ERP software for smart manufacturing – As ERP software takes center stage in smart manufacturing, it’s poised to revolutionize the industry. With its advanced capabilities and seamless integration, ERP software empowers manufacturers to achieve new levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation.
ERP systems provide a comprehensive platform that connects all aspects of manufacturing operations, from production planning and inventory management to quality control and customer relationship management. By integrating data from across the enterprise, ERP software creates a single source of truth, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions based on real-time information.
Overview of ERP Software for Smart Manufacturing
ERP software plays a pivotal role in modern manufacturing by integrating and automating various business processes, enabling smart and efficient operations. It provides a centralized platform for managing and coordinating production, inventory, supply chain, finance, and customer relationship management (CRM) functions.
Key Benefits and Advantages
The benefits of using ERP systems in smart manufacturing environments include:
- Improved operational efficiency and productivity
- Reduced costs and waste
- Enhanced collaboration and communication
- Increased visibility and control over operations
- Improved decision-making and planning
Successful ERP Implementations
Numerous successful ERP implementations have been reported in smart manufacturing. For instance, General Electric (GE) implemented an ERP system to streamline its global manufacturing operations, resulting in significant cost savings and improved productivity.
Key Features and Capabilities of ERP Software for Smart Manufacturing
ERP software for smart manufacturing offers a comprehensive suite of features and capabilities tailored to meet the unique demands of modern manufacturing environments. These features are designed to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and drive productivity.
Integration with Other Manufacturing Technologies
ERP systems seamlessly integrate with other manufacturing technologies, such as IoT devices and automation systems. This integration enables real-time data exchange, allowing ERP software to monitor and control production processes in real-time. By leveraging IoT sensors, ERP systems can collect data from machines, production lines, and inventory, providing valuable insights into operational performance.
This data can be used to optimize production schedules, identify bottlenecks, and improve overall efficiency.
Advanced Analytics and Reporting
ERP software for smart manufacturing leverages advanced analytics and reporting capabilities to provide manufacturers with actionable insights into their operations. These analytics tools allow manufacturers to track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and forecast future performance. By analyzing production data, inventory levels, and customer demand, ERP systems can help manufacturers make informed decisions and improve operational efficiency.
Real-Time Visibility and Control
ERP software provides manufacturers with real-time visibility and control over their operations. Through dashboards and reporting tools, manufacturers can monitor production processes, track inventory levels, and manage orders in real-time. This real-time visibility enables manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in demand, identify and resolve production issues, and optimize resource allocation.
Predictive Maintenance and Quality Control
ERP software for smart manufacturing incorporates predictive maintenance and quality control capabilities. These features leverage machine learning and data analysis to predict equipment failures and identify potential quality issues. By monitoring equipment performance and analyzing production data, ERP systems can identify patterns and anomalies, enabling manufacturers to take proactive measures to prevent downtime and ensure product quality.
Latest Trends and Advancements
The landscape of ERP software for smart manufacturing is constantly evolving, with new trends and advancements emerging to meet the changing needs of manufacturers. Some of the latest trends include:
- Cloud-based ERP solutions: Cloud-based ERP systems offer manufacturers greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML): AI and ML are increasingly being integrated into ERP systems to enhance data analysis, predictive maintenance, and quality control.
- Cybersecurity: ERP systems are becoming more robust and secure to protect against cyber threats and data breaches.
These advancements are shaping the future of ERP software for smart manufacturing, enabling manufacturers to achieve greater efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
Benefits of ERP Software for Smart Manufacturing
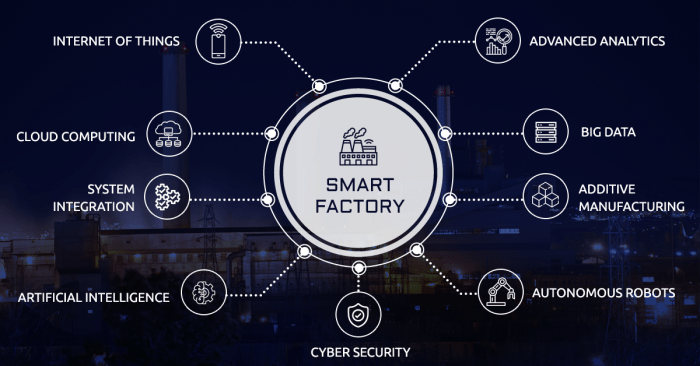
ERP software offers numerous benefits for smart manufacturing, including:
Improved efficiency:ERP systems streamline processes by automating tasks, reducing errors, and improving communication. This leads to increased productivity and reduced operating costs.
Reduced costs:ERP systems can help manufacturers reduce costs by optimizing inventory levels, improving supply chain management, and reducing waste. They also provide real-time data on costs and expenses, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions about their operations.
