, and project failure.
To communicate changes effectively, organizations should develop a clear communication plan that Artikels the rationale for the ERP system, its benefits, and the expected impact on users. Regular updates and open dialogue foster transparency and address concerns proactively.
Training and Support Programs
Training programs tailored to different user roles and responsibilities are essential. These programs should provide hands-on experience, simulation exercises, and access to resources to facilitate knowledge transfer and skill development.
Ongoing support through help desks, online forums, and mentorship programs ensures users have access to assistance when needed. By addressing user concerns promptly and effectively, organizations can minimize disruption and foster a positive change environment.
Process Optimization
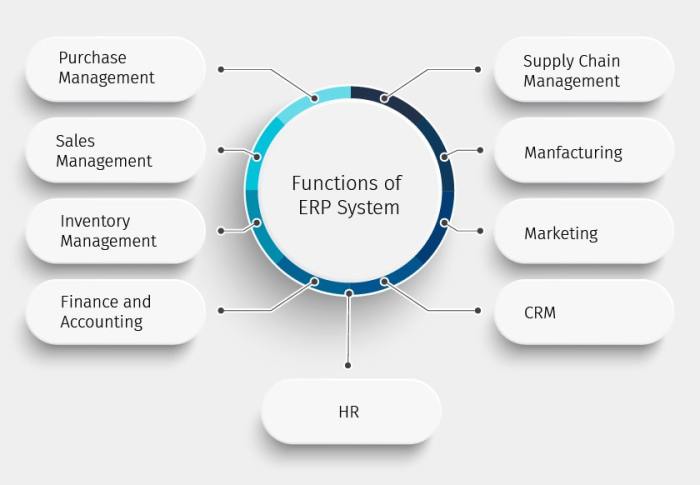
ERP systems play a crucial role in streamlining and optimizing business processes by providing a centralized platform that integrates various aspects of an organization’s operations. This integration eliminates redundant tasks, automates workflows, and enhances collaboration, leading to improved efficiency and cost reduction.
Benefits of ERP for Process Optimization
- Enhanced Data Visibility and Accessibility:ERP systems provide a single source of truth for all business data, enabling users to access real-time information and make informed decisions. This eliminates data silos and reduces the risk of errors caused by outdated or inconsistent information.
- Automated Workflows:ERP systems can automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as order processing, inventory management, and financial reporting. Automation frees up employees to focus on more strategic and value-added activities, increasing productivity and reducing operational costs.
- Improved Collaboration and Communication:ERP systems facilitate collaboration between different departments and teams by providing a shared platform for information sharing and communication. This breaks down barriers and improves coordination, leading to faster decision-making and enhanced operational efficiency.
Integration
ERP systems are not isolated entities within an organization. They interact with various other business applications, such as customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), and human capital management (HCM) systems. Integrating ERP with these applications is crucial for achieving a seamless flow of data and processes across the organization.Integrating ERP systems with other business applications provides several benefits.
It eliminates data silos, improves data accuracy and consistency, streamlines business processes, and enhances collaboration among different departments. For example, integrating ERP with CRM enables sales teams to access real-time customer data, such as order history, preferences, and support interactions.
This empowers them to provide personalized and efficient customer service.
Challenges and Best Practices of Data Integration
Data integration is a complex process that involves challenges such as data heterogeneity, data quality issues, and technical complexities. To overcome these challenges, organizations should adopt best practices such as:
- Establishing a data integration strategy that defines the scope, goals, and governance of the integration process.
- Using data integration tools and technologies that support various data formats and standards.
- Implementing data quality processes to ensure the accuracy and consistency of integrated data.
- Testing and validating integrated data to ensure its reliability and usability.
Examples of Successful ERP Integrations
Numerous organizations have successfully integrated ERP systems with other business applications to improve their business performance. Here are a few examples:
Nike
Integrated ERP with CRM to improve customer service and sales efficiency.
General Electric
Integrated ERP with SCM to optimize supply chain operations and reduce costs.
Coca-Cola
Integrated ERP with HCM to streamline HR processes and improve employee productivity.These successful integrations demonstrate the transformative power of ERP integration in enhancing business operations and driving organizational success.
Testing and Validation
Before an ERP system goes live, it is essential to conduct thorough testing and validation to ensure its accuracy, reliability, and functionality. This process helps identify and resolve any potential issues, ensuring a smooth transition and minimizing the risk of disruptions during implementation.
Various types of testing should be performed, including:
- Unit testing:Verifies the functionality of individual modules or components of the ERP system.
