ERP software for logistics management has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing the way businesses optimize their supply chains. By seamlessly integrating various logistics operations, ERP systems empower businesses to achieve unprecedented efficiency, visibility, and cost savings.
With its comprehensive capabilities, ERP software for logistics streamlines inventory management, transportation planning, warehousing operations, and customer order fulfillment. It provides real-time data visibility, enabling businesses to make informed decisions, reduce lead times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
ERP Software Overview
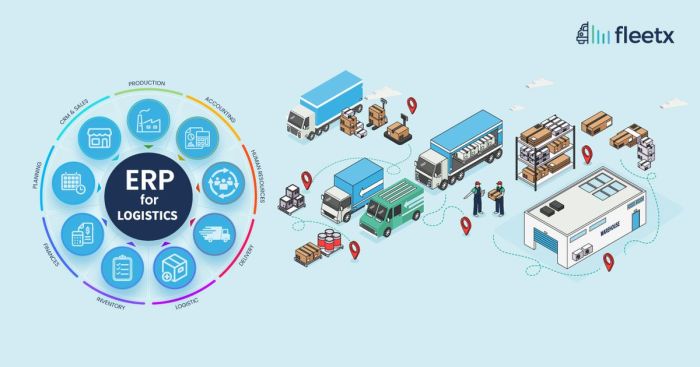
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive software suite that integrates various business processes into a single system. It offers a centralized platform for managing key business functions such as finance, supply chain management, manufacturing, and human resources.
ERP software typically consists of several core components, including:
- Financial Management:Tracks financial transactions, manages accounts receivable and payable, and provides financial reporting.
- Supply Chain Management:Oversees the flow of goods and materials from suppliers to customers, including inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation.
- Manufacturing:Manages production processes, including scheduling, capacity planning, and quality control.
- Human Resources:Handles employee information, payroll, benefits administration, and performance management.
ERP software can significantly streamline business processes by:
- Eliminating data redundancy:Centralizes data in a single system, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
- Improving communication and collaboration:Provides a common platform for all departments to share information and collaborate on projects.
- Automating tasks:Automates repetitive tasks, such as data entry and report generation, freeing up employees for more strategic initiatives.
- Enhancing visibility and control:Provides real-time visibility into business operations, enabling managers to make informed decisions.
Logistics Management with ERP
Integrating ERP software into logistics management brings numerous advantages to businesses. ERP systems provide a centralized platform that connects all aspects of logistics operations, enabling seamless data flow, improved visibility, and enhanced efficiency.
ERP software empowers logistics managers with real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and shipment tracking. This comprehensive view allows for proactive decision-making, reducing the risk of stockouts, delays, and costly errors.
Benefits of ERP for Logistics Management
- Improved supply chain visibility
- Enhanced inventory management
- Streamlined order processing
- Reduced shipping costs
- Improved customer service
Example: Enhanced Supply Chain Visibility
ERP software provides a comprehensive view of the entire supply chain, from suppliers to customers. This visibility enables logistics managers to identify bottlenecks, optimize inventory levels, and make informed decisions to improve overall efficiency. For instance, by tracking inventory levels in real-time, businesses can prevent overstocking and ensure that products are available when needed, reducing the risk of lost sales and improving customer satisfaction.
Features of ERP Software for Logistics
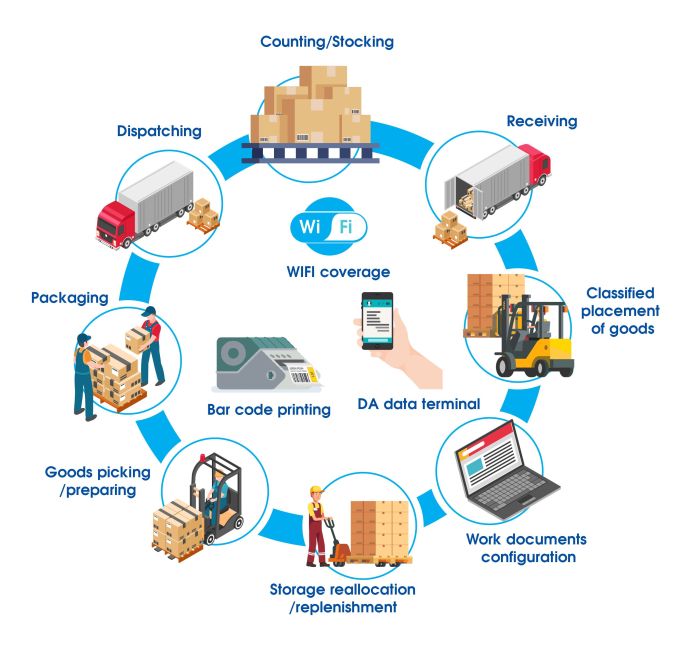
ERP software for logistics management offers a comprehensive suite of features tailored to optimize and streamline various logistics operations. These features provide visibility, control, and efficiency throughout the supply chain, from procurement to delivery.
