ERP software for reliability tools is a powerful tool that can help organizations improve their reliability processes. By integrating ERP with reliability tools, organizations can gain a comprehensive view of their reliability data, identify and mitigate risks, and improve collaboration among reliability engineers.
ERP software for reliability tools provides a centralized platform for managing all aspects of reliability, from data collection and analysis to maintenance and repair. This can help organizations to improve their efficiency and effectiveness, and to reduce the risk of downtime.
Introduction
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software plays a crucial role in reliability engineering by providing a centralized platform to manage and optimize various aspects of asset reliability.
Integrating ERP with reliability tools offers significant benefits, including improved data visibility, streamlined maintenance processes, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Data Visibility
ERP systems consolidate data from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive view of asset performance, maintenance history, and inventory levels. This enhanced data visibility enables reliability engineers to identify patterns, trends, and potential risks more effectively.
Streamlined Maintenance Processes, ERP software for reliability tools
ERP software automates maintenance processes, such as work order management, scheduling, and inventory tracking. This streamlines maintenance operations, reduces downtime, and improves asset availability.
Enhanced Decision-Making
The integration of ERP and reliability tools provides reliability engineers with real-time data and analytics. This enables them to make informed decisions about maintenance strategies, resource allocation, and risk mitigation, resulting in improved asset reliability and reduced operating costs.
Key Features of ERP Software for Reliability
ERP software for reliability provides comprehensive functionalities tailored to enhance reliability management processes. These features streamline data management, facilitate proactive maintenance, and improve decision-making, ultimately leading to increased asset uptime and reduced operational costs.
Core Functionalities
- Asset Management:Centralized asset inventory, maintenance history tracking, and performance monitoring for proactive maintenance and predictive analytics.
- Failure Tracking and Analysis:Comprehensive failure reporting, root cause analysis, and corrective action management to identify and address recurring reliability issues.
- Preventive Maintenance Scheduling:Automated scheduling of preventive maintenance tasks based on usage, condition monitoring, and historical data to prevent breakdowns and extend asset life.
- Work Order Management:Streamlined work order creation, tracking, and completion for efficient maintenance execution and improved accountability.
- Spare Parts Inventory Management:Real-time visibility into spare parts inventory, usage, and reorder levels to ensure availability and minimize downtime.
- Performance Monitoring and Reporting:Customizable dashboards and reports for key reliability metrics, such as mean time to failure (MTTF), mean time to repair (MTTR), and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Integration with Reliability Tools: ERP Software For Reliability Tools
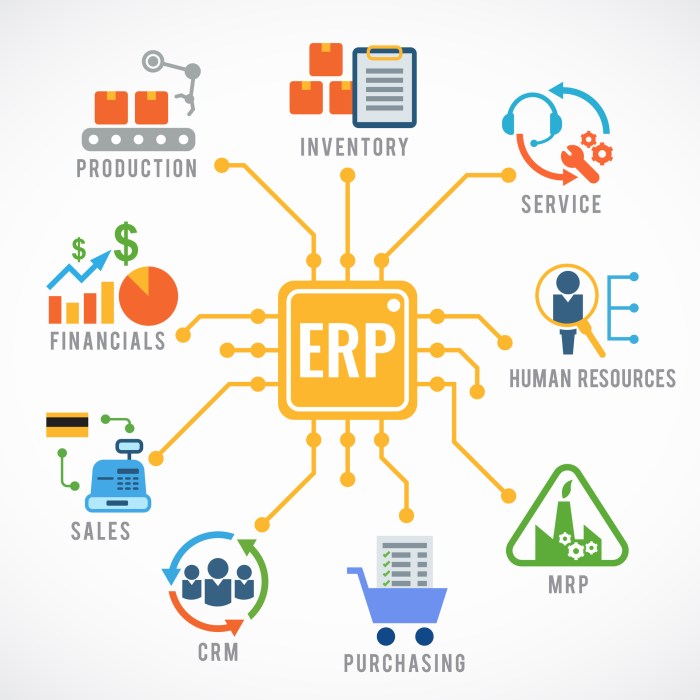
ERP software can be integrated with reliability tools to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of reliability engineering processes. This integration allows for the seamless flow of data between the two systems, enabling a more comprehensive and accurate view of asset reliability.There are several methods for integrating ERP software with reliability tools.
One common method is to use an application programming interface (API). APIs allow different software systems to communicate with each other by exchanging data and commands. By using an API, ERP software can send data to reliability tools, such as asset data, maintenance history, and operating conditions.
Reliability tools can then use this data to perform reliability analysis and generate reports.Another method for integrating ERP software with reliability tools is to use a middleware platform. Middleware is a software layer that sits between ERP software and reliability tools and facilitates communication between the two systems.
