ERP system integration is a transformative journey that unlocks a world of possibilities for businesses seeking to streamline operations, optimize decision-making, and gain a competitive edge. Embark on this enlightening exploration as we delve into the intricacies of ERP integration, uncovering its challenges, benefits, and best practices.
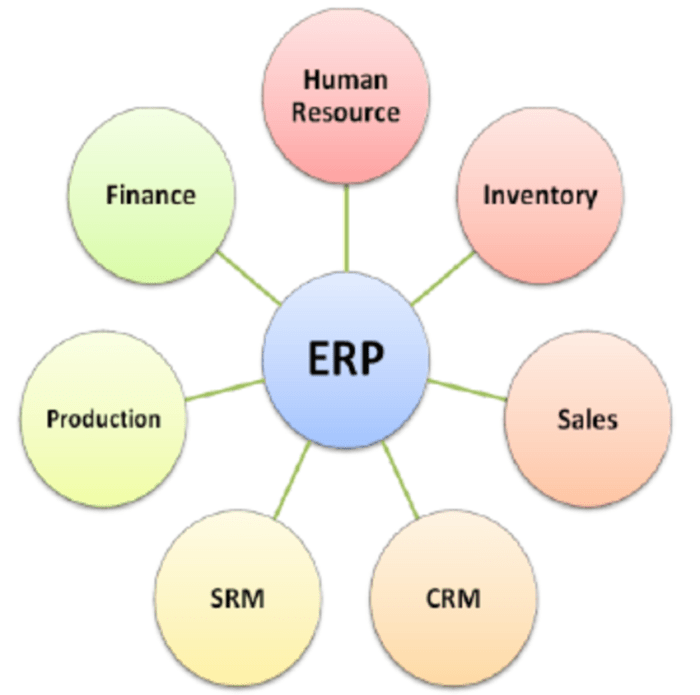
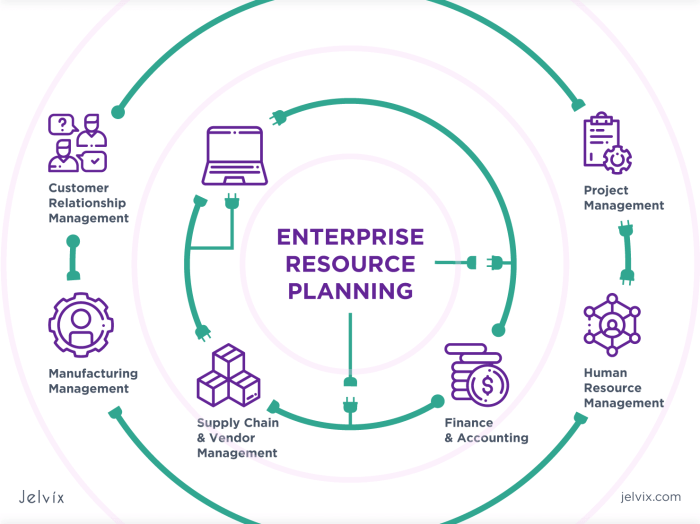
ERP systems, the cornerstone of modern business management, offer a comprehensive suite of integrated applications that seamlessly connect various aspects of an organization. From finance and accounting to supply chain management and customer relationship management, ERP systems provide a centralized platform for managing critical business processes.
ERP System Overview
An Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a comprehensive software suite that integrates and manages various business processes across an organization. It provides a centralized platform for data and information sharing, allowing for seamless collaboration and coordination among different departments and functions.
Key Components and Functionalities
ERP systems typically comprise several core components, including:
- Financial management: Manages financial transactions, accounting, and reporting.
- Human capital management: Handles employee data, payroll, and benefits administration.
- Supply chain management: Oversees procurement, inventory, and logistics.
- Customer relationship management (CRM): Manages customer interactions, sales, and marketing.
- Manufacturing and production: Plans and executes production processes.
- Business intelligence and analytics: Provides data analysis and reporting capabilities.
Market Share and Examples
The ERP market is dominated by a few major players, including:
- SAP: German multinational software corporation, holding approximately 22% market share.
- Oracle: American multinational technology corporation, holding approximately 19% market share.
- Microsoft Dynamics: American multinational technology corporation, holding approximately 12% market share.
ERP System Integration Challenges
ERP system integration presents a multifaceted array of technical and organizational hurdles.
Data migration, a critical aspect of integration, poses challenges in ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. The sheer volume and complexity of data involved can lead to errors and inconsistencies, impacting the reliability and usability of the integrated system.
