ERP software for maintainability tools empowers businesses to streamline maintenance operations, enhance asset management, and optimize maintenance schedules, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
ERP systems seamlessly integrate with various maintainability tools, enabling real-time data collection, predictive maintenance capabilities, and comprehensive work order management.
ERP Software Overview
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software systems are comprehensive software solutions that integrate various business functions into a single, unified system. They provide a centralized platform for managing core business processes, such as:
- Financial management
- Supply chain management
- Human resources management
- Customer relationship management
By integrating these functions, ERP systems provide a real-time view of the entire organization, enabling businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make more informed decisions.
Benefits of ERP Systems for Maintainability Management
Implementing ERP systems specifically for maintainability management offers several benefits, including:
- Improved asset visibility:ERP systems provide a comprehensive view of all assets, including their location, condition, and maintenance history.
- Streamlined maintenance planning:ERP systems help businesses plan and schedule maintenance activities more effectively, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing downtime.
- Enhanced maintenance execution:ERP systems provide mobile access to maintenance instructions, work orders, and other relevant information, enabling technicians to perform maintenance tasks more efficiently.
- Reduced maintenance costs:By optimizing maintenance planning and execution, ERP systems can help businesses reduce maintenance costs and improve asset uptime.
- Improved compliance:ERP systems help businesses track and document maintenance activities, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Maintainability Tools Integration

ERP software can seamlessly integrate with various maintainability tools to enhance maintenance processes and improve asset uptime.
By integrating with specialized maintainability tools, ERP systems gain access to advanced capabilities for managing maintenance tasks, tracking asset performance, and optimizing maintenance strategies.
Specific Maintainability Tools
- Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS): CMMS tools provide comprehensive functionality for managing maintenance activities, including work order management, asset tracking, and preventive maintenance scheduling.
- Condition Monitoring Systems (CMS): CMS tools monitor asset health and performance in real-time, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing unexpected failures.
- Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) Tools: RCM tools assist in identifying and prioritizing maintenance tasks based on criticality and risk analysis.
- Asset Performance Management (APM) Tools: APM tools provide insights into asset performance and utilization, helping optimize maintenance strategies and reduce downtime.
Data Management and Analytics

ERP software plays a crucial role in facilitating the collection and analysis of maintainability data. This data provides valuable insights into the performance and reliability of assets, enabling organizations to make informed decisions regarding maintenance strategies and resource allocation.The types of data that can be collected and analyzed using ERP systems include:
Asset Inventory and Maintenance History
- Detailed records of all assets, including their specifications, location, and maintenance history.
- This data allows for the tracking of asset utilization, maintenance costs, and downtime.
Work Order Management
- Comprehensive information on work orders, including their status, priority, and completion time.
- This data helps organizations monitor the efficiency of maintenance processes and identify areas for improvement.
Spare Parts Management
- Real-time inventory of spare parts, including their availability, cost, and lead time.
- This data ensures that the necessary parts are available when needed, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Condition Monitoring
- Data collected from sensors and other monitoring devices, providing insights into the health and performance of assets.
- This data allows for the early detection of potential issues and the implementation of preventive maintenance strategies.
Failure Analysis
- Detailed records of asset failures, including their causes, consequences, and corrective actions.
- This data helps organizations identify patterns and trends in asset failures, enabling them to develop targeted maintenance strategies.
By leveraging these data sources, ERP software provides a comprehensive view of asset maintainability, enabling organizations to optimize maintenance processes, reduce downtime, and improve overall asset performance.
Predictive Maintenance Capabilities
ERP software can be used to predict maintenance needs and optimize maintenance schedules by leveraging data from various sources, including equipment sensors, historical maintenance records, and operational data. This data is analyzed using advanced algorithms to identify patterns and trends that indicate potential maintenance issues.Predictive maintenance techniques that can be implemented using ERP systems include:
Condition Monitoring
- Monitors equipment condition in real-time using sensors to detect early signs of degradation.
- Helps identify potential failures before they occur, allowing for timely maintenance interventions.
Trend Analysis
- Analyzes historical maintenance data to identify patterns and trends that indicate potential maintenance issues.
- Helps predict future maintenance needs based on past performance and usage data.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Identifies potential failure modes and their impact on system performance.
- Helps prioritize maintenance tasks based on the criticality of the equipment and the likelihood of failure.
Work Order Management

