ERP system selection is a critical decision for businesses looking to streamline their operations and gain a competitive edge. This comprehensive guide will take you through the entire process, from defining your requirements to selecting and implementing the best ERP system for your organization.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are software solutions that integrate various business processes into a single, centralized platform. They provide real-time data visibility, improve collaboration, and automate tasks, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved decision-making.
ERP System Overview
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a comprehensive software suite that integrates and manages core business processes across an organization. It provides a single, unified platform for data and processes, streamlining operations and improving efficiency.
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved data accuracy and consistency:ERP systems eliminate data duplication and ensure that all departments use the same data.
- Increased efficiency and productivity:By automating processes and reducing manual tasks, ERP systems free up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Enhanced collaboration and communication:ERP systems provide a central platform for employees to share information and collaborate on projects.
- Improved decision-making:ERP systems provide real-time data and insights that help managers make informed decisions.
- Reduced costs:ERP systems can help organizations reduce costs by eliminating redundant processes and improving operational efficiency.
Key Components and Modules
ERP systems typically consist of the following core modules:
- Financial Management:Manages financial transactions, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, and general ledger.
- Human Capital Management:Manages employee information, including payroll, benefits, and performance evaluations.
- Supply Chain Management:Manages the flow of goods and materials, including purchasing, inventory, and logistics.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):Manages customer interactions, including sales, marketing, and customer service.
- Manufacturing:Manages production processes, including planning, scheduling, and quality control.
Industries and Businesses That Use ERP Systems
ERP systems are used by organizations of all sizes and across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Healthcare
- Financial services
- Government
- Non-profit organizations
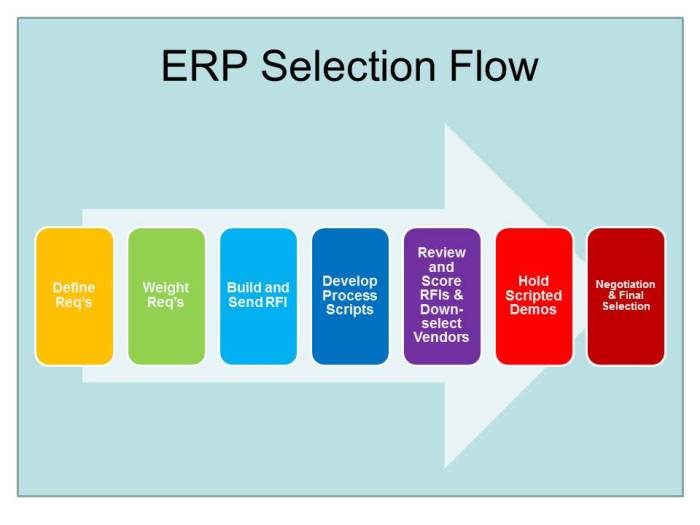
ERP System Selection Process
ERP system selection is a complex process that involves multiple steps and stakeholders. It is important to follow a structured approach to ensure that the selected ERP system meets the organization’s needs and objectives.The ERP system selection process typically involves the following steps:
- Define business requirements and objectives.
- Identify and evaluate potential ERP vendors.
- Develop a request for proposal (RFP).
- Evaluate vendor responses.
- Select an ERP vendor.
- Implement the ERP system.
Importance of Defining Business Requirements and Objectives
The first step in the ERP system selection process is to define the organization’s business requirements and objectives. This involves understanding the organization’s current business processes, identifying areas for improvement, and determining the specific goals that the ERP system should help the organization achieve.Defining business requirements and objectives is important because it helps to ensure that the selected ERP system is a good fit for the organization.
It also helps to avoid costly mistakes and delays during the implementation process.
Role of Stakeholders in the Selection Process
Stakeholders play a critical role in the ERP system selection process. Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have a vested interest in the success of the ERP system implementation. They may include executives, managers, employees, customers, and suppliers.It is important to involve stakeholders in the selection process early on.
This helps to ensure that their needs and concerns are taken into account. It also helps to build buy-in for the ERP system and increase the likelihood of a successful implementation.
Vendor Evaluation and Selection: ERP System Selection
Vendor evaluation and selection is a critical step in the ERP system selection process. It involves assessing the capabilities of potential vendors and their ability to meet the organization’s specific requirements.
There are several key criteria that should be considered when evaluating ERP vendors:
- Industry experience:The vendor should have experience in implementing ERP systems in organizations similar to yours in terms of size, industry, and complexity.