Core Features
- Inventory Management:ERP systems provide real-time inventory tracking, allowing businesses to monitor stock levels, optimize inventory allocation, and prevent stockouts.
- Warehouse Management:ERP software helps manage warehouse operations, including receiving, put-away, picking, packing, and shipping. It optimizes warehouse space utilization, reduces errors, and improves order fulfillment efficiency.
- Transportation Management:ERP systems facilitate the planning, execution, and tracking of transportation operations. They help businesses select carriers, optimize routes, and monitor shipments to ensure timely and cost-effective delivery.
- Order Management:ERP software streamlines the order fulfillment process, from order entry to invoicing. It provides visibility into order status, allows for order tracking, and facilitates seamless communication between departments.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):ERP systems include CRM modules that help businesses manage customer interactions, track sales opportunities, and provide personalized customer service.
Benefits of ERP Software for Logistics

ERP software can bring numerous benefits to logistics operations, leading to significant cost savings and operational improvements. These benefits include:
Cost Savings
- Reduced inventory costs:ERP software provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, enabling businesses to optimize inventory levels and reduce the risk of overstocking or understocking.
- Lower transportation costs:ERP software can optimize transportation routes and consolidate shipments, leading to reduced transportation costs.
- Improved labor efficiency:ERP software automates many tasks, such as order processing and inventory management, freeing up employees to focus on more value-added activities.
Operational Improvements
- Improved customer service:ERP software provides a centralized view of customer data, enabling businesses to provide faster and more accurate customer service.
- Increased productivity:ERP software automates many tasks, reducing the time and effort required to complete tasks.
- Improved collaboration:ERP software provides a single platform for all departments to share information and collaborate on projects.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the value of ERP software in logistics. For example, a leading automotive manufacturer implemented an ERP system and achieved a 20% reduction in inventory costs and a 15% increase in productivity.
Challenges of ERP Software Implementation
Implementing ERP software for logistics management brings about several challenges that need to be carefully addressed to ensure a successful implementation.
One of the key challenges is the complexity of ERP systems, which can make it difficult for organizations to fully understand and utilize the software’s capabilities. This can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and a lack of adoption by users.
Data Integration
ERP systems require a large amount of data from different sources, which can be a challenge to integrate and maintain. Data inconsistency and redundancy can occur if the data is not properly managed, leading to inaccurate reporting and decision-making.
Change Management
Implementing an ERP system can involve significant changes to business processes and workflows. This can be disruptive to the organization and requires effective change management strategies to ensure that users are trained and supported throughout the transition.
Cost and Resources, ERP software for logistics management
ERP software can be expensive to purchase and implement, and it requires ongoing maintenance and support. Organizations need to carefully assess the costs and resources required to ensure that they have the necessary budget and personnel to support the system.
Vendor Selection
Choosing the right ERP vendor is crucial for a successful implementation. Organizations need to evaluate the vendor’s experience, capabilities, and support offerings to ensure that they can provide the necessary expertise and support throughout the implementation and beyond.
Overcoming Challenges
To overcome these challenges, organizations should adopt a structured and phased approach to ERP implementation. This involves careful planning, data preparation, user training, and change management strategies. Additionally, organizations should consider partnering with experienced ERP vendors who can provide guidance and support throughout the process.
ERP Software Selection Criteria: ERP Software For Logistics Management
Selecting the most suitable ERP software for logistics management is critical for optimizing supply chain operations. To ensure an effective selection process, it is essential to establish key criteria that align with the organization’s specific requirements and goals.
A comprehensive checklist or decision matrix can provide a structured framework for evaluating and comparing different ERP software solutions. This tool should consider the following key aspects:
Functional Capabilities
- Core logistics functionality, including inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation planning.
- Integration with other business systems, such as CRM, accounting, and warehouse management systems.
- Support for specific industry-specific requirements, such as regulatory compliance or temperature-controlled storage.
Technical Considerations
- Scalability and flexibility to accommodate future growth and changing business needs.
- Deployment options, including cloud-based or on-premises solutions.
- Data security and compliance measures to protect sensitive information.
Vendor Support
- Reputation and experience in the logistics industry.
- Level of support and maintenance provided, including response times and technical expertise.