Process Alignment
Aligning business processes with the ERP system is crucial for successful integration. However, organizations often face challenges in adapting their existing processes to the system’s functionalities. This can lead to inefficiencies, redundancies, and resistance from employees who may be accustomed to their current workflows.
Change Management
ERP system integration inevitably brings about significant organizational change. Managing this change effectively is paramount to ensure user adoption and minimize disruption. Resistance to change, lack of communication, and inadequate training can hinder the successful implementation and utilization of the new system.
Benefits of ERP System Integration
ERP system integration offers numerous benefits to organizations, spanning operational, financial, and strategic aspects. By seamlessly connecting different business functions and streamlining data flow, ERP systems can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive informed decision-making.
Operational Benefits
ERP systems streamline business processes, eliminating redundancies and automating tasks. This improves operational efficiency, reduces errors, and increases productivity. For example, a manufacturing company integrated an ERP system that automated inventory management, production planning, and order fulfillment. The result was a 25% reduction in lead times and a 15% increase in production output.
Financial Benefits
ERP systems provide real-time visibility into financial data, enabling better financial planning and control. They automate accounting processes, reduce errors, and improve cash flow management. For instance, a retail chain integrated an ERP system that centralized financial data from multiple stores.
This resulted in a 10% reduction in accounting costs and a 5% increase in profit margins.
Strategic Benefits
ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of business operations, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning. They enable organizations to identify trends, analyze performance, and make data-driven decisions. For example, a healthcare provider integrated an ERP system that integrated patient data, clinical information, and financial data.
This enabled the provider to optimize patient care, reduce costs, and improve patient satisfaction.
Integration Planning and Preparation
ERP system integration planning and preparation are crucial to ensure a successful implementation. It involves a systematic approach to define the scope, timelines, resources, and strategies for integrating the ERP system with existing business processes and systems.Effective integration planning requires stakeholder involvement from various departments to gather requirements, address concerns, and ensure alignment with business objectives.
Data analysis is essential to understand the current data landscape, identify data inconsistencies, and develop a data migration strategy. Process mapping helps visualize and document existing business processes, allowing for a clear understanding of how the ERP system will impact them and facilitating the identification of potential integration challenges.
Stakeholder Involvement
Stakeholder involvement is vital for gathering diverse perspectives, ensuring buy-in, and addressing concerns early on. Key stakeholders include executives, department heads, end-users, and IT personnel. Their involvement helps define project scope, prioritize requirements, and establish communication channels for ongoing updates.
Data Analysis
Data analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the existing data landscape. It involves assessing data quality, identifying data inconsistencies, and determining the appropriate data migration strategy. Data analysis helps ensure data integrity and accuracy during the integration process.
Process Mapping
Process mapping involves documenting and analyzing existing business processes. It provides a visual representation of how tasks are performed, identifies areas for improvement, and facilitates the design of integrated processes that align with the ERP system’s capabilities.
Integration Methodology
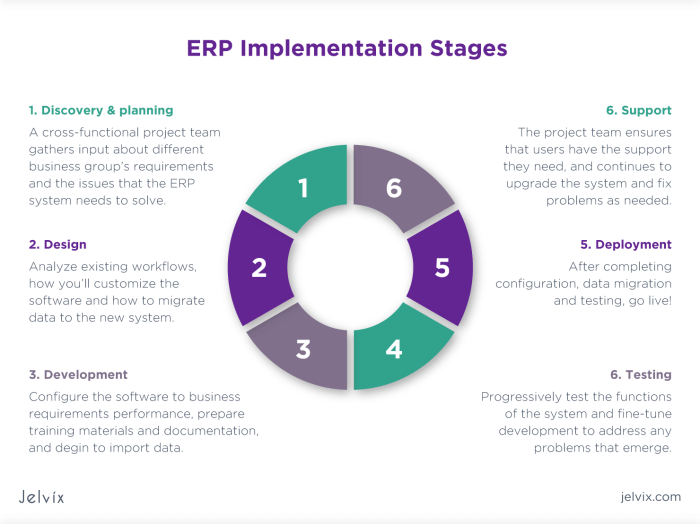
ERP system integration methodologies are structured approaches to implementing an ERP system. These methodologies guide the project team through the various stages of integration, from planning and preparation to implementation and post-implementation support.The choice of integration methodology depends on the project scope and complexity.
