ERP software for industry benchmarks sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with science with analytical tone style and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the depths of this topic, we will explore the concept of industry benchmarks for ERP software, identify key performance indicators (KPIs) used to evaluate ERP performance, and discuss the importance of industry-specific benchmarks.
By understanding how ERP software can be compared using industry benchmarks, organizations can gain valuable insights into their own performance and identify areas for improvement.
ERP Software Industry Benchmark Overview
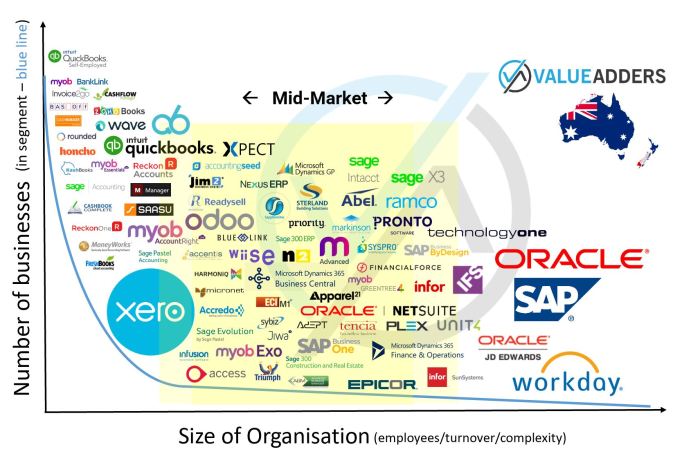
ERP software industry benchmarks provide a valuable tool for businesses to assess their performance against industry standards and best practices. By understanding how their systems compare to others, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about their ERP investments.
Common industry benchmarks used to measure ERP performance include:
- Cost of ownership (TCO):This metric measures the total cost of owning and operating an ERP system, including hardware, software, maintenance, and support.
- Return on investment (ROI):This metric measures the financial benefits of an ERP system, such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
- Time to value (TTV):This metric measures the amount of time it takes to implement and realize the benefits of an ERP system.
- User adoption:This metric measures the extent to which users are satisfied with and using an ERP system.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for ERP Software
KPIs are quantifiable measurements used to assess the effectiveness and efficiency of ERP software. They provide insights into key areas of performance, allowing organizations to compare their systems to industry benchmarks and identify areas for improvement.
ERP software KPIs encompass a wide range of metrics, including:
- Cost Savings:Measures the financial benefits of implementing ERP software, such as reduced operational costs, improved inventory management, and increased efficiency.
- Time Savings:Quantifies the time saved by automating tasks and streamlining processes, resulting in faster order fulfillment, improved customer service, and increased productivity.
- Return on Investment (ROI):Calculates the financial return generated by the ERP software investment, considering the costs of implementation and maintenance.
- Customer Satisfaction:Measures the level of customer satisfaction with the ERP software, including ease of use, functionality, and support.
- Data Integrity:Assesses the accuracy and consistency of data within the ERP system, ensuring reliable decision-making and efficient operations.
- Security:Evaluates the effectiveness of security measures implemented in the ERP software, protecting data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Scalability:Measures the ability of the ERP software to adapt to changing business needs and accommodate future growth, ensuring it can support the organization’s long-term objectives.
- Integration:Assesses the ease and effectiveness of integrating the ERP software with other systems, such as CRM, SCM, and financial applications, ensuring seamless data flow and efficient collaboration.
- User Adoption:Quantifies the extent to which users have adopted the ERP software, indicating its usability, acceptance, and impact on organizational efficiency.
Industry-Specific Benchmarks
Industry-specific benchmarks are crucial for ERP software as they provide tailored metrics and performance indicators that are relevant to specific industry verticals. These benchmarks enable businesses to compare their performance against industry peers and identify areas for improvement.
Industry-specific benchmarks can vary significantly due to the unique characteristics and requirements of different industries. For instance, the following are examples of how industry-specific benchmarks may differ:
Retail, ERP software for industry benchmarks
- Inventory turnover rate
- Gross profit margin
- Customer lifetime value
Manufacturing
- Production efficiency
- Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
- Quality control metrics
Healthcare
- Patient satisfaction
- Medical error rates
- Cost per patient encounter
ERP Software Comparison
ERP software comparison using industry benchmarks enables organizations to assess their performance against industry standards and identify areas for improvement.By leveraging industry benchmarks, organizations can:
- Establish performance targets
- Identify areas of strength and weakness
- Make informed decisions about ERP software selection and implementation
Comparison Process
The ERP software comparison process involves the following steps:
Identify relevant industry benchmarks
Determine the most appropriate industry-specific benchmarks based on the organization’s size, industry, and business processes.