ERP software plays a crucial role in streamlining work order management, enabling organizations to efficiently create, track, and complete work orders. By integrating various aspects of work order management into a centralized platform, ERP systems enhance operational efficiency and visibility.
ERP systems offer comprehensive features to support efficient work order management, including:
Work Order Creation and Tracking
- Automated work order generation based on predefined triggers or conditions
- Centralized repository for work orders, providing a comprehensive view of all active and completed work orders
- Real-time tracking of work order status, including progress updates, delays, and completion
Work Order Scheduling and Assignment
- Optimized scheduling algorithms to assign work orders to the most appropriate technicians based on availability, skills, and workload
- Integration with resource planning modules to ensure efficient utilization of technicians and equipment
- Automated notifications and reminders to keep technicians informed of upcoming work orders and deadlines
Work Order Execution and Completion
- Mobile-friendly interfaces for technicians to access work order details, update status, and record materials used
- Integration with inventory management systems to track material availability and consumption
- Automated workflow triggers to initiate follow-up actions, such as inspections, preventive maintenance, or warranty claims
Work Order Reporting and Analytics
- Comprehensive reporting capabilities to analyze work order trends, identify bottlenecks, and measure technician performance
- Integration with business intelligence tools for advanced data analysis and insights
- Dashboards and visualizations to provide real-time visibility into work order metrics and KPIs
Asset Management

ERP software provides comprehensive asset management capabilities, enabling organizations to effectively manage and track their maintenance assets throughout their lifecycle. This includes tracking asset details, maintenance history, and current status, allowing for efficient asset utilization and proactive maintenance planning.
ERP systems offer a range of asset management capabilities, including:
Asset Tracking
- Centralized repository for all asset information, including location, usage, and maintenance history.
- Asset tagging and barcoding for easy identification and tracking.
- Real-time asset visibility, providing insights into asset availability and utilization.
Maintenance Scheduling
- Automated maintenance scheduling based on asset usage and condition monitoring data.
- Integration with computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) for detailed maintenance planning and execution.
- Optimization of maintenance intervals to minimize downtime and maximize asset lifespan.
Preventive Maintenance
- Scheduling of preventive maintenance tasks based on asset condition and manufacturer recommendations.
- Tracking of maintenance history and identification of recurring issues for proactive maintenance planning.
- Integration with predictive maintenance tools for early detection of potential failures.
Preventive Maintenance Planning
ERP software plays a crucial role in assisting organizations with planning and scheduling preventive maintenance tasks. It enables the creation of comprehensive maintenance plans that define the tasks to be performed, their frequency, and the resources required.
Utilizing ERP systems for preventive maintenance planning offers several advantages. It streamlines the process by automating task scheduling, ensuring that maintenance is performed on a timely basis, reducing the likelihood of equipment failures and unplanned downtime.
Benefits of ERP Systems for Preventive Maintenance Planning
- Enhanced visibility into maintenance schedules, allowing for better planning and resource allocation.
- Improved communication and coordination among maintenance teams, reducing the risk of missed or delayed tasks.
- Reduced maintenance costs by optimizing resource utilization and minimizing unplanned downtime.
- Increased equipment uptime and reliability, leading to improved productivity and reduced operational risks.
- Enhanced compliance with industry regulations and standards, ensuring adherence to best practices.
Mobile Accessibility
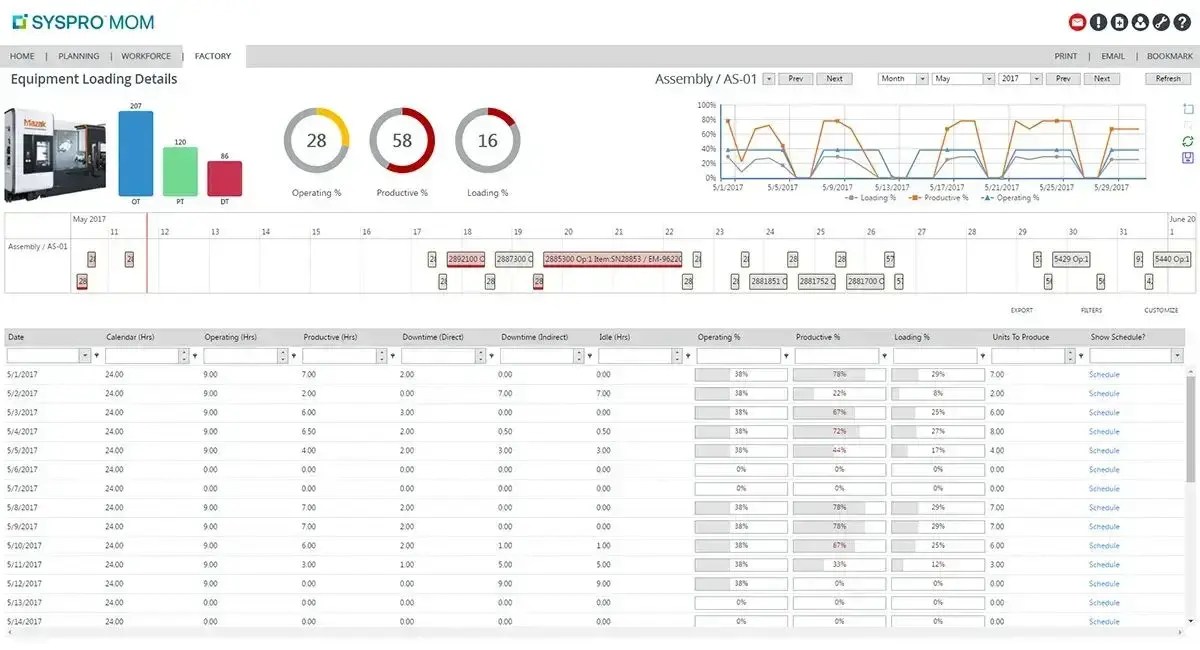
Mobile accessibility in ERP software provides the ability to access and manage maintainability tools remotely using mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.
This offers numerous advantages, including:
- Increased flexibility and convenience for maintenance technicians who can access information and perform tasks on the go.
- Improved productivity by enabling technicians to complete tasks faster and more efficiently.
- Enhanced collaboration by allowing technicians to share information and updates with colleagues in real-time.
Features and Capabilities