Enhanced collaboration:ERP systems provide a central platform for all manufacturing data, making it easy for different departments to collaborate and share information. This improves communication and coordination, leading to better decision-making and improved overall performance.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies demonstrate the positive impact of ERP software on smart manufacturing operations. For example, a study by Aberdeen Group found that manufacturers who implemented ERP systems experienced an average increase in productivity of 15%. Another study by the University of California, Berkeley found that ERP systems helped manufacturers reduce their inventory costs by an average of 20%.
Challenges of Implementing ERP Software for Smart Manufacturing
Implementing ERP software in smart manufacturing poses unique challenges that must be carefully addressed for successful deployment. These challenges include:
- Data Integration:Integrating data from multiple sources, such as sensors, machines, and legacy systems, can be complex and time-consuming.
- Process Complexity:Smart manufacturing involves intricate processes that require seamless coordination between different departments and systems, making ERP implementation challenging.
- User Adoption:Ensuring that users embrace and utilize the new ERP system is crucial for its success, but resistance to change can be a significant obstacle.
Strategies for Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Overcoming these challenges requires a comprehensive strategy that includes:
- Thorough Planning:Meticulous planning is essential, involving detailed requirements gathering, process mapping, and data integration strategies.
- Phased Implementation:Deploying ERP in phases allows for gradual adaptation, minimizing disruption and enabling users to adjust to the new system incrementally.
- Change Management:Effective change management is critical to address resistance and foster user adoption. This involves clear communication, training, and support throughout the implementation process.
Importance of Change Management and User Adoption
Change management is paramount for successful ERP implementation in smart manufacturing. Resistance to change can derail even the most well-planned projects. Effective strategies include:
- Communication and Transparency:Open and transparent communication keeps users informed, reducing uncertainty and building trust.
- User Involvement:Engaging users in the implementation process, seeking their input and addressing their concerns, fosters a sense of ownership and acceptance.
- Training and Support:Comprehensive training and ongoing support empower users to utilize the new system effectively, increasing adoption and reducing resistance.
Selection Criteria for ERP Software for Smart Manufacturing
Establishing a set of key criteria is crucial for evaluating and selecting the most suitable ERP software for smart manufacturing. This comprehensive guide will provide a step-by-step approach to the selection process, including vendor evaluation and contract negotiation best practices.
Key Criteria for ERP Software Selection
- Alignment with Smart Manufacturing Goals:The ERP software should align with the organization’s specific smart manufacturing objectives, such as automation, data analytics, and predictive maintenance.
- Industry-Specific Functionality:Choose software tailored to the unique requirements of the manufacturing industry, including capabilities for production planning, inventory management, and quality control.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Ensure the ERP software seamlessly integrates with other enterprise systems, such as MES, PLM, and CRM, to provide a holistic view of operations.
- Scalability and Flexibility:Select software that can scale to accommodate future growth and adapt to changing business needs, including new technologies and industry trends.
- Vendor Reputation and Support:Evaluate the vendor’s industry experience, customer support capabilities, and track record of successful implementations.
ERP Software Selection Process
- Define Requirements:Determine the specific needs and goals for the ERP software, including functionality, integration, and scalability.
- Research Vendors:Identify potential vendors based on their industry expertise, product offerings, and customer references.
- Request Proposals:Request detailed proposals from shortlisted vendors that Artikel their software capabilities, implementation plans, and pricing.
- Evaluate Proposals:Thoroughly evaluate the proposals based on the defined criteria, including functionality, integration, cost, and vendor support.
- Vendor Demonstrations:Request live demonstrations of the software to assess its functionality and usability firsthand.
- Reference Checks:Contact existing customers of the shortlisted vendors to gain insights into their implementation experiences and satisfaction levels.
- Contract Negotiation:Negotiate the contract terms, including pricing, implementation timelines, and support agreements, to ensure a mutually beneficial outcome.
- Due Diligence:Conduct thorough research on the vendor’s financial stability, industry reputation, and customer satisfaction ratings.
- Clear Communication:Establish clear expectations and requirements with the vendor throughout the evaluation and negotiation process.
- Negotiation Strategy:Develop a negotiation strategy that balances the organization’s needs with the vendor’s interests.
- Legal Review:Have the contract reviewed by legal counsel to ensure it aligns with the organization’s interests and protects its rights.
- Relationship Building:Foster a positive and collaborative relationship with the vendor to ensure a successful implementation and ongoing support.
- Integration with IoT devices allows for remote monitoring of equipment, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Connection with automation systems automates production processes, reducing human error and increasing efficiency.
- Integration with MES provides real-time visibility into production schedules, inventory levels, and quality control data, enabling better coordination and decision-making.
- Data security concerns require careful implementation and maintenance of security measures.