Collect data
Gather data on key performance indicators (KPIs) from the organization’s ERP system.
Compare performance
Compare the organization’s KPIs to the industry benchmarks to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement.
Analyze results
Determine the root causes of any performance gaps and develop strategies to address them.
Implement improvements
Implement process improvements or software upgrades to enhance performance and achieve industry-leading benchmarks.
Benchmarking Methodologies
Benchmarking ERP software involves comparing its performance metrics against industry standards or best practices to identify areas for improvement. Different methodologies are used for benchmarking, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Functional Benchmarking
Functional benchmarking compares the functionality and features of an ERP software to those of similar products in the market. This helps organizations assess the software’s ability to meet their specific business requirements and identify potential gaps or areas for improvement.
Process Benchmarking
Process benchmarking focuses on comparing the business processes supported by the ERP software to industry best practices. This helps organizations identify inefficiencies or bottlenecks in their processes and make improvements to optimize performance and efficiency.
Performance Benchmarking
Performance benchmarking compares the performance metrics of an ERP software, such as speed, reliability, and scalability, to industry standards or benchmarks. This helps organizations assess the software’s ability to meet their performance requirements and identify areas for improvement.
Cost Benchmarking
Cost benchmarking compares the cost of an ERP software, including implementation, maintenance, and support, to industry benchmarks. This helps organizations assess the cost-effectiveness of the software and make informed decisions about their investment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Benchmarking Methodologies
Each benchmarking methodology has its advantages and disadvantages. Functional benchmarking provides a detailed comparison of features, but it can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Process benchmarking helps identify process inefficiencies, but it may require significant changes to existing processes. Performance benchmarking provides insights into software performance, but it can be difficult to compare different software products due to variations in testing environments.
Cost benchmarking helps assess cost-effectiveness, but it may not consider other factors such as functionality or performance.
Best Practices for ERP Benchmarking
To derive meaningful insights from ERP benchmarking, it is crucial to adhere to best practices that ensure data accuracy, analysis rigor, and effective reporting.
Data Collection:Establish clear data collection criteria and gather data from multiple sources to ensure comprehensiveness and reliability.
Data Analysis
- Data Standardization:Normalize data to ensure consistency and comparability across different systems and organizations.
- Trend Analysis:Identify patterns and trends in performance metrics over time to monitor progress and areas for improvement.
- Comparative Analysis:Compare performance metrics to industry benchmarks or best-in-class organizations to identify gaps and opportunities.
Reporting
- Clear and Concise:Reports should present findings in a clear and concise manner, highlighting key insights and recommendations.
- Actionable Insights:Identify specific areas where improvements can be made, providing actionable recommendations supported by data.
- Regular Monitoring:Establish a regular reporting schedule to track progress and identify areas for ongoing improvement.
Case Studies and Examples
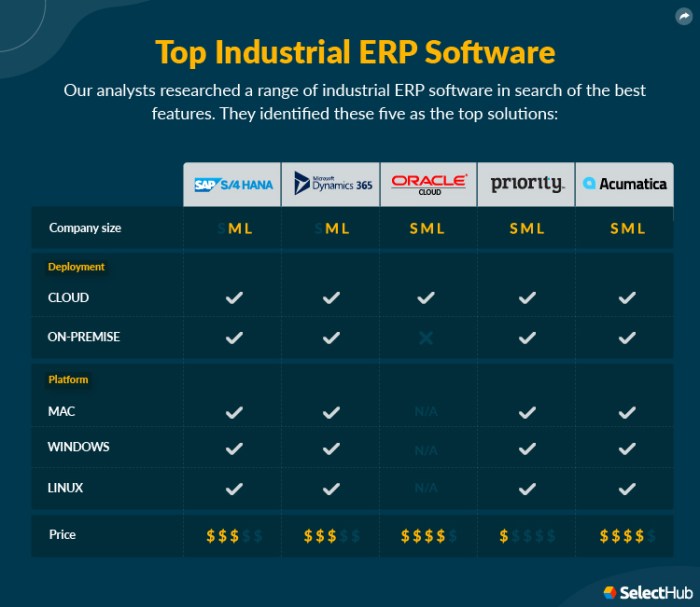
ERP software benchmarking has been successfully implemented in various industries, leading to significant benefits and improved performance.
One notable case study is a manufacturing company that implemented ERP benchmarking to identify areas for improvement in its supply chain management. By comparing its performance to industry benchmarks, the company identified inefficiencies in its inventory management and logistics processes.
This led to the implementation of new strategies that resulted in a 15% reduction in inventory costs and a 10% improvement in on-time delivery performance.
