ERP software for security tools has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of cybersecurity, empowering organizations to streamline operations, bolster threat detection, and elevate their overall security posture.
With its robust feature set and seamless integration capabilities, ERP software for security tools empowers organizations to elevate their security operations to new heights, ensuring comprehensive protection against evolving threats.
ERP Software for Security Tools
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are software solutions that integrate various business processes, including security management. Integrating ERP with security tools provides a comprehensive and centralized platform for managing and monitoring security operations, enhancing overall security posture and efficiency.
Benefits of Using ERP Software for Security Management
- Centralized Data Management:ERP systems consolidate data from various security tools, providing a single source of truth for security information. This eliminates data silos and improves data accuracy and consistency.
- Improved Visibility and Control:ERP software provides real-time visibility into security events, alerts, and incidents. This enables security teams to monitor threats, identify vulnerabilities, and respond promptly to security breaches.
- Enhanced Compliance Management:ERP systems help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements by providing automated reporting, audit trails, and documentation. This streamlines compliance processes and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity:ERP software automates security tasks, such as incident reporting, threat analysis, and risk assessment. This frees up security teams to focus on strategic initiatives and improve overall productivity.
- Cost Savings:ERP systems can reduce security costs by eliminating the need for multiple, disparate security tools. They also improve efficiency, reducing the need for additional staff or resources.
Key Features and Functionality
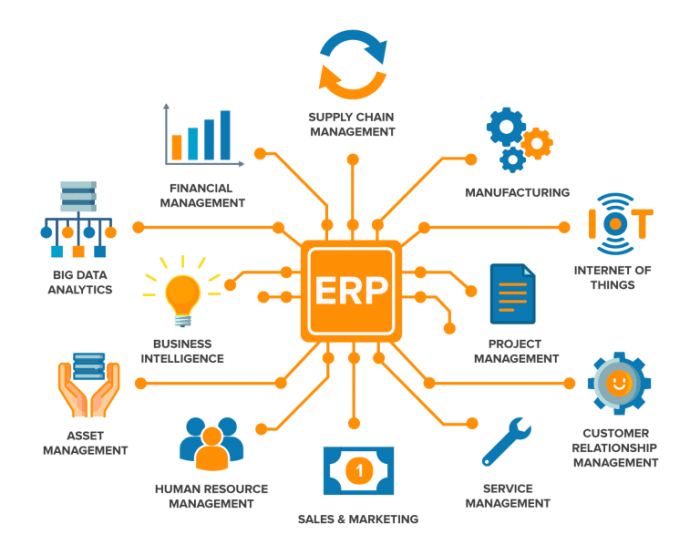
ERP software for security tools offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to enhance security operations. These features include:
- Centralized data management: ERP software consolidates data from multiple sources, providing a single source of truth for security teams.
- Automated workflows: ERP software automates repetitive tasks, freeing up security analysts to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Real-time monitoring: ERP software provides real-time visibility into security events, allowing teams to respond quickly to threats.
- Incident management: ERP software provides a centralized platform for managing security incidents, from initial detection to resolution.
- Reporting and analytics: ERP software provides robust reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling security teams to identify trends and make informed decisions.
These features work together to provide security teams with a comprehensive view of their security posture. By automating tasks, centralizing data, and providing real-time visibility, ERP software can help security teams improve their efficiency and effectiveness.
Implementation Considerations
The implementation of ERP software for security tools is a complex process that requires careful planning, deployment, and integration. By following these steps, organizations can ensure a successful implementation that meets their specific needs.
The key steps involved in implementing ERP software for security tools include:
- Planning: This phase involves defining the project scope, identifying stakeholders, and developing a detailed implementation plan.
- Deployment: This phase involves installing the ERP software, configuring it to meet the organization’s specific needs, and training users on the new system.
- Integration: This phase involves integrating the ERP software with other existing systems, such as security information and event management (SIEM) systems and physical security systems.
Planning, ERP software for security tools
The planning phase is critical to the success of any ERP software implementation. During this phase, organizations should define the project scope, identify stakeholders, and develop a detailed implementation plan.
The project scope should clearly define the goals and objectives of the ERP software implementation. This will help to ensure that the project is aligned with the organization’s overall security strategy.
Stakeholders should be identified early in the planning process. These stakeholders may include security managers, IT staff, and end users. It is important to involve all stakeholders in the planning process to ensure that their needs are met.
The implementation plan should Artikel the steps that will be taken to implement the ERP software. This plan should include timelines, budgets, and resource allocations.