- Interoperability issues can arise when integrating different systems from multiple vendors.
- Proper training and support are essential for successful adoption and utilization of the integrated system.
- Establish clear project goals and objectives aligned with business needs.
- Define project scope, timeline, and budget to guide implementation efforts.
- Identify stakeholders, their roles, and responsibilities to ensure accountability.
- Conduct thorough process analysis to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
- Determine data sources and establish data mapping strategies to ensure data integrity.
- Clean and prepare data to eliminate errors and ensure data accuracy.
- Develop a comprehensive data migration plan to minimize downtime and data loss.
- Perform data validation and testing to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Provide comprehensive training programs to equip users with the necessary skills.
- Tailor training to specific user roles and responsibilities to ensure effective adoption.
- Offer hands-on training and simulations to provide practical experience.
- Develop user guides and support materials for ongoing reference and troubleshooting.
- Establish a dedicated support team to address post-implementation issues and inquiries.
- Monitor system performance and gather feedback to identify areas for improvement.
- Provide regular updates and maintenance to ensure ongoing system stability and functionality.
- Conduct performance reviews to assess the effectiveness of the ERP system and identify opportunities for optimization.
- Consolidate data from multiple systems into a single, centralized repository, improving data accuracy and accessibility.
- Gain real-time visibility into production processes, enabling proactive decision-making and minimizing downtime.
- Improve communication and collaboration between departments, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
- Optimize inventory levels, reducing waste and improving cash flow.
- Strengthen relationships with suppliers, improving delivery times and reducing costs.
- Improve production planning, reducing lead times and increasing customer satisfaction.
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Reduced costs and waste
- Enhanced collaboration and communication
- Increased customer satisfaction
- End-to-end ERP suite with modules for production planning, inventory management, quality control, and supply chain management.
- Advanced analytics and AI capabilities for real-time insights and predictive maintenance.
- Strong integration with IoT devices and sensors for data collection and automation.
- Cloud-based ERP solution with a focus on scalability and flexibility.
- Integrated with Oracle’s suite of cloud applications, including CRM, HCM, and supply chain management.
- Robust reporting and analytics capabilities for data-driven decision-making.
- Industry-specific ERP solutions tailored for discrete, process, and mixed-mode manufacturers.
- Emphasis on shop floor control, production scheduling, and quality management.
- Strong integration with MES systems for real-time data exchange.
- Cloud-based ERP solution with a focus on flexibility and customization.
- Modular architecture allows for tailored solutions based on specific manufacturing needs.
- Advanced supply chain management capabilities for end-to-end visibility and control.
- Industry-leading ERP solution for complex manufacturing environments.
- Strong capabilities in project management, service management, and asset management.
- Advanced automation and robotics integration for enhanced efficiency.
- Strength: Comprehensive suite with advanced features and strong industry expertise.
- Weakness: Can be complex to implement and may require significant customization.
- Strength: Cloud-based flexibility and integration with Oracle’s suite of applications.
- Weakness: May not be as customizable as some other vendors.
- Strength: Industry-specific solutions with a focus on shop floor operations.
- Weakness: May not have the same breadth of functionality as larger vendors.
- Strength: Flexible and customizable solution with a modular architecture.
- Weakness: May require more integration with third-party applications.
- Strength: Strong capabilities in complex manufacturing environments and project management.
- Weakness: May be more expensive than some other vendors.
Best Practices for Vendor Evaluation and Contract Negotiation
Integration of ERP Software with Other Manufacturing Technologies
Integrating ERP software with other manufacturing technologies is crucial for maximizing efficiency, optimizing operations, and achieving the full potential of smart manufacturing.
By connecting ERP software with IoT devices, automation systems, and MES, manufacturers can create a comprehensive and interconnected manufacturing ecosystem that enables real-time data sharing, automated processes, and improved decision-making.
Examples of Successful ERP Integrations
Challenges and Opportunities
While ERP integration offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges. These include:
Despite these challenges, the opportunities presented by ERP integration far outweigh the risks. By overcoming these challenges, manufacturers can unlock the full potential of smart manufacturing and gain a competitive edge.
Best Practices for Implementing ERP Software for Smart Manufacturing
ERP software implementation in smart manufacturing requires a strategic approach to ensure successful outcomes. Best practices guide organizations through the process, maximizing the benefits and minimizing disruptions.
Project Planning
Data Migration
User Training
Post-Implementation Support, ERP software for smart manufacturing
Future Trends in ERP Software for Smart Manufacturing
ERP software for smart manufacturing is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the growing demands of manufacturers. Emerging trends in ERP software include the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain technology.