- Product functionality:The vendor’s ERP system should offer the functionality that you need to support your business processes.
- Technical capabilities:The vendor should have the technical expertise to implement and support your ERP system.
- Financial stability:The vendor should be financially stable to ensure that they will be able to support your ERP system over the long term.
- Customer references:The vendor should be able to provide references from customers who have successfully implemented their ERP system.
Vendor Demonstrations and Site Visits
Vendor demonstrations and site visits are an important part of the vendor evaluation process. They allow you to see the ERP system in action and to ask questions to the vendor about its capabilities.
When attending a vendor demonstration, be sure to focus on the following:
- The user interface: Is the ERP system easy to use and navigate?
- The functionality: Does the ERP system offer the functionality that you need?
- The integration: Can the ERP system be integrated with your other business systems?
When conducting a site visit, be sure to talk to the vendor’s customers about their experiences with the ERP system.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an ERP Vendor
When selecting an ERP vendor, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The vendor’s overall fit with your organization:The vendor should be a good fit for your organization in terms of size, culture, and values.
- The vendor’s ability to meet your specific requirements:The vendor should be able to meet your specific requirements in terms of functionality, technical capabilities, and financial stability.
- The vendor’s commitment to customer satisfaction:The vendor should be committed to providing excellent customer service and support.
4. Implementation Planning and Management
ERP implementation is a complex and multifaceted process that requires careful planning and management. The key phases of ERP implementation include:
- Planning: This phase involves defining the project scope, objectives, and timelines. It also includes identifying the resources that will be needed to implement the ERP system.
- Analysis: This phase involves gathering and analyzing data about the organization’s current business processes. This information is used to design the new ERP system and to identify any changes that will need to be made to the organization’s processes.
- Design: This phase involves designing the new ERP system. This includes defining the system’s architecture, functionality, and user interface.
- Development: This phase involves developing the new ERP system. This includes coding the system and testing it to ensure that it meets the organization’s requirements.
- Deployment: This phase involves deploying the new ERP system to the organization’s users. This includes training users on the new system and providing them with support.
- Maintenance: This phase involves maintaining the ERP system after it has been deployed. This includes making updates to the system and fixing any bugs that may occur.
Change management and user training are critical to the success of any ERP implementation. Change management involves helping employees to understand the changes that the new ERP system will bring and to adapt to those changes. User training involves teaching employees how to use the new ERP system.
There are a number of risks associated with ERP implementation, including:
- Cost overruns
- Time delays
- System failure
- Data loss
- User resistance
There are a number of best practices that can be used to manage ERP implementation risks, including:
- Establishing a clear project plan and budget
- Getting buy-in from key stakeholders
- Involving users in the implementation process
- Testing the system thoroughly before deployment
- Providing ongoing support to users
System Integration and Customization
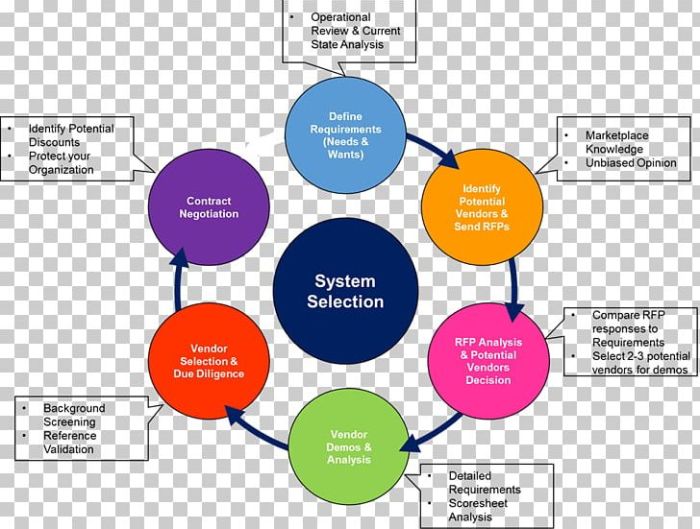
Integrating ERP systems with other applications and customizing them to meet specific business needs are crucial aspects of successful ERP implementations.
ERP systems are designed to integrate with a variety of other applications, including customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), and financial management systems. This integration allows businesses to create a single, unified view of their operations and improve data accuracy and consistency.
However, integrating ERP systems with other applications can be challenging. Some of the challenges include:
- Data compatibility: Different applications may use different data formats, which can make it difficult to integrate them.