- Integration testing:Ensures that different modules of the ERP system work together seamlessly and exchange data effectively.
- System testing:Evaluates the overall functionality of the ERP system as a whole, including its interactions with other systems and applications.
- User acceptance testing (UAT):Involves end-users testing the ERP system to ensure it meets their requirements and expectations.
User acceptance testing is crucial for successful ERP implementation. It allows users to provide feedback, identify any usability issues, and ensure that the system meets their business needs. During UAT, users should perform real-world tasks and scenarios to validate the system’s functionality and identify areas for improvement.
System verification involves comparing the ERP system’s performance against established requirements and specifications. It ensures that the system meets the agreed-upon functional and technical criteria and aligns with the organization’s business objectives.
By following these best practices for testing and validation, organizations can minimize the risk of implementation failures and ensure that their ERP system is ready for a successful go-live.
Deployment and Go-Live
ERP system deployment and go-live are critical stages that require careful planning and execution. A well-defined go-live plan ensures a smooth transition from the old system to the new ERP system.
The deployment phase involves installing the ERP software on the organization’s servers, configuring it according to the specific requirements, and migrating data from the legacy system.
Go-Live Plan
A go-live plan Artikels the steps and activities necessary to transition to the new ERP system. It includes:
- Timeline for data migration, testing, and training
- Communication plan to inform users about the transition
- Support plan to address any issues during go-live
- Rollback plan in case of unforeseen circumstances
Ensuring a Smooth Go-Live
To ensure a successful go-live:
- Conduct thorough testing and validation to identify and resolve any issues.
- Provide comprehensive training to users on the new system’s functionality.
- Establish a dedicated support team to assist users during the transition.
- Monitor the system closely and address any issues promptly.
- Communicate regularly with users to provide updates and address concerns.
Post-Implementation Support
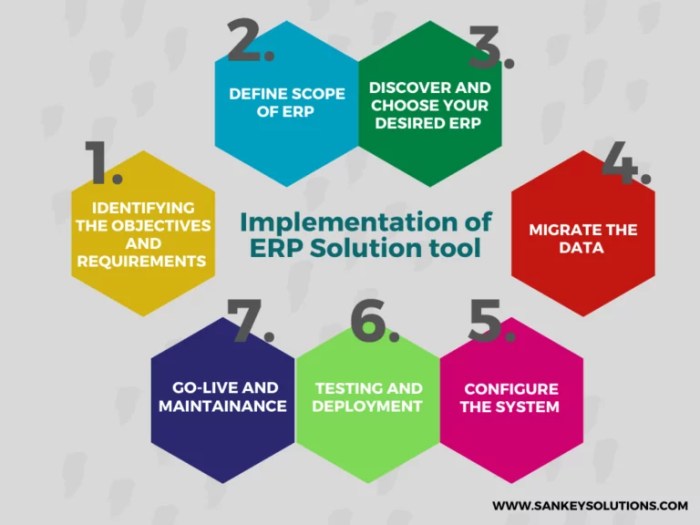
Ensuring ongoing support after ERP implementation is crucial for sustained success. It helps organizations address unforeseen challenges, optimize system utilization, and maximize return on investment.
Post-implementation support encompasses various types of assistance, including:
Technical Support
- Troubleshooting hardware and software issues
- Providing technical guidance and documentation
- Applying software updates and patches
Functional Support
- Answering user queries and providing training
- Assisting with process optimization and system configuration
- Monitoring system performance and identifying areas for improvement
Change Management Support
- Facilitating user adoption and managing resistance to change
- Providing training and communication to support ongoing process improvements
- Monitoring and evaluating the impact of change on users and business processes
Best Practices for Managing User Feedback and Resolving Issues, How to implement an ERP system successfully
- Establish a clear process for collecting and addressing user feedback
- Prioritize issues based on impact and urgency
- Communicate regularly with users to keep them informed of progress and solutions
- Use a ticketing system or other tracking tool to manage issues and monitor resolution times
Vendor Selection: How To Implement An ERP System Successfully
Selecting the right ERP vendor is crucial for a successful implementation. Consider the following factors:
Vendor Capabilities
- Evaluate the vendor’s experience, industry knowledge, and technical capabilities.
- Assess their understanding of your business requirements and ability to provide tailored solutions.
- Inquire about their research and development (R&D) efforts to ensure they stay up-to-date with industry trends.
Vendor References
Contact existing customers to obtain feedback on the vendor’s performance, support, and ability to meet expectations.
Negotiating a Vendor Contract
- Clearly define the scope of work, deliverables, timelines, and costs.