Mobile ERP systems for maintainability management typically offer a range of features and capabilities, including:
- Work order management: Create, assign, and track work orders from anywhere.
- Asset management: View and manage asset information, including location, history, and maintenance schedules.
- Preventive maintenance planning: Schedule and manage preventive maintenance tasks to prevent equipment failures.
- Data collection: Capture data on maintenance activities, such as inspections, repairs, and parts replacements.
- Reporting: Generate reports on maintenance performance, asset utilization, and other key metrics.
Reporting and Visualization
ERP software provides robust reporting and visualization capabilities for maintainability data, enabling users to easily access, analyze, and present data in meaningful ways. These capabilities empower organizations to make informed decisions and optimize their maintenance operations.ERP systems can generate a wide range of reports and visualizations, including:
Customizable Reports
- Work order history reports to track the status, completion time, and associated costs of work orders.
- Asset performance reports to assess the reliability, availability, and utilization of assets.
- Preventive maintenance reports to monitor the adherence to maintenance schedules and identify potential issues.
Interactive Dashboards
- Real-time dashboards to provide an overview of key maintenance metrics, such as work order volume, asset availability, and mean time to repair (MTTR).
- Predictive maintenance dashboards to identify potential asset failures and schedule proactive maintenance.
These reports and visualizations can be tailored to specific user needs and preferences, allowing organizations to focus on the most relevant data for their operations. The ability to easily access and analyze maintainability data enables organizations to identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to enhance their maintenance strategies.
Integration with Other Systems: ERP Software For Maintainability Tools
ERP software can integrate with other systems, such as CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems), to enhance maintainability management. CMMS helps organizations manage maintenance activities, track assets, and optimize maintenance schedules. Integrating ERP and CMMS allows for seamless data sharing, improved communication, and better decision-making.
Benefits of ERP and CMMS Integration, ERP software for maintainability tools
- Centralized data management:ERP and CMMS integration eliminates data silos and ensures that all relevant maintenance information is stored in a single system. This improves data accuracy and accessibility, enabling organizations to make informed decisions based on real-time data.
- Improved communication:Integration facilitates effective communication between maintenance and other departments, such as procurement and finance. Real-time updates on maintenance activities, work orders, and asset status can be shared across the organization, ensuring everyone has the latest information.
- Enhanced decision-making:With integrated data, organizations can analyze maintenance trends, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. This can lead to optimized maintenance schedules, reduced downtime, and improved asset utilization.
- Increased efficiency:Integration automates tasks and streamlines processes, such as work order creation and approval. This eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and frees up maintenance personnel to focus on more value-added activities.
End of Discussion

By leveraging ERP software for maintainability tools, organizations gain a competitive edge through improved asset utilization, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced maintenance planning, ultimately maximizing uptime and optimizing maintenance processes.
FAQ Overview
How does ERP software enhance maintainability management?
ERP software provides centralized data management, predictive maintenance capabilities, streamlined work order management, and asset tracking, leading to improved maintenance efficiency.
What are the key benefits of using ERP software for maintainability tools?
ERP software improves asset utilization, reduces maintenance costs, enhances maintenance planning, and optimizes maintenance schedules, resulting in increased uptime and cost savings.
How does ERP software facilitate predictive maintenance?
ERP software collects and analyzes maintenance data, enabling businesses to identify patterns and predict maintenance needs, optimizing maintenance schedules and preventing unexpected downtime.
What are the advantages of mobile accessibility in ERP software for maintainability tools?
Mobile ERP systems provide real-time access to maintenance data, work orders, and asset information, allowing maintenance teams to respond quickly and efficiently to maintenance requests.