ERP software for utilities is a powerful tool that can help utility companies streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance customer service. By integrating disparate systems and providing a single source of truth, ERP software can help utilities gain a competitive advantage and better serve their customers.
ERP software for utilities can help companies manage a wide range of tasks, including asset management, work order management, billing, and customer relationship management. By providing a centralized platform for managing these tasks, ERP software can help utilities improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
ERP Software Overview
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are comprehensive software solutions that integrate various business functions into a single platform. They provide a centralized hub for managing core processes such as finance, human resources, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), and manufacturing.
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy and consistency, streamlined processes, increased efficiency, and enhanced decision-making. However, implementing ERP software can be a complex and challenging process that requires careful planning and execution.
ERP Software Vendors
Several leading ERP software vendors offer a range of solutions tailored to the specific needs of different industries. Some of the most prominent vendors include:
- SAP
- Oracle
- Microsoft
- Infor
- Epicor
ERP for Utilities
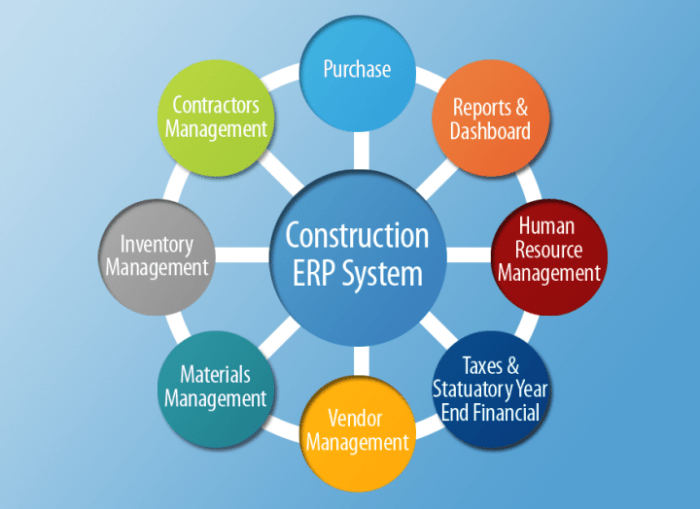
Utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water companies, face unique challenges in managing their complex operations. These challenges include managing customer accounts, billing, work orders, inventory, and assets. ERP software can help utilities streamline these operations and improve efficiency.
Specific Requirements of Utilities for ERP Software
Utilities have specific requirements for ERP software, including:
- Customer management:ERP software must be able to manage customer accounts, including billing, payments, and service requests.
- Work order management:ERP software must be able to track work orders, including scheduling, dispatching, and tracking progress.
- Inventory management:ERP software must be able to track inventory levels, including materials, equipment, and supplies.
- Asset management:ERP software must be able to track assets, including equipment, vehicles, and buildings.
- Financial management:ERP software must be able to manage financial transactions, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, and budgeting.
How ERP Software Can Streamline Operations and Improve Efficiency
ERP software can help utilities streamline operations and improve efficiency in a number of ways, including:
- Centralized data:ERP software provides a single, centralized repository for all utility data, which can improve data accuracy and accessibility.
- Automated processes:ERP software can automate many tasks, such as billing, work order management, and inventory management, which can free up employees to focus on other tasks.
- Improved communication:ERP software can improve communication between different departments within a utility, which can lead to better decision-making.
- Increased visibility:ERP software can provide managers with increased visibility into the utility’s operations, which can help them make better decisions.
Case Studies of Successful ERP Implementations in the Utility Industry, ERP software for utilities
There are a number of successful ERP implementations in the utility industry. Here are a few examples:
- Duke Energy:Duke Energy implemented an ERP system in 2009. The system has helped Duke Energy improve customer service, reduce costs, and increase efficiency.
- Southern Company:Southern Company implemented an ERP system in 2012. The system has helped Southern Company improve financial reporting, reduce costs, and improve customer service.
- Xcel Energy:Xcel Energy implemented an ERP system in 2015. The system has helped Xcel Energy improve customer service, reduce costs, and increase efficiency.