Benefits of Benchmarking
- Improved decision-making: Benchmarking provides data-driven insights that help organizations make informed decisions about their ERP systems.
- Increased efficiency: By identifying areas for improvement, organizations can optimize their ERP systems to achieve greater efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced costs: Benchmarking can help organizations identify areas where they can reduce costs by streamlining processes and eliminating inefficiencies.
- Enhanced competitiveness: By comparing their performance to industry leaders, organizations can identify areas where they need to improve to remain competitive.
Tools and Resources for ERP Benchmarking

ERP benchmarking tools and resources can streamline data collection, analysis, and reporting, providing valuable insights into an organization’s performance relative to industry standards.
Data Collection Tools
Data collection tools facilitate the gathering of relevant data from various sources, including ERP systems, financial records, and industry reports. These tools can automate data extraction, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
Analysis Tools
Analysis tools help organizations compare their performance against industry benchmarks and identify areas for improvement. These tools provide statistical analysis, trend analysis, and visualization capabilities, enabling users to interpret data and make informed decisions.
Reporting Tools
Reporting tools generate comprehensive reports that summarize benchmarking results and provide actionable insights. These reports can be customized to meet specific organizational needs and shared with stakeholders to facilitate decision-making.
Emerging Trends in ERP Benchmarking
The landscape of ERP benchmarking is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Emerging trends are shaping the future of ERP performance evaluation, enabling organizations to gain deeper insights and make data-driven decisions.
Cloud-Based Benchmarking
Cloud-based platforms are gaining traction for ERP benchmarking, offering scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud-based solutions provide real-time data access, enabling organizations to continuously monitor and compare their performance against industry benchmarks.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming ERP benchmarking by automating data analysis and identifying patterns. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify trends, anomalies, and best practices. ML models can predict future performance and provide recommendations for improvement.
Process Mining
Process mining techniques are increasingly used to analyze ERP system data and identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks. By visualizing and analyzing process flows, organizations can identify areas for optimization and streamline their operations.
Integrated Benchmarking
ERP benchmarking is becoming more integrated with other performance management tools, such as business intelligence (BI) and data analytics platforms. This integration allows organizations to gain a holistic view of their performance and identify areas for improvement across multiple dimensions.
Industry-Specific Benchmarks
The importance of industry-specific benchmarks is growing as organizations recognize the need for tailored comparisons. Industry-specific benchmarks provide more relevant insights and enable organizations to compare their performance against peers operating in similar markets and facing similar challenges.
Future Directions for ERP Benchmarking
ERP benchmarking is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing business landscapes. Future directions include:
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML algorithms will automate data collection, analysis, and reporting, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of benchmarking. Predictive analytics will enable proactive identification of areas for improvement.
Real-Time Benchmarking
Cloud-based ERP systems and data analytics platforms will facilitate real-time benchmarking, providing continuous insights into performance compared to industry peers. This enables organizations to respond swiftly to changing market conditions.
Industry-Specific and Functional Benchmarks
The focus will shift towards developing industry-specific and functional benchmarks, catering to the unique needs of different sectors and business functions. This will provide more granular insights and enable targeted improvements.
Integration with Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
ERP benchmarking data will be integrated with BI tools, enabling organizations to gain a comprehensive view of their performance across various aspects of their business. This holistic approach will support data-driven decision-making.
Adoption of Cloud-Based Benchmarking Platforms
Cloud-based benchmarking platforms will simplify the process of data collection and analysis, making it more accessible to organizations of all sizes. These platforms will provide standardized metrics and industry-wide data for comparison.
Collaboration and Data Sharing
Industry consortia and partnerships will promote collaboration and data sharing among organizations. This will facilitate the development of comprehensive benchmarks and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, ERP software for industry benchmarks provides a powerful tool for organizations to measure their performance and identify areas for improvement. By leveraging the methodologies, best practices, and tools discussed in this article, organizations can gain a competitive advantage and achieve greater success in their respective industries.
Detailed FAQs: ERP Software For Industry Benchmarks
What are industry benchmarks for ERP software?
Industry benchmarks for ERP software are a set of performance metrics that measure how well ERP systems perform in specific industries. These benchmarks can be used to compare the performance of different ERP systems and to identify areas for improvement.
What are some common KPIs used to evaluate ERP software performance?
Some common KPIs used to evaluate ERP software performance include cost reduction, improved efficiency, increased productivity, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Why are industry-specific benchmarks important for ERP software?
Industry-specific benchmarks are important for ERP software because they provide a more accurate comparison of performance within a specific industry. This is because different industries have different requirements and expectations for ERP systems.