ERP software for implementation tools takes center stage in this comprehensive guide, providing businesses with an in-depth exploration of the tools and strategies that drive successful ERP implementations. From identifying key tools to understanding their capabilities, this narrative offers a wealth of insights for organizations seeking to optimize their operations.
ERP software implementation is a transformative journey, and this guide serves as a roadmap, navigating readers through the complexities of selecting, customizing, and integrating ERP systems. With real-world case studies and expert analysis, this narrative empowers businesses to maximize the value of their ERP investments.
ERP Software Overview

ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a comprehensive business management system that integrates various aspects of an organization’s operations, such as finance, supply chain, human resources, manufacturing, and customer relationship management. It provides a central platform for data management and collaboration, enabling businesses to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions.
Benefits of ERP Software
Implementing ERP software offers numerous benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved data accuracy and consistency:ERP systems provide a single source of truth for data, eliminating data silos and ensuring accuracy across the organization.
- Enhanced efficiency and productivity:By automating processes and eliminating manual tasks, ERP software streamlines operations and improves productivity.
- Increased collaboration and communication:ERP systems provide a platform for cross-functional collaboration, breaking down departmental barriers and improving communication.
- Better decision-making:ERP systems provide real-time access to data and analytics, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
- Improved customer service:ERP systems provide a centralized view of customer interactions, enabling businesses to provide better customer support and build stronger relationships.
Implementation Tools for ERP Software
ERP software implementation tools are crucial for streamlining and enhancing the deployment process. These tools provide various features and capabilities that support efficient planning, execution, and monitoring of ERP implementations.
Key Implementation Tools
Essential tools used in ERP software implementation include:
- Project Management Software:Facilitates project planning, scheduling, resource allocation, and progress tracking.
- Data Migration Tools:Automate the transfer of data from legacy systems to the new ERP system, ensuring accuracy and data integrity.
- Testing Tools:Enable thorough testing of the ERP system to identify and resolve issues before go-live, reducing risks and ensuring functionality.
- Training Tools:Provide interactive and comprehensive training materials to educate users on the new ERP system, promoting adoption and proficiency.
- Change Management Tools:Support the management of organizational change associated with ERP implementation, addressing resistance and ensuring a smooth transition.
Popular Implementation Tools and Use Cases
Prominent ERP implementation tools include:
- SAP Activate:SAP’s implementation methodology and toolset, providing best practices and guidance for successful ERP deployments.
- Oracle Cloud ERP Implementation Services:Oracle’s suite of implementation tools, offering cloud-based solutions for efficient ERP deployments.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Implementation Tools:Microsoft’s tools for implementing Dynamics 365 ERP, including project management, data migration, and testing capabilities.
- Infor Implementation Accelerators:Infor’s tools for accelerating ERP implementations, leveraging pre-built configurations and industry-specific templates.
These tools empower organizations to implement ERP systems effectively, reducing project risks, improving data accuracy, ensuring user adoption, and facilitating organizational change management.
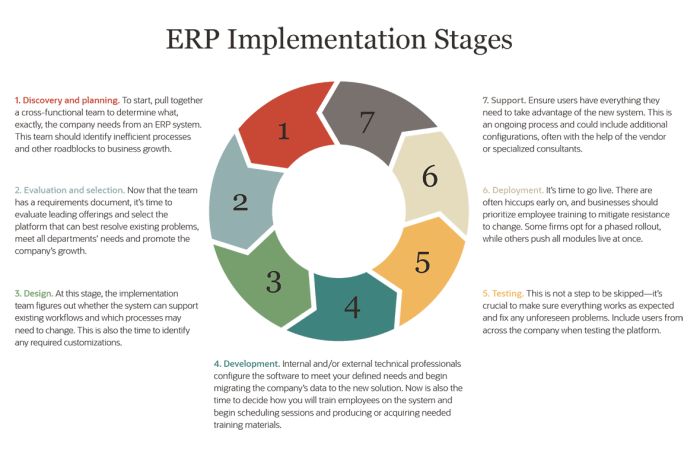
ERP Software Implementation Process

ERP software implementation is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. The steps involved in a typical ERP software implementation process include:
- Planning:This phase involves defining the project scope, objectives, and timeline. It also includes identifying the resources that will be needed to implement the software.
- Design:This phase involves designing the new ERP system and customizing it to meet the specific needs of the organization. It also includes developing a data migration plan and a training plan for users.
- Implementation:This phase involves installing the ERP software and migrating data from the old system to the new system. It also includes training users on the new system and providing support during the transition.
- Post-implementation:This phase involves monitoring the performance of the new ERP system and making any necessary adjustments. It also includes providing ongoing support to users and developing a plan for future upgrades.
ERP software implementation can be a challenging and risky process. Some of the challenges and risks associated with ERP software implementation include:
- Cost:ERP software implementation can be expensive, and it is important to budget for all of the costs involved, including software, hardware, implementation services, and training.
- Time:ERP software implementation can take a long time, and it is important to plan for the time it will take to complete the project.
- Complexity:ERP software is complex, and it can be difficult to implement it successfully. It is important to have a team of experienced professionals to help with the implementation.
