ERP software for process integration has emerged as a transformative tool, empowering businesses to seamlessly connect their operations and elevate efficiency to unprecedented heights. As we delve into the intricacies of this innovative solution, we will explore its multifaceted benefits, unravel its key features, and provide practical guidance for successful implementation.
ERP systems act as the central nervous system of an organization, orchestrating a symphony of processes and fostering collaboration across departments. By integrating disparate systems and automating workflows, ERP software eliminates silos, streamlines communication, and ensures data integrity throughout the enterprise.
ERP Software Overview
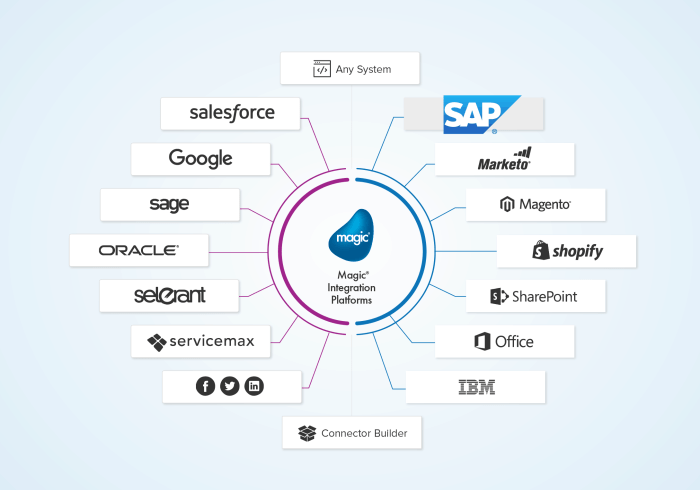
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive suite of integrated applications that helps businesses manage and automate their core processes. It provides a single, centralized platform for managing all aspects of a business, from finance and accounting to supply chain management and customer relationship management (CRM).
ERP systems offer a number of benefits, including improved efficiency, increased productivity, and reduced costs. They can also help businesses improve their customer service, make better decisions, and gain a competitive advantage.
Benefits of ERP Systems
- Improved efficiency: ERP systems can help businesses improve efficiency by automating tasks and streamlining processes. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Increased productivity: ERP systems can help businesses increase productivity by providing employees with the tools they need to be more efficient and effective.
- Reduced costs: ERP systems can help businesses reduce costs by eliminating redundant processes and improving efficiency.
- Improved customer service: ERP systems can help businesses improve customer service by providing a single, centralized view of all customer interactions.
- Better decision-making: ERP systems can help businesses make better decisions by providing them with real-time data and insights.
- Competitive advantage: ERP systems can help businesses gain a competitive advantage by providing them with the tools they need to be more efficient, productive, and customer-focused.
Challenges of ERP Systems
While ERP systems offer a number of benefits, they also come with some challenges. These challenges include the cost of implementation, the complexity of the software, and the need for organizational change.
- Cost of implementation: ERP systems can be expensive to implement. The cost of software, hardware, and consulting services can be significant.
- Complexity of the software: ERP systems are complex software applications. This can make them difficult to implement and use.
- Need for organizational change: ERP systems can require significant organizational change. This can be disruptive to the business and can lead to resistance from employees.
Process Integration with ERP
ERP software plays a pivotal role in integrating business processes by providing a centralized platform that connects different departments and functions within an organization. This integration streamlines workflows, improves collaboration, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
ERP systems integrate processes across various departments, such as finance, supply chain management, human resources, and customer relationship management. By eliminating data silos and automating tasks, ERP systems reduce redundancies, improve data accuracy, and enhance communication.
Streamlined Workflows, ERP software for process integration
ERP systems automate and streamline business processes, eliminating manual tasks and reducing the time required to complete operations. For example, an ERP system can automate purchase orders, inventory management, and invoicing, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Improved Collaboration
ERP systems provide a shared platform for employees across different departments to access and share information in real-time. This fosters collaboration and improves decision-making. For example, the sales team can access inventory data to provide accurate delivery timelines to customers, while the finance team can track project costs and expenses in real-time.
Key Features of ERP Software for Process Integration

ERP software offers a comprehensive suite of features that facilitate seamless process integration within an organization. These features enable efficient data sharing, automation of workflows, and real-time visibility across various business functions.
The key features of ERP software for process integration include:
Centralized Data Repository
ERP systems provide a centralized data repository that stores and manages all critical business data, including customer information, inventory levels, sales orders, and financial transactions. This central repository eliminates data silos and ensures that all departments have access to the same up-to-date information.
Data Integration and Exchange
ERP software enables seamless data integration and exchange between different modules and applications. It provides standardized interfaces and protocols that allow data to flow smoothly between various systems, such as CRM, supply chain management, and accounting.
Workflow Automation
ERP systems offer workflow automation capabilities that streamline business processes and reduce manual tasks. They can automate tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and financial reporting, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
Real-Time Visibility and Reporting
ERP software provides real-time visibility into business operations through dashboards and reports. This allows managers to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Flexibility and Customization
Modern ERP systems are designed to be flexible and customizable to meet the specific needs of different organizations. They can be configured to adapt to industry-specific processes and workflows, ensuring a seamless fit with existing business practices.
