In the realm of industrial maintenance, ERP software for predictive maintenance emerges as a transformative solution, empowering businesses to optimize their operations and maximize asset performance.
This innovative technology seamlessly integrates with enterprise resource planning systems, providing real-time insights into equipment health, enabling proactive maintenance strategies that minimize downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
Definition and Overview of ERP Software for Predictive Maintenance

Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive software suite that integrates various business processes into a single, centralized system. It offers a range of modules that cover different functional areas, such as finance, supply chain management, manufacturing, and human resources.
Predictive maintenance is a maintenance strategy that uses data analysis and machine learning algorithms to predict when equipment is likely to fail. By leveraging real-time data from sensors and historical maintenance records, ERP software can help businesses identify potential problems early on and schedule maintenance accordingly.
Benefits of Using ERP Software for Predictive Maintenance
There are numerous benefits to using ERP software for predictive maintenance, including:
- Reduced downtime:By identifying potential problems early on, businesses can schedule maintenance before equipment fails, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
- Lower maintenance costs:Predictive maintenance helps businesses avoid unnecessary maintenance and repairs, as well as costly emergency repairs.
- Improved asset utilization:By optimizing maintenance schedules, businesses can ensure that their equipment is operating at peak efficiency and extend its lifespan.
- Increased safety:Predictive maintenance can help identify potential safety hazards and prevent accidents.
- Enhanced decision-making:ERP software provides businesses with real-time data and insights that can help them make informed decisions about maintenance and asset management.
Key Features of ERP Software for Predictive Maintenance
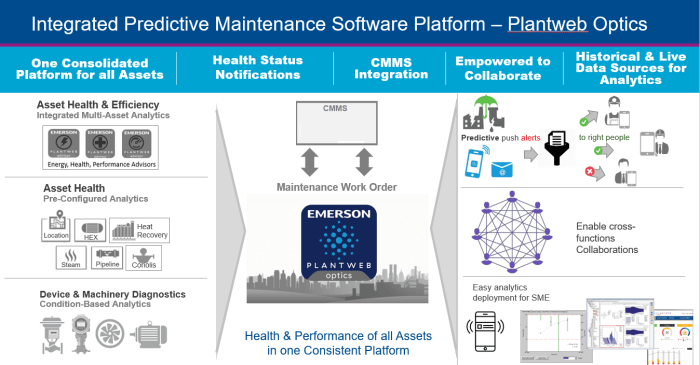
ERP software for predictive maintenance offers a comprehensive suite of features that empower organizations to optimize their maintenance strategies, minimize downtime, and enhance asset performance. These features include:
Data Collection and Integration
ERP software seamlessly integrates with various data sources, such as sensors, IoT devices, and CMMS systems, to collect real-time data on asset performance, usage patterns, and environmental conditions. This data consolidation provides a comprehensive view of asset health and enables accurate predictive maintenance analysis.
Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling
Advanced analytics capabilities within ERP software leverage collected data to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies in asset performance. Predictive models are then developed to forecast potential failures and prioritize maintenance tasks based on the likelihood and severity of equipment issues.
Maintenance Scheduling and Optimization
ERP software provides automated maintenance scheduling based on predictive insights. It optimizes maintenance intervals, assigns technicians, and schedules tasks to minimize downtime and ensure timely intervention. The system considers factors such as asset criticality, maintenance history, and resource availability.
Work Order Management
ERP software streamlines work order management by providing a centralized platform to create, track, and manage maintenance requests. It enables collaboration between maintenance teams, technicians, and other stakeholders, ensuring efficient coordination and execution of maintenance tasks.
Asset Management
ERP software provides comprehensive asset management capabilities, including asset tracking, inventory control, and spare parts management. It helps organizations maintain an accurate and up-to-date inventory of assets, ensuring availability of critical spare parts and reducing downtime.
Reporting and Analytics
ERP software generates detailed reports and analytics that provide insights into asset performance, maintenance effectiveness, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). These reports help organizations evaluate the effectiveness of their predictive maintenance strategies and identify areas for improvement.
Examples of ERP Software with Predictive Maintenance Features
- SAP S/4HANA
- Oracle E-Business Suite
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Infor CloudSuite Industrial
- IFS Applications
Benefits of Using ERP Software for Predictive Maintenance

Implementing ERP software for predictive maintenance offers a range of benefits that can significantly enhance maintenance operations. These advantages extend beyond cost savings and encompass improved efficiency, increased equipment uptime, and enhanced decision-making.
Reduced Maintenance Costs
ERP software enables businesses to optimize maintenance schedules and reduce unnecessary repairs. By leveraging data analytics and condition monitoring, ERP systems can identify potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns. This proactive approach helps organizations minimize downtime, spare part inventory, and maintenance labor costs.
For instance, a manufacturing company using ERP software for predictive maintenance reported a 25% reduction in maintenance costs within the first year of implementation. The software identified early warning signs of equipment failure, allowing for timely interventions and preventing catastrophic breakdowns.