Security Benefits
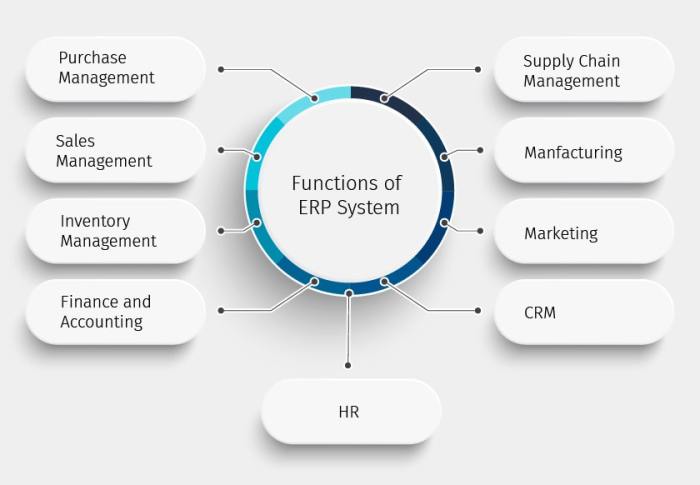
ERP software offers significant security benefits, enhancing an organization’s ability to protect sensitive data, detect and respond to threats, and maintain compliance with regulatory standards.
By integrating security tools into a centralized platform, ERP software provides a comprehensive view of security-related information, allowing organizations to:
Threat Detection
- Detect and identify security threats in real-time using advanced threat detection algorithms.
- Monitor network traffic and user activity for suspicious patterns, reducing the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
- Provide early warnings and alerts to security teams, enabling them to take proactive measures to mitigate threats.
Incident Response
- Automate incident response processes, reducing the time and effort required to contain and remediate security incidents.
- Provide centralized visibility into security incidents, allowing organizations to quickly assess the scope and impact of an attack.
- Enable collaboration between security teams and other departments, ensuring a coordinated and effective response to security breaches.
Compliance
- Help organizations meet regulatory compliance requirements, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR.
- Provide auditable logs and reports to demonstrate compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Automate compliance checks and assessments, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
Operational Efficiency
ERP software streamlines security operations by centralizing and automating various tasks, enhancing overall efficiency and effectiveness. It provides a unified platform for managing security-related processes, enabling organizations to streamline their workflows and optimize resource utilization.
Automation
ERP software automates repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as incident reporting, asset tracking, and compliance monitoring. This automation frees up security personnel to focus on more strategic and value-added activities, such as threat analysis and risk management.
Data Management and Analytics
ERP software for security tools offers robust data management capabilities, enabling the consolidation and centralization of security-related data from various sources. This data includes security events, alerts, incident reports, vulnerability assessments, and compliance information. By integrating data from multiple systems, ERP software provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s security posture.The centralized data repository allows for efficient data analysis and reporting.
Security teams can use the software to generate reports on security trends, identify patterns, and perform root cause analysis. This information helps organizations make informed decisions about security investments, prioritize risks, and improve their overall security posture.
Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning
Advanced ERP software incorporates machine learning algorithms to enhance data analysis capabilities. These algorithms can detect anomalies, identify potential threats, and predict future security risks. By leveraging machine learning, organizations can automate threat detection and response, reducing the burden on security teams and improving the efficiency of security operations.
Real-Time Data Monitoring
ERP software provides real-time data monitoring capabilities, allowing security teams to stay abreast of security events and respond promptly to potential threats. The software can generate alerts and notifications based on predefined rules and thresholds, ensuring that critical security events are addressed in a timely manner.
Integration with Other Security Tools
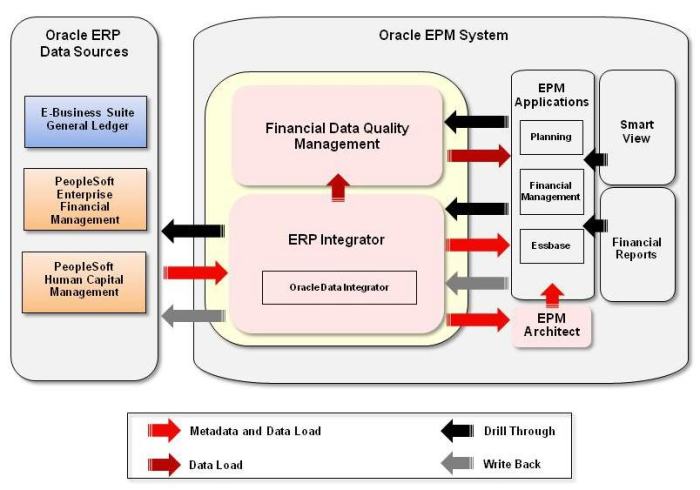
ERP software can integrate with various security tools to enhance the overall security posture of an organization. These tools may include:
- Network security tools, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS)
- Endpoint security tools, such as antivirus software, anti-malware software, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions
- Identity and access management (IAM) tools, such as single sign-on (SSO) solutions and multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools, which collect and analyze security data from various sources to provide a comprehensive view of the security posture
Integrating ERP software with these security tools offers several benefits:
- Centralized management: ERP software provides a single platform for managing and monitoring all security tools, simplifying administration and reducing the risk of security breaches.