- Establish performance metrics and service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure accountability.
- Consider intellectual property (IP) rights, data ownership, and termination clauses.
System Customization
ERP systems can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization. This can involve modifying the system’s functionality, user interface, or data structure.Customization can provide several benefits, including:
- Improved fit with business processes
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced user satisfaction
However, customization also carries some risks:
- Increased cost and complexity
- Reduced vendor support
- Potential for errors and system instability
It is important to carefully consider the benefits and risks of customization before making a decision. In general, it is best to keep customization to a minimum and only customize those aspects of the system that are essential to the organization’s business processes.
Balancing Customization with Vendor Support
When customizing an ERP system, it is important to balance the need for customization with the need for vendor support. Too much customization can make it difficult to get support from the vendor, as they may not be familiar with the customized code.
This can lead to delays and increased costs.It is important to work closely with the vendor to determine which customizations are necessary and which can be avoided. The vendor can also provide guidance on how to customize the system in a way that minimizes the risk of errors and system instability.
Examples of Successful ERP Customizations
There are many examples of successful ERP customizations that have improved business outcomes. For example, one company customized its ERP system to automate its order fulfillment process. This resulted in a significant reduction in order processing time and a corresponding increase in customer satisfaction.Another company customized its ERP system to integrate with its CRM system.
This allowed the company to have a single view of its customers, which improved sales and marketing effectiveness.These are just a few examples of the many ways that ERP systems can be customized to improve business outcomes. By carefully considering the benefits and risks of customization, and by working closely with the vendor, organizations can achieve the full potential of their ERP systems.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous evaluation and improvement of an ERP system is crucial for its long-term effectiveness. Ongoing monitoring ensures the system remains aligned with evolving business needs and technological advancements.User feedback plays a vital role in identifying areas for improvement. Regular surveys and focus groups can gather insights on system usability, functionality, and potential pain points.
Data analysis, including usage logs and performance metrics, provides quantitative evidence of system effectiveness and areas where optimizations can be made.Continuous improvement initiatives can lead to significant benefits, such as:
- Increased system efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced user satisfaction and adoption
- Reduced costs and improved ROI
- Improved compliance and risk management
Examples of continuous improvement initiatives include:
- Automating manual processes to reduce errors and increase efficiency
- Implementing dashboards and reporting tools to improve data visibility and decision-making
- Integrating with other systems to streamline workflows and eliminate data silos
- Providing ongoing training and support to users to ensure optimal system utilization
Final Conclusion
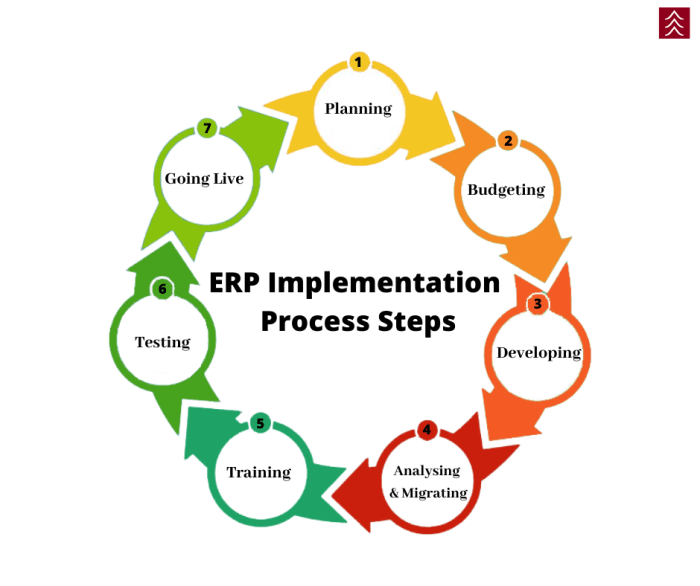
By following the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can increase your chances of successfully implementing an ERP system that meets your business needs and drives growth. Remember, the key to success lies in careful planning, effective change management, and ongoing evaluation and improvement.
FAQ Summary
What are the key challenges of ERP implementation?
Some common challenges include data migration, change management, and process optimization. It’s crucial to address these challenges proactively to ensure a smooth implementation.
How can I ensure successful data migration during ERP implementation?
Data migration is a critical step. Ensure data accuracy and completeness by involving IT professionals, cleansing and validating data, and testing the migration process thoroughly.
What is the role of change management in ERP implementation?
Effective change management is essential for user adoption. Communicate changes clearly, address concerns, provide training and support, and involve key stakeholders throughout the process.