Factors to consider include the size of the organization, the number of modules being integrated, and the availability of resources.There are three main ERP system integration methodologies:
Big Bang
The Big Bang methodology is a single, large-scale implementation of an ERP system. This approach is typically used for small to medium-sized organizations with a limited number of modules to integrate. The Big Bang methodology is relatively quick and inexpensive, but it can be risky if the implementation is not properly planned and executed.
Phased
The Phased methodology involves implementing the ERP system in stages. This approach is typically used for large organizations with a complex ERP system. The Phased methodology allows the organization to minimize risk by implementing the system in smaller, more manageable chunks.
However, the Phased methodology can be more time-consuming and expensive than the Big Bang methodology.
Parallel
The Parallel methodology involves running the old and new ERP systems simultaneously for a period of time. This approach is typically used for organizations that cannot afford to disrupt their business operations during the implementation of the new ERP system.
The Parallel methodology is the most expensive and time-consuming of the three methodologies, but it is also the least risky.
Data Migration and Conversion
Data migration and conversion are crucial steps in ERP system integration, ensuring that data from legacy systems is seamlessly transferred and adapted to the new ERP system.
The process involves data extraction from the legacy system, cleansing and transforming it to conform to the new ERP system’s data structure and requirements, and finally loading it into the ERP system.
Challenges
- Data integrity and accuracy: Ensuring data is complete, accurate, and consistent throughout the migration process.
- Data mapping: Establishing a clear and comprehensive mapping between the legacy and ERP system data structures.
- Data volume: Handling large volumes of data and managing the time and resources required for migration.
- Data conversion: Converting data from legacy formats to the new ERP system’s data format.
Best Practices
- Data cleansing: Removing duplicate, incomplete, or invalid data to ensure data integrity.
- Data transformation: Applying data conversion rules to ensure data meets the new ERP system’s requirements.
- Data validation: Verifying the accuracy and completeness of data after migration to ensure data integrity.
- Phased approach: Migrating data in phases to minimize disruption and ensure data integrity.
- Testing and validation: Thoroughly testing the data migration process to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
Process Alignment and Optimization
Integrating an ERP system necessitates the alignment of business processes with the system’s capabilities to maximize its effectiveness. This involves identifying and optimizing process gaps and inefficiencies to ensure seamless integration and value realization.
Process alignment involves mapping existing processes against the new ERP system’s functionalities, identifying areas of overlap, duplication, or redundancy. This analysis helps streamline processes, eliminate unnecessary steps, and enhance efficiency.
Process Optimization Techniques
- Value Stream Mapping:Visualizing the flow of activities and materials within a process to identify and eliminate waste and non-value-added steps.
- Business Process Reengineering (BPR):Fundamentally redesigning processes to achieve significant improvements in performance, efficiency, and cost reduction.
- Lean Six Sigma:Applying a data-driven approach to identify and eliminate process variations, defects, and waste.
- Process Mining:Analyzing event logs and data to identify patterns, bottlenecks, and opportunities for process improvement.
Change Management and Adoption
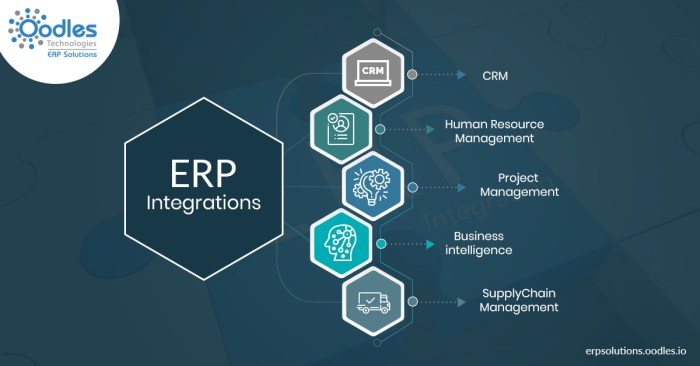
The successful integration of an ERP system requires effective change management and user adoption strategies to ensure the system is embraced and utilized effectively by the organization.
Communication
- Communicate the benefits and objectives of the ERP system to all stakeholders to foster understanding and buy-in.
- Establish clear communication channels to keep users informed about the integration process, timelines, and potential impacts.
- Provide regular updates and progress reports to maintain transparency and address concerns.
Training
- Provide comprehensive training programs to equip users with the necessary skills and knowledge to operate the ERP system effectively.