Middleware can translate data between different formats, handle data security, and provide other services that make integration easier and more efficient.The integration of ERP software with reliability tools offers several benefits. First, it can improve the accuracy and completeness of reliability data.
By integrating the two systems, data can be automatically transferred from ERP software to reliability tools, eliminating the need for manual data entry. This reduces the risk of errors and ensures that reliability tools have the most up-to-date information available.Second, integration can improve the efficiency of reliability engineering processes.
By automating the flow of data between ERP software and reliability tools, engineers can spend less time on data management and more time on analysis and decision-making. This can lead to improved productivity and cost savings.Third, integration can provide a more comprehensive view of asset reliability.
By combining data from ERP software and reliability tools, engineers can gain a better understanding of the factors that affect asset reliability. This information can be used to make more informed decisions about asset maintenance and replacement strategies.However, there are also some challenges associated with integrating ERP software with reliability tools.
One challenge is the cost of integration. Integration can be a complex and time-consuming process, and it can require significant investment in hardware, software, and consulting services.Another challenge is the need for data standardization. ERP software and reliability tools often use different data formats, which can make integration difficult.
To ensure that data can be exchanged seamlessly between the two systems, it is important to establish a common data standard.Finally, there is the challenge of security. Integrating ERP software with reliability tools can create new security risks. It is important to implement appropriate security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and misuse.Despite these challenges, the benefits of integrating ERP software with reliability tools can be significant.
By carefully planning and implementing an integration solution, organizations can improve the accuracy, efficiency, and comprehensiveness of their reliability engineering processes.
Data Management and Analysis
ERP software plays a vital role in the efficient collection, storage, and analysis of reliability data. This centralized data repository enables organizations to track and manage various aspects of their reliability programs, including asset performance, maintenance history, and failure analysis.
By leveraging advanced data analytics capabilities, ERP software provides insights into reliability trends, root cause analysis, and predictive maintenance. This information empowers organizations to make informed decisions and proactively address potential issues, leading to improved asset uptime and reduced downtime.
Data Visualization and Reporting
ERP software offers robust data visualization and reporting capabilities that enable users to easily access and interpret reliability data. Interactive dashboards, charts, and graphs provide a comprehensive overview of key metrics, allowing users to quickly identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
Customizable reports can be generated to meet specific requirements, providing detailed insights into asset performance, maintenance costs, and failure analysis. These reports can be exported in various formats for further analysis and sharing.
Maintenance and Repair Management
ERP software plays a vital role in managing maintenance and repair activities within an organization. It provides a comprehensive platform to track, schedule, and execute maintenance tasks, ensuring optimal equipment performance and minimizing downtime.
The integration of ERP software with computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) further enhances maintenance and repair management capabilities. CMMS provides detailed information about equipment, maintenance history, and spare parts inventory. By integrating with ERP, organizations can streamline maintenance processes, improve asset utilization, and reduce maintenance costs.
CMMS Integration Benefits
- Centralized maintenance data and history
- Improved work order management
- Optimized spare parts inventory management
- Enhanced asset performance monitoring
- Reduced downtime and maintenance costs
Risk Management
ERP software aids in identifying and mitigating reliability risks through a comprehensive approach that involves risk assessment, mitigation planning, and monitoring. This integrated risk management capability enhances the reliability of assets and operations by proactively addressing potential failures and disruptions.
ERP software assists in identifying reliability risks by leveraging data from various sources, such as maintenance history, equipment performance data, and industry best practices. This data is analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and potential vulnerabilities that could lead to asset failures or operational disruptions.
Advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive analytics and machine learning, can be utilized to further enhance risk identification and prioritization.
Risk Assessment
- ERP software enables organizations to conduct comprehensive risk assessments to evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks. These assessments consider factors such as asset criticality, failure modes, and operational dependencies. The results of risk assessments help prioritize risks and allocate resources effectively for mitigation efforts.
Risk Mitigation
- Once risks have been identified and assessed, ERP software facilitates the development and implementation of mitigation strategies. These strategies may include preventive maintenance, condition monitoring, spare parts management, and redundancy measures. ERP software provides tools for tracking and managing mitigation actions, ensuring timely execution and follow-up.
Monitoring and Review
- ERP software enables continuous monitoring of risks and the effectiveness of mitigation strategies. Real-time data from sensors, maintenance records, and operational performance indicators is collected and analyzed to identify any changes or deviations that could indicate emerging risks. Regular reviews of risk management plans and mitigation actions ensure that they remain aligned with changing conditions and operational priorities.