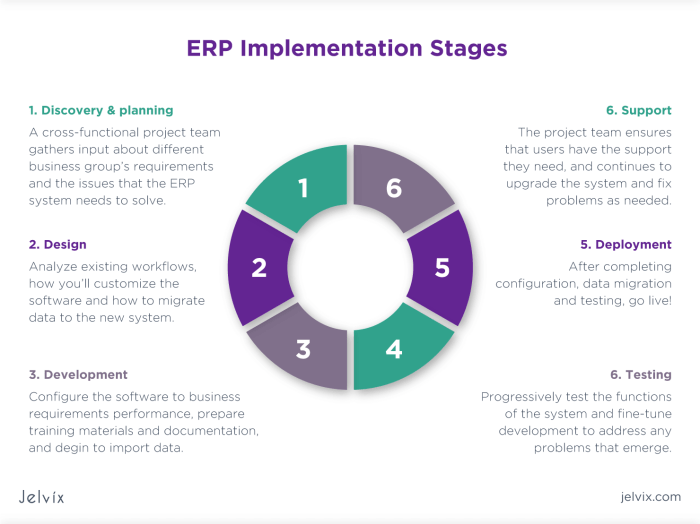
Implementation Considerations
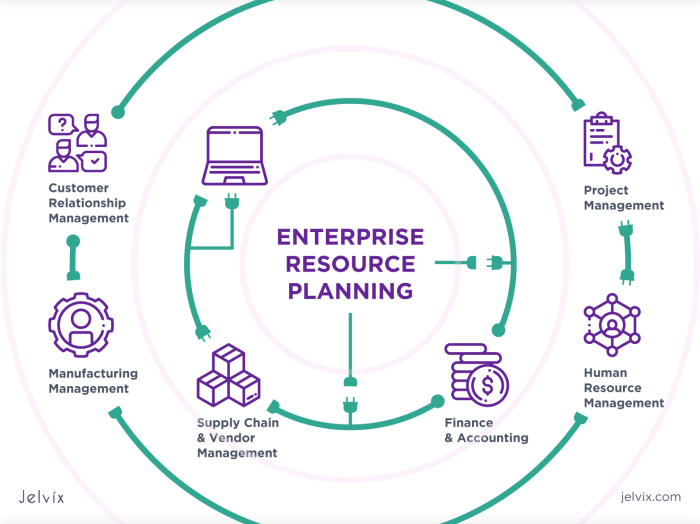
ERP software implementation for process integration is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. Several factors must be considered to ensure a successful implementation.
Key considerations include data migration, user training, and change management. Data migration involves transferring existing data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. This process can be challenging, especially for large and complex organizations. It is essential to plan carefully and ensure that the data is migrated accurately and completely.
User Training
User training is another critical aspect of ERP implementation. Users must be adequately trained on the new system to use it effectively. Training should be comprehensive and cover all aspects of the system, from basic navigation to advanced functionality. It is also essential to provide ongoing support to users after the implementation to ensure they can use the system effectively.
Change Management
ERP implementation can also impact organizational processes and workflows. Change management is essential to minimize disruption and ensure that the organization can adapt to the new system. This involves communicating the changes to users, providing training, and developing strategies to manage resistance to change.
Industry-Specific Applications
ERP software for process integration offers significant benefits across various industries. By streamlining operations and automating tasks, businesses can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
Specific advantages vary depending on the industry, but some common benefits include:
Manufacturing
- Improved production planning and scheduling
- Reduced inventory levels and costs
- Enhanced quality control and traceability
li>Increased production efficiency and output
Retail
- Optimized inventory management and replenishment
- Improved customer service and loyalty
- Increased sales and profitability
- Enhanced supply chain visibility and collaboration
Healthcare
- Improved patient care coordination and outcomes
- Reduced medical errors and costs
- Increased operational efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced patient satisfaction and loyalty
Financial Services
- Improved risk management and compliance
- Reduced operational costs and increased efficiency
- Enhanced customer service and satisfaction
- Increased revenue and profitability
Case Studies
Numerous successful ERP implementations have been documented across industries. For example, in the manufacturing sector, a leading automotive manufacturer implemented an ERP system to integrate its production, supply chain, and customer relationship management processes. This resulted in a 20% reduction in inventory costs, a 15% increase in production efficiency, and a 10% improvement in customer satisfaction.
In the healthcare industry, a major hospital implemented an ERP system to streamline its patient care, financial, and administrative processes. This led to a 12% reduction in medical errors, a 10% increase in patient satisfaction, and a 5% reduction in operating costs.
Final Thoughts
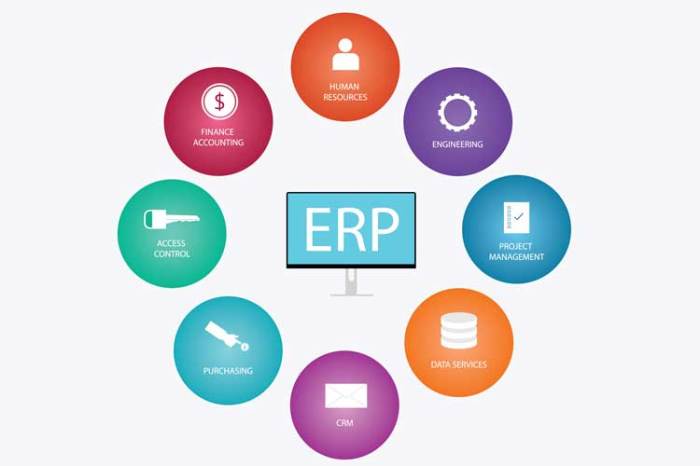
In conclusion, ERP software for process integration is a game-changer for businesses seeking to optimize operations, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive edge. By embracing the transformative power of ERP, organizations can unlock a world of seamless processes, improved collaboration, and unparalleled efficiency.
FAQ: ERP Software For Process Integration
What are the key benefits of ERP software for process integration?
ERP software streamlines workflows, improves collaboration, eliminates data silos, enhances decision-making, and provides a comprehensive view of business operations.
What are the essential features of ERP software for process integration?
Essential features include workflow automation, data integration, reporting and analytics, customization, and user-friendly interfaces.
How can I ensure a successful implementation of ERP software for process integration?
Successful implementation requires careful planning, data migration, user training, change management, and ongoing support.