- Business process alignment: The business processes supported by different applications may not be aligned, which can lead to inefficiencies and errors.
- Technical complexity: Integrating ERP systems with other applications can be technically complex and time-consuming.
Despite these challenges, integrating ERP systems with other applications can provide significant benefits, including:
- Improved data accuracy and consistency
- Increased operational efficiency
- Reduced costs
- Improved customer service
In addition to integrating with other applications, ERP systems can also be customized to meet specific business needs. This customization can include:
- Adding new fields or tables to the database
- Modifying the user interface
- Creating custom reports
- Developing new integrations with other applications
Customizing ERP systems can provide a number of benefits, including:
- Improved fit with business processes
- Increased user adoption
- Reduced costs
However, customizing ERP systems can also be challenging. Some of the challenges include:
- Increased complexity: Customizations can make ERP systems more complex and difficult to manage.
- Reduced vendor support: Vendors may not support customized ERP systems.
- Increased risk of errors: Customizations can introduce errors into ERP systems.
Despite these challenges, customizing ERP systems can provide significant benefits for businesses that have unique needs. When considering customizing an ERP system, it is important to carefully weigh the benefits and risks.
Examples of Successful ERP System Integrations and Customizations
There are many examples of successful ERP system integrations and customizations. One example is the integration of an ERP system with a CRM system. This integration allows businesses to track customer interactions and sales activities in a single system. This can improve customer service and increase sales.
Another example is the customization of an ERP system to meet the specific needs of a manufacturing company. This customization included the addition of new fields to the database to track production data. This customization improved the company’s ability to track and manage its production process.
6. Data Migration and Conversion
Data migration and conversion are crucial steps in ERP system implementations. They involve transferring data from legacy systems or other sources into the new ERP system. Successful data migration ensures that the ERP system contains accurate and complete data, which is essential for effective decision-making and operations.
Data Migration Techniques and Tools
There are various data migration techniques, including:
- Batch Migration:Moves data in bulk from the source to the target system.
- Incremental Migration:Transfers data gradually in smaller batches over time.
- Real-Time Migration:Moves data in real-time as it is generated or updated.
Data migration tools can automate the process and reduce errors. They can map data fields, transform data formats, and validate data integrity.
Best Practices for Data Integrity, ERP system selection
To ensure data integrity during migration, it is important to follow best practices such as:
- Data Validation:Verifying the accuracy and completeness of data before migration.
- Data Cleansing:Removing duplicate, invalid, or incomplete data.
- Data Transformation:Converting data into a format compatible with the new ERP system.
- Data Testing:Ensuring that the migrated data is accurate and functional in the new system.
ERP System Optimization and Maintenance
Optimizing and maintaining an ERP system is crucial for ensuring its efficiency and longevity. This involves implementing strategies to enhance system performance, addressing regular updates and maintenance, and establishing best practices for monitoring and troubleshooting.
Strategies for Optimizing ERP System Performance
Optimizing ERP system performance involves implementing measures to enhance its speed, reliability, and efficiency. Key strategies include:
- Hardware upgrades:Upgrading hardware components such as servers, storage, and network infrastructure can improve system performance significantly.
- Database optimization:Optimizing database structures, indexes, and queries can reduce data retrieval times and improve overall system responsiveness.
- Code optimization:Reviewing and optimizing custom code and scripts can eliminate inefficiencies and enhance system performance.
- Process automation:Automating repetitive tasks and workflows can streamline processes, reduce errors, and improve system efficiency.
- Performance monitoring:Regularly monitoring system performance metrics such as response times, resource utilization, and error logs can identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
Importance of Regular System Updates and Maintenance
Regular system updates and maintenance are essential for ensuring the ERP system remains up-to-date, secure, and functioning optimally. Updates typically include bug fixes, security patches, and new features that enhance system functionality and stability.
- Security updates:Installing security updates promptly helps protect the ERP system from vulnerabilities and cyber threats.
- Bug fixes:Updates often include fixes for reported bugs and errors, improving system stability and reliability.
- New features:Updates may introduce new features and enhancements that improve system capabilities and user experience.
- Performance improvements:Updates can include optimizations and enhancements that improve system performance and efficiency.
Best Practices for Monitoring and Troubleshooting ERP Systems
Effective monitoring and troubleshooting practices are essential for proactively identifying and resolving issues within the ERP system. Best practices include:
- Establish monitoring tools:Implementing monitoring tools such as performance monitors, log analyzers, and alert systems can provide real-time visibility into system performance and identify potential issues.