Improved Equipment Uptime, ERP software for predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance capabilities within ERP software empower businesses to maximize equipment uptime. By continuously monitoring equipment performance and analyzing data, ERP systems can predict when maintenance is required, ensuring timely interventions to prevent unplanned downtime.
A study conducted by an industry research firm revealed that organizations using ERP software for predictive maintenance experienced an average increase of 15% in equipment uptime. This improved availability of critical assets translated into increased productivity and reduced production losses.
Enhanced Decision-Making
ERP software provides a centralized platform for managing maintenance data, enabling businesses to make informed decisions. The system consolidates information from various sources, including sensors, maintenance logs, and historical data, providing a comprehensive view of equipment performance.
With this centralized data, maintenance managers can analyze trends, identify patterns, and develop proactive maintenance strategies. The software also offers reporting and analytics tools that help businesses track key performance indicators (KPIs) and measure the effectiveness of their maintenance operations.
Challenges of Implementing ERP Software for Predictive Maintenance
Implementing ERP software for predictive maintenance can bring numerous benefits, but it also comes with potential challenges. Identifying these challenges and developing strategies to mitigate them is crucial for successful implementation.
One major challenge is data integration. ERP systems require a large amount of data from various sources, including maintenance records, sensor data, and production schedules. Integrating this data into the ERP system can be complex and time-consuming, especially if the data is not standardized or if there are compatibility issues.
Data Integration
- Standardize data formats and establish clear data ownership.
- Use data integration tools to automate the data transfer process.
- Conduct thorough data cleansing and validation to ensure data accuracy.
Another challenge is the lack of skilled resources. Predictive maintenance requires specialized knowledge and expertise in both ERP systems and maintenance engineering. Finding and training staff with these skills can be difficult, especially for small and medium-sized businesses.
Lack of Skilled Resources
- Invest in training and development programs for existing staff.
- Partner with external consultants or service providers for specialized expertise.
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for ERP implementation and maintenance.
Finally, there is the challenge of change management. Implementing ERP software can significantly change existing maintenance processes and workflows. This can lead to resistance and disruption if not managed properly.
Change Management
- Involve stakeholders in the planning and implementation process.
- Communicate the benefits and value of the new system to users.
- Provide training and support to help users adapt to the new system.
Industry Use Cases of ERP Software for Predictive Maintenance
ERP software for predictive maintenance has found widespread adoption across various industries, leading to significant improvements in asset uptime, maintenance efficiency, and overall operational performance.
One prominent industry where ERP software for predictive maintenance has made a notable impact is manufacturing. By integrating data from sensors, equipment logs, and maintenance records, manufacturers can gain real-time insights into the health and performance of their production lines.
This enables them to identify potential failures early on, schedule maintenance interventions proactively, and minimize unplanned downtime. For example, a leading automotive manufacturer implemented an ERP system with predictive maintenance capabilities, resulting in a 20% reduction in unplanned downtime and a 15% increase in production output.
Energy and Utilities
In the energy and utilities sector, ERP software for predictive maintenance plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of critical infrastructure. By monitoring the condition of equipment such as transformers, turbines, and pipelines, utilities can identify anomalies and potential failures before they escalate into major incidents.
This proactive approach helps prevent power outages, gas leaks, and other disruptions, ensuring a stable and reliable supply of energy to consumers. For instance, a major utility company implemented an ERP system with predictive maintenance capabilities, leading to a 30% reduction in equipment failures and a 10% improvement in overall system efficiency.
Transportation and Logistics
The transportation and logistics industry heavily relies on vehicles and equipment to move goods and people efficiently. ERP software for predictive maintenance enables fleet managers to monitor the condition of vehicles, track maintenance schedules, and identify potential issues before they lead to breakdowns or accidents.
By proactively scheduling maintenance based on real-time data, transportation companies can minimize downtime, reduce operating costs, and ensure the safety and reliability of their fleets. For example, a leading trucking company implemented an ERP system with predictive maintenance capabilities, resulting in a 15% reduction in maintenance costs and a 25% increase in vehicle uptime.
Final Thoughts: ERP Software For Predictive Maintenance
As ERP software for predictive maintenance continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of maintenance management. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, businesses can gain unprecedented visibility into their assets, optimize maintenance schedules, and ultimately drive significant improvements in productivity, profitability, and sustainability.
Expert Answers
What are the key benefits of using ERP software for predictive maintenance?
ERP software for predictive maintenance offers numerous benefits, including reduced downtime, improved asset utilization, optimized maintenance costs, enhanced safety, and increased operational efficiency.
How does ERP software support predictive maintenance?
ERP software provides a centralized platform that integrates data from various sources, including sensors, maintenance records, and production schedules. This data is analyzed to identify patterns and predict potential equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance actions.
What are the challenges of implementing ERP software for predictive maintenance?
Potential challenges include data integration, user adoption, and the need for skilled resources. However, these challenges can be overcome with careful planning, effective communication, and training.