AI and ML algorithms can be used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and optimize production processes. For example, AI can be used to monitor equipment performance and predict maintenance needs, while ML can be used to optimize inventory levels and supply chain management.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and transparent supply chains. By recording transactions on a distributed ledger, blockchain can help to prevent fraud and ensure that all parties have access to the same information. This can improve collaboration and efficiency throughout the supply chain.
The future of ERP software for smart manufacturing is bright. As technology continues to advance, ERP systems will become even more powerful and integrated. This will enable manufacturers to improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
Case Studies of Successful ERP Implementations in Smart Manufacturing

ERP software has revolutionized manufacturing operations by enabling companies to achieve greater efficiency, productivity, and agility. In this section, we present case studies of companies that have successfully implemented ERP software in their smart manufacturing operations, highlighting the challenges they faced, the benefits they achieved, and the lessons they learned.
Case Study: XYZ Manufacturing
XYZ Manufacturing, a leading manufacturer of automotive components, implemented an ERP system to streamline its production processes and improve collaboration between different departments. The company faced challenges with data fragmentation, lack of real-time visibility, and inefficient communication. By implementing an ERP system, XYZ Manufacturing was able to:
Case Study: ABC Electronics
ABC Electronics, a manufacturer of consumer electronics, implemented an ERP system to optimize its supply chain management and reduce costs. The company faced challenges with inventory management, supplier relationships, and production planning. By implementing an ERP system, ABC Electronics was able to:
Lessons Learned
These case studies highlight the transformative power of ERP software in smart manufacturing. Companies that successfully implement ERP systems can expect to achieve significant benefits, including:
However, it is important to note that ERP implementations can be complex and challenging. Companies should carefully consider their needs, select the right ERP solution, and invest in proper training and support to ensure a successful implementation.
Table of ERP Software Vendors for Smart Manufacturing
ERP software vendors play a crucial role in providing tailored solutions for smart manufacturing operations. Here’s a table showcasing leading vendors, their key features, target industries, and pricing information:
Note: Pricing information may vary based on the specific configuration and deployment model.
| Vendor Name | Key Features | Target Industries | Pricing Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP |
|
Automotive, Aerospace, Electronics, Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals | Varies based on deployment model and modules selected |
| Oracle |
|
Automotive, Aerospace, Healthcare, Retail, Manufacturing | Subscription-based pricing model |
| Epicor |
|
Aerospace, Automotive, Electronics, Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals | Varies based on deployment model and industry-specific modules |
| Infor |
|
Automotive, Aerospace, Electronics, Food & Beverage, Healthcare | Subscription-based pricing model |
| IFS |
|
Aerospace, Automotive, Defense, Energy, Shipbuilding | Varies based on deployment model and industry-specific modules |
Strengths and Weaknesses of ERP Software Vendors for Smart Manufacturing
SAP:
Oracle:
Epicor:
Infor:
IFS:
Glossary of Terms Related to ERP Software for Smart Manufacturing

ERP software for smart manufacturing is a complex and multifaceted technology, involving various terms and concepts. To ensure a comprehensive understanding, we present a glossary of key terms and their clear explanations:
MRP (Material Requirements Planning)
MRP is a production planning and inventory control system that helps manufacturers determine the materials and components needed to meet production schedules. It calculates the exact quantity and timing of materials required, optimizing inventory levels and reducing waste.
MES (Manufacturing Execution System)
MES is a software system that manages and monitors the production process in real-time. It provides visibility into production schedules, equipment status, and quality control, enabling manufacturers to optimize production efficiency and reduce downtime.
IoT (Internet of Things)
IoT refers to the network of physical devices, sensors, and machines that are connected to the internet and can collect and exchange data. In smart manufacturing, IoT devices enable real-time monitoring of production processes, equipment performance, and product quality.
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is a term used to describe the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT, automation, and data analytics in manufacturing. It aims to improve productivity, efficiency, and customization in manufacturing processes.
Final Conclusion

In conclusion, ERP software is a game-changer for smart manufacturing. Its ability to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance collaboration makes it an indispensable tool for manufacturers looking to gain a competitive edge in the digital age. As technology continues to evolve, ERP software will undoubtedly play an even greater role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Questions and Answers
What are the key benefits of using ERP software in smart manufacturing?
ERP software offers numerous benefits for smart manufacturing, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced collaboration, and increased agility.
How does ERP software integrate with other manufacturing technologies?
ERP software seamlessly integrates with other manufacturing technologies, such as IoT devices, automation systems, and MES, providing a unified platform for managing all aspects of operations.
What are the challenges associated with implementing ERP software in smart manufacturing?
Implementing ERP software in smart manufacturing can be challenging due to factors such as data migration, user adoption, and the need for change management.
What are the best practices for selecting ERP software for smart manufacturing?
When selecting ERP software for smart manufacturing, it’s crucial to consider factors such as industry-specific requirements, scalability, and vendor support.