- Availability of training and documentation resources.
Cost and Implementation
- Total cost of ownership, including software licensing, implementation, and ongoing maintenance.
- Estimated implementation timeline and resource requirements.
- Potential return on investment (ROI) and cost-saving opportunities.
User Experience
- Ease of use and intuitiveness of the user interface.
- Ability to customize the software to meet specific user needs.
- Availability of mobile or remote access capabilities.
By carefully considering these criteria and developing a comprehensive selection process, organizations can increase the likelihood of choosing an ERP software solution that effectively meets their logistics management requirements and drives operational efficiency.
Integration with Other Systems
ERP software is not an isolated system; it interacts with various other business systems to exchange data and facilitate seamless operations. Integrating ERP with other systems is crucial for ensuring data consistency, eliminating redundancies, and improving overall efficiency.
Challenges of Integration
Integrating ERP with other systems can pose challenges, including:
- Data compatibility issues between different systems
- Lack of standardized data formats and communication protocols
- Complexity of legacy systems and their resistance to change
Best Practices for Seamless Integration
To ensure seamless integration, it is essential to:
- Map data fields and establish clear data conversion rules
- Use standardized data formats and communication protocols
- Implement middleware or integration platforms to facilitate data exchange
- Test and validate the integration thoroughly before deployment
- Establish a governance framework to manage data ownership and security
Future Trends in ERP Software for Logistics
The future of ERP software for logistics is poised to be shaped by a number of emerging trends and innovations. These trends will have a profound impact on the way that logistics operations are managed, making them more efficient, effective, and responsive.
One of the most significant trends is the increasing adoption of cloud-based ERP systems. Cloud-based ERP systems offer a number of advantages over on-premises systems, including lower costs, greater flexibility, and easier scalability. As a result, cloud-based ERP systems are becoming increasingly popular among logistics companies of all sizes.
Another important trend is the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in ERP software. AI and ML can be used to automate a variety of tasks, such as data entry, order processing, and inventory management. This can free up logistics professionals to focus on more strategic tasks, such as customer service and supply chain optimization.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed database that is used to maintain a continuously growing list of records, called blocks. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. By design, blockchain is inherently resistant to modification of the data.
This is because once a block is added to the chain, it is very difficult to alter it without altering all subsequent blocks, which requires collusion of the network majority.
Real-time Visibility
Real-time visibility is the ability to track the status of shipments and inventory in real time. This can be achieved through the use of GPS tracking devices, RFID tags, and other technologies. Real-time visibility can help logistics companies to improve their efficiency and customer service by providing them with up-to-date information on the status of their shipments.
Best Practices for ERP Software Implementation
ERP software implementation is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. By following best practices, organizations can increase the chances of a successful implementation.One of the most important best practices is to involve all stakeholders in the implementation process.
This includes not only the IT team but also users from all levels of the organization. By getting buy-in from all stakeholders, organizations can ensure that the ERP system is aligned with the needs of the business.Another best practice is to create a detailed implementation plan.
This plan should include a timeline, budget, and resource allocation. By having a clear plan in place, organizations can avoid delays and cost overruns.It is also important to test the ERP system thoroughly before going live. This will help to identify and fix any bugs or issues.
By testing the system thoroughly, organizations can reduce the risk of disruptions during the go-live process.Finally, it is important to provide ongoing training and support to users. This will help to ensure that users are able to get the most out of the ERP system.
By providing ongoing training and support, organizations can maximize the return on their investment in ERP software.
Step-by-Step Guide to ERP Software Implementation
- Define the project scope and objectives.
- Create a detailed implementation plan.
- Involve all stakeholders in the implementation process.
- Test the ERP system thoroughly before going live.
- Provide ongoing training and support to users.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, ERP software for logistics management is an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to optimize their supply chains. Its robust features, coupled with seamless integration capabilities, empower businesses to achieve operational excellence, drive cost savings, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market landscape.
Quick FAQs
What are the key benefits of using ERP software for logistics management?
ERP software for logistics management offers numerous benefits, including improved supply chain visibility, reduced lead times, optimized inventory levels, enhanced customer service, and significant cost savings.
How does ERP software improve supply chain visibility?
ERP software provides a centralized platform that integrates data from all aspects of the supply chain, giving businesses a comprehensive view of their operations. This real-time visibility enables businesses to identify bottlenecks, optimize inventory levels, and make informed decisions to improve overall efficiency.
What are some common challenges faced when implementing ERP software for logistics management?
Common challenges include data migration, user adoption, and integration with existing systems. However, with proper planning, effective change management, and a phased implementation approach, these challenges can be successfully overcome.