Collaboration and Communication
ERP software serves as a central hub for reliability engineers to collaborate and share knowledge, fostering a collaborative environment for improved reliability management.
It provides a shared platform for engineers to access real-time data, discuss reliability issues, and develop solutions collectively. This eliminates communication silos, improves coordination, and ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page.
Centralized Knowledge Base
- ERP software creates a centralized knowledge base where engineers can store and share best practices, lessons learned, and technical documentation.
- This repository of knowledge ensures that information is readily accessible to all team members, reducing the risk of knowledge loss and promoting continuous learning.
Real-Time Communication
- ERP software enables real-time communication through instant messaging, chat rooms, and discussion forums.
- This facilitates prompt resolution of issues, quick sharing of updates, and effective coordination among geographically dispersed teams.
Document Management
- ERP software provides a centralized repository for storing and managing reliability-related documents, such as maintenance records, failure reports, and risk assessments.
- This ensures easy access to critical information, reduces the risk of document loss, and enables seamless collaboration among team members.
Case Studies and Best Practices
ERP software has proven its effectiveness in reliability engineering through numerous successful implementations. These case studies showcase the benefits and challenges faced during real-world applications, providing valuable insights and best practices for organizations seeking to enhance their reliability efforts.
Best practices derived from these case studies emphasize the importance of a well-defined implementation strategy, tailored to the specific needs of the organization. Effective communication, stakeholder engagement, and continuous improvement are crucial for maximizing the value of ERP software in reliability engineering.
Lessons Learned from Real-World Applications
- Thorough planning and preparation ensure a smooth implementation and minimize disruptions.
- Engaging stakeholders and securing their buy-in is essential for successful adoption and utilization.
- Data integration and standardization are critical for accurate and meaningful analysis.
- Continuous monitoring and feedback loops allow for timely adjustments and improvements.
- Collaboration and knowledge sharing among team members foster innovation and best practice dissemination.
Emerging Trends

The ERP software for reliability is continuously evolving, with new technologies emerging that are changing the way organizations manage their reliability programs. Some of the most important trends to watch for include:
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) to automate tasks and improve decision-making. AI can be used to identify patterns in data, predict failures, and recommend corrective actions. This can help organizations to improve their reliability performance and reduce costs.
The adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT) to connect physical assets to the internet. IoT devices can collect data on the performance of assets, which can be used to improve maintenance and repair planning. This can help organizations to avoid unplanned downtime and improve their overall reliability.
The increasing use of cloud computing to deliver ERP software. Cloud computing offers several advantages, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. This is making it easier for organizations of all sizes to implement ERP software for reliability.
Impact of AI, IoT, and Cloud Computing
The convergence of these technologies is having a significant impact on the ERP software for reliability market. AI, IoT, and cloud computing are making it possible for organizations to collect and analyze more data than ever before. This data can be used to improve decision-making, automate tasks, and predict failures.
As a result, organizations are seeing significant improvements in their reliability performance.
Vendor Landscape
The vendor landscape for ERP software in reliability engineering is diverse, with a range of vendors offering solutions tailored to specific industry needs. Key players in the market include SAP, Oracle, Infor, IFS, and Epicor.
These vendors offer a comprehensive suite of features, including maintenance and repair management, risk management, data management and analysis, and collaboration tools. They also provide industry-specific solutions for sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, and utilities.
Vendor Comparison
When selecting an ERP software vendor, it is important to compare and contrast their offerings based on several key factors:
- Features:Assess the range of features offered by each vendor, ensuring that they align with your specific reliability engineering requirements.
- Pricing:Consider the upfront costs, subscription fees, and any additional expenses associated with implementing and maintaining the software.
- Customer Reviews:Research feedback from existing customers to gain insights into the vendor’s reliability, support quality, and overall user experience.
Ultimate Conclusion
ERP software for reliability tools is a valuable investment for any organization that wants to improve its reliability processes. By providing a comprehensive view of reliability data, identifying and mitigating risks, and improving collaboration among reliability engineers, ERP software can help organizations to achieve their reliability goals.
FAQ Summary
What are the benefits of using ERP software for reliability tools?
ERP software for reliability tools can provide a number of benefits, including improved efficiency and effectiveness, reduced risk of downtime, and improved collaboration among reliability engineers.
How does ERP software integrate with reliability tools?
ERP software can integrate with reliability tools in a number of ways, including through the use of APIs, data connectors, and middleware.
What are the key features of ERP software for reliability tools?
ERP software for reliability tools typically includes a number of key features, such as data collection and analysis, maintenance and repair management, risk management, and collaboration tools.