- Improved visibility: Integration enables ERP software to collect and analyze data from all security tools, providing a comprehensive view of the security posture and identifying potential threats.
- Automated response: ERP software can automate the response to security incidents, such as triggering alerts, isolating infected systems, and launching recovery procedures.
However, integrating ERP software with other security tools also presents some challenges:
- Complexity: Integrating multiple security tools can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and configuration.
- Data compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between different security tools and ERP software can be challenging, especially if the tools use different data formats or protocols.
- Security risks: Integration points between ERP software and other security tools can introduce new security risks, such as vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of integrating ERP software with other security tools outweigh the risks. By carefully planning and implementing the integration, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture and reduce the risk of security breaches.
Vendor Selection and Evaluation: ERP Software For Security Tools

Selecting the right ERP software vendor for security tools is crucial to ensure a successful implementation and maximize the benefits. Here are the key criteria to consider during the vendor selection process:
Thoroughly evaluate the vendor’s expertise in security tool integration, industry knowledge, and customer support capabilities.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
- Security Expertise:Assess the vendor’s understanding of the security landscape, their experience in integrating ERP systems with security tools, and their ability to provide comprehensive security solutions.
- Industry Knowledge:Determine the vendor’s familiarity with the specific industry and its unique security challenges. This ensures that they can provide tailored solutions that align with your organization’s needs.
- Customer Support:Evaluate the vendor’s customer support capabilities, including response times, availability, and the level of technical expertise provided. Reliable support is essential for addressing any issues promptly and minimizing disruptions.
- Integration Capabilities:Assess the vendor’s ability to seamlessly integrate their ERP software with your existing security tools. This includes evaluating the compatibility of their software with your current infrastructure and ensuring a smooth data flow between systems.
- Scalability and Flexibility:Consider the vendor’s ability to scale their software to meet your growing needs and adapt to changing security requirements. Flexibility is crucial for accommodating future expansions and enhancements.
- Cost and Licensing:Evaluate the vendor’s pricing model, licensing terms, and ongoing maintenance costs. Ensure that the investment aligns with your budget and provides a clear return on investment.
- References and Case Studies:Request references from the vendor’s previous customers and review case studies to gain insights into their implementation experience, success stories, and areas for improvement.
Case Studies and Examples
ERP software implementations for security tools have demonstrated significant success in various organizations. These case studies provide valuable insights into the benefits, challenges, and lessons learned during these implementations.
Successful Implementations
- Case Study:A large financial institution implemented an ERP system for its security operations. The system integrated disparate security tools, providing a centralized view of security events and streamlining incident response processes. This resulted in a 20% reduction in incident response time and a 15% increase in security analyst productivity.
- Example:A government agency deployed an ERP system for its cybersecurity program. The system automated security assessments, vulnerability management, and compliance reporting. This led to a 30% improvement in security posture and a 10% reduction in audit time.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
ERP software implementations for security tools also present challenges that organizations must address:
- Data Integration:Integrating data from multiple security tools can be complex and time-consuming. Organizations must ensure data consistency and accuracy to avoid false positives or missed alerts.
- User Adoption:Security analysts and other users must be trained and supported to effectively use the ERP system. Resistance to change or lack of training can hinder adoption and reduce the system’s effectiveness.
Lessons learned from successful implementations include:
- Early Stakeholder Engagement:Involving key stakeholders in the planning and implementation phases ensures buy-in and support for the system.
- Phased Implementation:Implementing the system in phases allows organizations to manage the complexity and minimize disruption.
- Continuous Improvement:Ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the system helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that the system remains aligned with the organization’s security needs.
Closing Notes

In conclusion, ERP software for security tools is an invaluable asset for organizations seeking to strengthen their security posture and optimize their operational efficiency. Its advanced features, data management capabilities, and integration potential empower organizations to navigate the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape with confidence.
FAQ Resource
What are the key benefits of using ERP software for security tools?
ERP software for security tools offers numerous benefits, including enhanced threat detection, improved compliance, streamlined operations, and data-driven decision-making.
How does ERP software integrate with other security tools?
ERP software for security tools can integrate with a wide range of security tools, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control systems, enabling a comprehensive and cohesive security architecture.
What are the key considerations for selecting an ERP software vendor for security tools?
When selecting an ERP software vendor for security tools, organizations should consider factors such as vendor reputation, product functionality, integration capabilities, and ongoing support.