- Offer customized training based on user roles and responsibilities to ensure they receive relevant and applicable information.
- Utilize a combination of training methods, such as classroom sessions, online modules, and hands-on exercises, to cater to different learning styles.
Support
- Establish a dedicated support team to provide ongoing assistance and troubleshooting to users.
- Create knowledge bases and user guides to provide self-help resources for common issues.
- Monitor system usage and gather feedback to identify areas for improvement and provide targeted support.
Integration Testing and Validation
Integration testing and validation are crucial steps in the implementation of an ERP system to ensure its successful integration with existing systems and business processes.
Integration testing involves testing the interfaces between the ERP system and other systems, such as legacy systems, databases, and third-party applications, to verify that data is exchanged accurately and seamlessly.
Types of Integration Testing, ERP system integration
- Unit testing:Tests individual components of the integration.
- Interface testing:Tests the communication between different components of the integration.
- System testing:Tests the integration as a whole, including all components and interfaces.
- Performance testing:Tests the performance of the integration under various load conditions.
User acceptance testing (UAT) is another critical aspect of integration testing. UAT involves end-users testing the ERP system to ensure that it meets their requirements and expectations.
Performance Evaluation
Performance evaluation is essential to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of the ERP system integration. This includes measuring metrics such as response time, throughput, and resource utilization to ensure that the system meets the performance requirements of the organization.
Post-Integration Support and Maintenance
ERP system integration is an ongoing process that requires continuous support and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and alignment with business needs.
Post-integration support and maintenance involve various activities, including system updates, performance monitoring, and continuous improvement initiatives.
System Updates
- Regular software updates and patches are essential to address bugs, enhance functionality, and improve security.
- Updates should be carefully planned and tested to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition.
Performance Monitoring
- Continuously monitoring system performance is crucial to identify potential issues, bottlenecks, and areas for optimization.
- Performance metrics such as response time, resource utilization, and user satisfaction should be tracked and analyzed.
Continuous Improvement
- Regularly reviewing and evaluating the ERP system’s performance and alignment with business objectives is essential for continuous improvement.
- Feedback from users and stakeholders should be gathered and analyzed to identify areas for enhancement and optimization.
ERP System Integration Best Practices
Successful ERP system integration hinges on adhering to a set of best practices that ensure seamless implementation and long-term success. These practices encompass stakeholder engagement, project management, and continuous improvement.
Stakeholder Engagement
Active engagement of stakeholders is crucial for successful ERP integration. This includes identifying and involving key users, decision-makers, and external partners throughout the process. Effective communication, regular feedback loops, and addressing concerns proactively are essential for ensuring alignment and buy-in.
Project Management
Effective project management is paramount for ERP integration. Establishing a clear project plan, defining roles and responsibilities, and utilizing project management tools ensure smooth execution. Regular monitoring, risk management, and contingency planning are essential for mitigating potential challenges.
Continuous Improvement
ERP integration is not a one-time event but an ongoing process of improvement. Continuously monitoring system performance, gathering feedback, and implementing upgrades and enhancements ensure that the ERP system remains aligned with evolving business needs and technological advancements.
Last Word: ERP System Integration
ERP system integration is not merely a technological endeavor; it is a strategic investment that can profoundly impact an organization’s trajectory. By embracing a holistic approach that encompasses stakeholder engagement, data analysis, process optimization, and change management, businesses can harness the full potential of ERP systems.
The rewards are substantial: enhanced operational efficiency, improved financial performance, and a solid foundation for sustained growth.
As you navigate the complexities of ERP system integration, remember that it is a journey, not a destination. Continuous improvement and ongoing support are essential to maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of your integrated system. By embracing a mindset of innovation and agility, you can ensure that your ERP system remains a driving force for success in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Questions and Answers
What are the key challenges of ERP system integration?
ERP system integration presents technical challenges, such as data migration, process alignment, and system compatibility. Organizational challenges include change management, stakeholder resistance, and the need for effective communication and training.
What are the benefits of successful ERP system integration?
ERP system integration can lead to improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced decision-making, increased customer satisfaction, and a competitive advantage.
How can I ensure a smooth ERP system integration process?
To ensure a smooth ERP system integration process, it is crucial to involve stakeholders, conduct thorough data analysis and process mapping, select an appropriate integration methodology, and implement effective change management strategies.
What are the best practices for ERP system integration?
Best practices for ERP system integration include stakeholder engagement, project management, data integrity, process optimization, change management, and continuous improvement.