- Define performance thresholds:Establishing performance thresholds and alerts can trigger notifications when certain metrics exceed predefined limits, allowing for prompt investigation and resolution.
- Document troubleshooting procedures:Creating documented troubleshooting procedures for common issues can guide users through the necessary steps to resolve problems quickly and efficiently.
- Regular system audits:Conducting regular system audits can identify potential issues, configuration errors, or security vulnerabilities that may impact system performance or stability.
- User training:Providing training to users on how to identify and report issues can facilitate early detection and resolution, reducing system downtime.
ERP System Benefits and ROI
ERP systems offer a wide range of benefits that can significantly enhance business operations and drive ROI. These benefits can be quantified and measured to demonstrate the value of the ERP investment.
Quantifying Potential Benefits
The potential benefits of ERP system implementations can be quantified in several ways, including:
- Increased efficiency:Reduced time spent on manual tasks, streamlined processes, and improved communication can lead to significant efficiency gains.
- Cost reduction:Lowered operating costs through automation, reduced inventory levels, and improved purchasing practices.
- Improved customer service:Enhanced customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities, faster order fulfillment, and improved product quality.
- Increased revenue:Expanded sales opportunities, improved marketing effectiveness, and better product development.
- Improved decision-making:Real-time access to data and analytics provides insights for informed decision-making.
Measuring ERP System ROI
Several methods can be used to measure the ROI of an ERP system implementation, including:
- Financial metrics:Return on investment (ROI), net present value (NPV), and payback period.
- Operational metrics:Efficiency gains, cost reductions, and improved customer service.
- Strategic metrics:Improved decision-making, increased revenue, and expanded sales opportunities.
Case Studies of Successful ERP Implementations
Numerous businesses have successfully realized the benefits of ERP system implementations. Here are a few case studies:
- Nike:Implemented an ERP system to improve supply chain management, resulting in a 20% reduction in inventory levels and a 15% increase in sales.
- Toyota:Implemented an ERP system to streamline production processes, resulting in a 10% increase in productivity and a 5% reduction in manufacturing costs.
- Walmart:Implemented an ERP system to improve inventory management, resulting in a 15% reduction in inventory levels and a 10% increase in sales.
These case studies demonstrate the significant benefits that ERP systems can deliver to businesses of all sizes and industries. By quantifying the potential benefits and measuring the ROI, organizations can make informed decisions about investing in an ERP system.
Trends and Innovations in ERP Systems

ERP systems are continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. Emerging technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and mobile devices are having a significant impact on the way ERP systems are designed and used.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a major trend in the ERP market. Cloud-based ERP systems offer several advantages over on-premises systems, including lower costs, greater flexibility, and easier access to data. As a result, more and more businesses are choosing to move their ERP systems to the cloud.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is another emerging technology that is having a significant impact on ERP systems. AI-powered ERP systems can automate many tasks that are currently performed manually, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. AI can also be used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of ERP systems.
Mobile Devices
Mobile devices are becoming increasingly popular for accessing ERP systems. Mobile ERP apps allow employees to access ERP data and functionality from anywhere, at any time. This can improve productivity and collaboration, and make it easier for businesses to make informed decisions.
The Future of ERP Systems
The future of ERP systems is bright. As emerging technologies continue to evolve, ERP systems will become even more powerful and versatile. ERP systems will play an increasingly important role in helping businesses to improve their operations and achieve their goals.
ERP System Selection Best Practices

Successful ERP system selection is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize their operations. By adhering to established best practices, organizations can increase their chances of selecting the right ERP system that aligns with their unique requirements and delivers substantial value.
Key best practices for ERP system selection include:
- Define clear business objectives:Identify the specific pain points, goals, and expected outcomes that the ERP system should address.
- Assemble a cross-functional team:Engage stakeholders from various departments, including finance, operations, IT, and end-users, to ensure diverse perspectives and buy-in.
- Conduct thorough research:Explore different ERP vendors, their offerings, and industry reputation. Attend webinars, read case studies, and seek references from existing customers.
- Create a detailed RFP:Develop a comprehensive request for proposal (RFP) that Artikels the business requirements, evaluation criteria, and vendor expectations.
- Evaluate vendors rigorously:Conduct thorough vendor demonstrations, assess their technical capabilities, financial stability, and customer support.