Key Features of ERP for Utilities

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software plays a crucial role in optimizing operations and improving efficiency in the utility sector. To meet the specific needs of utilities, ERP systems offer a comprehensive suite of modules that address key business processes. Essential modules include asset management, work order management, and billing functionality.
Asset Management
Asset management is critical for utilities as they manage vast networks of physical assets, including power lines, transformers, and pipelines. An effective ERP system provides a centralized platform to track and manage these assets throughout their lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal.
It enables utilities to optimize asset utilization, reduce maintenance costs, and improve asset reliability.
For example, SAP ERP offers a comprehensive asset management module that provides utilities with real-time visibility into their asset inventory, condition, and maintenance history. This information helps utilities make informed decisions about asset maintenance and replacement, reducing downtime and improving overall asset performance.
Work Order Management
Work order management is essential for managing maintenance and repair activities in the utility sector. An ERP system provides a central repository for work orders, enabling utilities to track the status of work orders, assign resources, and monitor progress. This helps utilities improve response times, reduce costs, and ensure that maintenance activities are completed efficiently.
Oracle ERP offers a robust work order management module that provides utilities with the ability to create, track, and manage work orders from initiation to completion. It includes features such as automated scheduling, resource allocation, and real-time progress updates, enabling utilities to streamline their maintenance operations.
Billing Functionality
Billing functionality is essential for utilities to accurately and efficiently bill customers for services rendered. An ERP system provides a centralized platform for managing customer accounts, calculating charges, and generating invoices. This helps utilities improve billing accuracy, reduce billing errors, and streamline the billing process.
Microsoft Dynamics ERP offers a comprehensive billing module that provides utilities with the ability to create flexible billing plans, manage customer accounts, and generate invoices based on usage or consumption. It includes features such as automated billing, online payment processing, and detailed billing reports, enabling utilities to improve customer satisfaction and optimize revenue collection.
Integration with Utility Systems
For utility companies, ERP software needs to integrate with other utility systems, such as SCADA, AMI, and GIS, to achieve operational efficiency and improve decision-making. Seamless integration enables data sharing and process automation, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors.
However, integrating ERP with utility systems can be challenging due to the complexity and diversity of these systems. Utilities must consider data compatibility, security protocols, and communication standards to ensure seamless integration.
Best Practices for Integration
- Establish clear integration goals and objectives.
- Identify the data that needs to be shared between systems.
- Define data formats and communication protocols.
- Use industry-standard integration tools and technologies.
- Test and validate the integration thoroughly.
Examples of ERP Software Integration
- SAP ERP integrates with SCADA systems to monitor and control utility assets in real-time.
- Oracle Utilities integrates with AMI systems to collect and analyze smart meter data.
- Microsoft Dynamics AX integrates with GIS systems to visualize and manage utility infrastructure.
Data Management and Analytics
In the dynamic and data-intensive utility industry, effective data management and analytics are crucial for optimizing operations, enhancing decision-making, and driving business growth. ERP software plays a pivotal role in empowering utilities with robust data management and analytics capabilities, enabling them to harness the value of their data.
ERP software provides utilities with a centralized platform to capture, store, and manage vast volumes of data from various sources, including customer information, asset data, financial transactions, and operational metrics. This comprehensive data repository facilitates real-time data access, enabling utilities to gain a holistic view of their operations and make informed decisions.
Advanced Data Analytics Capabilities
Modern ERP software goes beyond data management by incorporating advanced data analytics capabilities that empower utilities to extract meaningful insights from their data. These capabilities include:
- Predictive analytics:Leverages historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast future trends, identify potential risks, and optimize decision-making.
- Prescriptive analytics:Provides recommendations and actionable insights based on data analysis, helping utilities optimize their operations and improve performance.
- Real-time analytics:Analyzes data as it is generated, enabling utilities to respond swiftly to changing conditions and make informed decisions in real time.
Examples of ERP Software with Advanced Data Analytics
Several ERP software providers offer robust data analytics capabilities. Some notable examples include:
- SAP S/4HANA:SAP’s flagship ERP solution features an in-memory database and advanced analytics tools that provide real-time insights and predictive capabilities.