- Negotiate and contract carefully:Review the vendor’s contract thoroughly, including pricing, implementation timelines, and ongoing support arrangements.
Checklist for ERP Selection Journey
To ensure a successful ERP selection journey, businesses should consider the following:
- Identify the scope of the ERP implementation.
- Assess the organization’s readiness for change.
- Develop a realistic budget and timeline.
- Secure executive sponsorship and support.
- Establish a clear communication plan.
- Consider industry-specific requirements.
- Evaluate the vendor’s experience and expertise.
- Assess the vendor’s financial stability and reputation.
- Plan for ongoing maintenance and support.
Insights from Industry Experts
Industry experts emphasize the importance of a thorough and well-planned ERP selection process. According to Gartner, “Organizations that take the time to carefully evaluate their ERP options are more likely to achieve successful implementations that deliver significant business value.”
ERP expert Dave Garrett advises businesses to “avoid the temptation to rush the selection process. Take the time to understand your business needs, research vendors thoroughly, and negotiate a contract that protects your interests.”
Common ERP System Selection Pitfalls
ERP system selection is a complex and challenging process, and many businesses fall into common pitfalls that can lead to a failed implementation. These pitfalls can include:
Lack of Proper Planning
One of the most common pitfalls is a lack of proper planning. Businesses often rush into ERP selection without taking the time to define their business needs, establish a project timeline, and allocate sufficient resources. This can lead to a poorly defined project scope, unrealistic expectations, and a lack of stakeholder buy-in.
Inadequate Vendor Evaluation
Another common pitfall is inadequate vendor evaluation. Businesses often rely on vendor presentations and marketing materials to make their selection, without conducting a thorough evaluation of the vendor’s capabilities, financial stability, and track record. This can lead to selecting a vendor that is not a good fit for the business, or that is unable to deliver on its promises.
Underestimating the Cost and Complexity of Implementation
Many businesses underestimate the cost and complexity of ERP implementation. This can lead to budget overruns, project delays, and disruption to business operations. It is important to carefully estimate the total cost of ownership (TCO) of an ERP system, including hardware, software, implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance.
Lack of Change Management
ERP implementation can have a significant impact on business processes and workflows. Businesses that fail to adequately manage change can encounter resistance from employees, disruption to operations, and a lack of adoption of the new system. It is important to develop a comprehensive change management plan that includes communication, training, and support for employees throughout the implementation process.
Poor Data Management
ERP systems rely on accurate and timely data to function effectively. Businesses that fail to properly manage their data can encounter data quality issues, integration problems, and a lack of visibility into key business metrics. It is important to establish a data governance framework and implement data cleansing and integration processes to ensure the accuracy and reliability of data in the ERP system.
Examples of Businesses that have Encountered ERP System Selection Pitfalls
- In 2016, the UK government abandoned a £10 billion ERP project after it was plagued by delays, cost overruns, and technical problems.
- In 2015, the Australian Department of Defence scrapped a $1 billion ERP project after it failed to meet the department’s requirements.
- In 2014, the US Department of Veterans Affairs awarded a $10 billion ERP contract to Cerner Corporation. However, the project was plagued by delays, cost overruns, and technical problems, and was eventually terminated in 2018.
These are just a few examples of the many businesses that have encountered ERP system selection pitfalls. By avoiding these pitfalls, businesses can increase their chances of a successful ERP implementation.
End of Discussion
ERP system selection is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can increase your chances of selecting the right system and achieving the desired benefits. Remember to involve key stakeholders, conduct thorough vendor evaluations, and consider the long-term implications of your decision.
With the right ERP system in place, your business can unlock a world of possibilities and gain a significant competitive advantage.
FAQ Guide
What is the purpose of an ERP system?
An ERP system integrates various business processes, such as finance, supply chain management, and human resources, into a single platform. It provides real-time data visibility, improves collaboration, and automates tasks, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved decision-making.
What are the benefits of implementing an ERP system?
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy and consistency, increased operational efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced collaboration, and better decision-making.
What are the key steps involved in the ERP system selection process?
The ERP system selection process typically involves defining business requirements, evaluating vendors, conducting demos and site visits, selecting a vendor, and implementing the system.
What are some common pitfalls to avoid during ERP system selection?
Common pitfalls to avoid during ERP system selection include rushing the process, failing to involve key stakeholders, not defining clear requirements, and underestimating the cost and complexity of implementation.