- Oracle Utilities Opower:Oracle’s cloud-based ERP solution for utilities offers advanced data analytics capabilities, including predictive analytics for customer engagement and energy consumption optimization.
- Infor EAM:Infor’s ERP solution for asset-intensive industries provides data analytics capabilities for asset management, maintenance planning, and inventory optimization.
Security and Compliance
ERP software for utilities must meet stringent security and compliance requirements to protect sensitive data and ensure regulatory compliance. It must safeguard against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks. By implementing robust security measures, ERP software helps utilities maintain data integrity, protect customer information, and comply with industry regulations.
Compliance Support
ERP software designed for utilities often includes features that facilitate compliance with industry standards and regulations, such as NERC CIP, ISO 27001, and GDPR. These features help utilities demonstrate compliance, reduce the risk of penalties, and maintain customer trust.
7. Implementation Considerations: ERP Software For Utilities
Implementing ERP software for utilities is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. Several key factors must be considered to ensure a successful implementation.
Project planning is crucial, as it provides a roadmap for the implementation process. The plan should Artikel the project scope, timelines, resources, and budget. Stakeholder engagement is also essential, as it ensures that all stakeholders are aware of the project and have a voice in the decision-making process.
Data migration is another critical aspect of implementation, as it involves transferring data from the existing systems to the new ERP system. A well-planned and executed data migration process is essential to ensure data integrity and minimize disruptions during the transition.
Step-by-Step Guide to ERP Implementation for Utilities
- Project Planning:Define the project scope, timelines, resources, and budget.
- Stakeholder Engagement:Identify and engage all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers.
- Data Migration:Plan and execute the data migration process to transfer data from the existing systems to the new ERP system.
- System Configuration:Configure the ERP system to meet the specific needs of the utility.
- Training and User Adoption:Provide training to users on the new ERP system and support them during the transition.
- Go-Live and Monitoring:Launch the ERP system and monitor its performance to ensure it meets expectations.
- Continuous Improvement:Regularly review the ERP system and make improvements as needed to ensure it continues to meet the evolving needs of the utility.
Cost and Return on Investment
Implementing ERP software for utilities involves upfront costs and ongoing expenses. The total cost can vary depending on the size and complexity of the utility, the number of modules implemented, and the chosen deployment method (on-premises or cloud-based).
Despite the initial investment, ERP software can provide significant returns on investment through:
- Improved efficiency:Streamlining processes and automating tasks can reduce operating costs and improve productivity.
- Reduced costs:Centralizing data and eliminating redundant systems can lower hardware, software, and maintenance expenses.
- Enhanced customer service:Providing a single point of contact for customer inquiries and improved access to account information can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies demonstrate the financial benefits of ERP implementation in the utility industry:
- National Grid:Implemented an ERP system to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve customer service. The company reported a 20% reduction in operating costs and a 15% increase in customer satisfaction.
- Southern California Edison:Implemented an ERP system to improve billing accuracy, reduce IT costs, and enhance data security. The company achieved a 10% reduction in IT expenses and a 95% reduction in billing errors.
Emerging Trends in ERP for Utilities
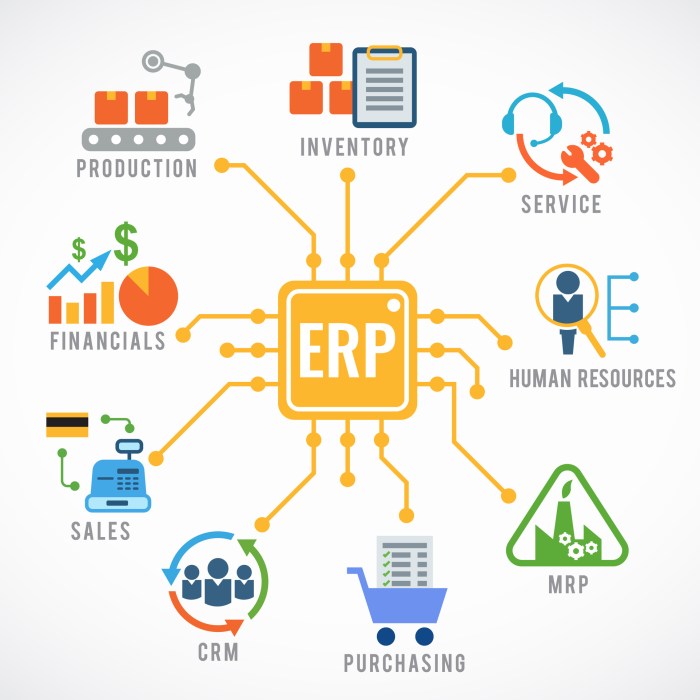
ERP software for utilities is undergoing a transformation, driven by emerging technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These trends are reshaping the way utilities manage their operations and deliver services to customers.
Cloud-based ERP
Cloud-based ERP systems are gaining popularity in the utility industry. These systems offer a number of advantages over on-premises ERP systems, including:
- Reduced costs:Cloud-based ERP systems are typically less expensive to implement and maintain than on-premises systems.
- Increased flexibility:Cloud-based ERP systems can be easily scaled up or down to meet the changing needs of a utility.
- Improved security:Cloud-based ERP systems are typically more secure than on-premises systems, as they are managed by experienced security professionals.
Artificial Intelligence
AI is being used to automate a variety of tasks in the utility industry, including:
- Predictive maintenance:AI can be used to predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing utilities to take proactive steps to prevent outages.
- Customer service:AI-powered chatbots can be used to provide customer service 24/7.
- Fraud detection:AI can be used to detect fraudulent activity, such as meter tampering.
IoT
IoT devices are being used to collect data from a variety of sources, including:
- Smart meters:Smart meters can be used to collect data on energy consumption, which can be used to improve billing accuracy and identify areas where energy efficiency can be improved.
- Sensors:Sensors can be used to collect data on a variety of factors, such as temperature, humidity, and water pressure.
- Drones:Drones can be used to inspect power lines and other infrastructure, which can help to identify potential problems before they become major outages.
These emerging trends are having a major impact on the utility industry. Cloud-based ERP, AI, and IoT are enabling utilities to improve their operations, reduce costs, and provide better service to their customers.
Epilogue
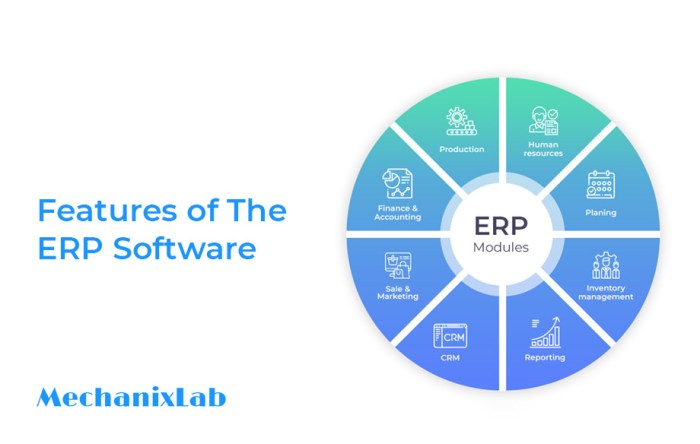
ERP software is an essential tool for utilities that want to improve their operations and better serve their customers. By providing a single source of truth and integrating disparate systems, ERP software can help utilities gain a competitive advantage and succeed in the increasingly competitive utility industry.
Helpful Answers
What are the benefits of ERP software for utilities?
ERP software for utilities can provide a number of benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer service.
How can ERP software help utilities improve efficiency?
ERP software can help utilities improve efficiency by automating tasks, streamlining processes, and providing a single source of truth.
How can ERP software help utilities reduce costs?
ERP software can help utilities reduce costs by improving efficiency, reducing waste, and improving customer service.
How can ERP software help utilities enhance customer service?
ERP software can help utilities enhance customer service by providing a single point of contact for customers, improving communication, and resolving issues quickly and efficiently.