- Change management:ERP software implementation can lead to significant changes in the way an organization operates. It is important to manage these changes carefully to avoid disruption to the business.
There are a number of best practices that can help to ensure a successful ERP software implementation. Some of these best practices include:
- Define clear goals and objectives:It is important to have a clear understanding of what you want to achieve with your ERP software implementation. This will help you to make decisions about the software, the implementation process, and the training that will be needed.
- Get buy-in from stakeholders:It is important to get buy-in from all of the stakeholders who will be affected by the ERP software implementation. This will help to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the implementation is successful.
- Choose the right software:There are a number of different ERP software solutions available, and it is important to choose the one that is right for your organization. Consider your organization’s size, industry, and specific needs.
- Plan carefully:ERP software implementation is a complex process, and it is important to plan carefully. This includes defining the project scope, objectives, timeline, and budget.
- Implement in phases:It is often helpful to implement ERP software in phases. This can help to reduce the risk of disruption to the business and to make the implementation more manageable.
- Provide training and support:It is important to provide training and support to users throughout the ERP software implementation process. This will help to ensure that users are able to use the software effectively and that they are able to get the most out of it.
ERP Software Selection Criteria
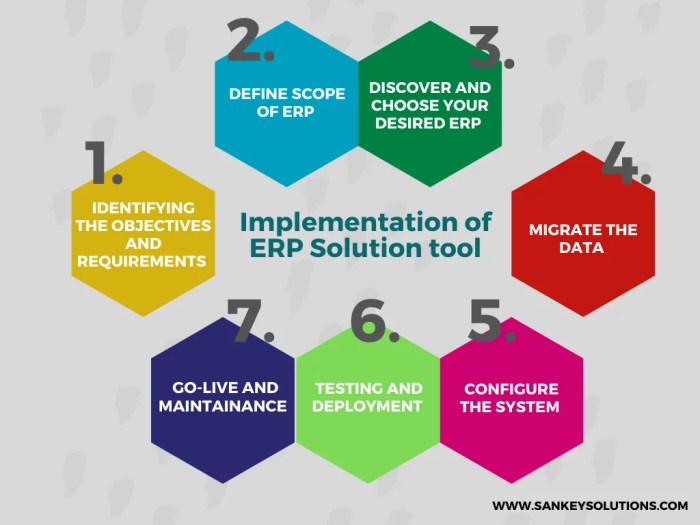
Selecting the right ERP software is crucial for successful implementation. Key factors to consider include:
- Business requirements:Define specific business needs and processes that the ERP system should address.
- Industry fit:Choose software designed for your industry, ensuring alignment with industry-specific processes and regulations.
- Scalability:Consider future growth plans and select software that can accommodate expansion and changing business needs.
- Integration capabilities:Evaluate the software’s ability to integrate with existing systems, such as CRM and supply chain management.
- User-friendliness:Ensure the software is intuitive and easy to use for employees, promoting adoption and efficiency.
Vendor Capabilities and Industry Expertise
Evaluating vendor capabilities and industry expertise is essential:
- Financial stability:Ensure the vendor is financially sound to provide ongoing support and development.
- Implementation experience:Assess the vendor’s track record in implementing ERP systems successfully.
- Industry knowledge:Choose a vendor with deep understanding of your industry’s specific requirements.
- Customer references:Seek feedback from existing customers to gauge vendor performance and customer satisfaction.
ERP Software Vendor Comparison Table, ERP software for implementation tools
| Vendor | Industry Focus | Scalability | Integration Capabilities | User-friendliness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAP | Manufacturing, retail | High | Extensive | Average |
| Oracle | Finance, healthcare | High | Good | Below average |
| Microsoft Dynamics | SMB, retail | Medium | Good | High |
| NetSuite | Cloud-based, SMB | Medium | Excellent | High |
This table provides a high-level comparison of key ERP software vendors based on specific criteria. Actual vendor selection should involve a thorough evaluation process tailored to your specific business requirements.
ERP Software Customization
ERP software is often customized to meet the specific requirements of a business. This customization can involve modifying the software’s functionality, user interface, or data structure. Customization can be necessary for a variety of reasons, such as:
- To improve the software’s fit with the business’s unique processes.
- To integrate the software with other systems used by the business.
- To meet the specific regulatory requirements of the business’s industry.
There are a number of different methods for customizing ERP software. One common method is to use the software’s built-in customization tools. These tools allow users to modify the software’s functionality, user interface, and data structure without having to write custom code.
Another method of customization is to use third-party software development tools. These tools can be used to create custom code that extends the functionality of the ERP software.
There are many examples of successful ERP software customization projects. One example is the customization of the SAP ERP software by the clothing retailer Zara. Zara used SAP ERP to create a system that allowed it to manage its global supply chain and retail operations.
The system was customized to meet the specific needs of Zara’s business, such as its need for fast and flexible production. Another example of successful ERP software customization is the customization of the Oracle ERP software by the food and beverage company PepsiCo.
PepsiCo used Oracle ERP to create a system that allowed it to manage its global operations. The system was customized to meet the specific needs of PepsiCo’s business, such as its need for strong financial controls and its need for a system that could support its complex supply chain.
ERP Software Integration
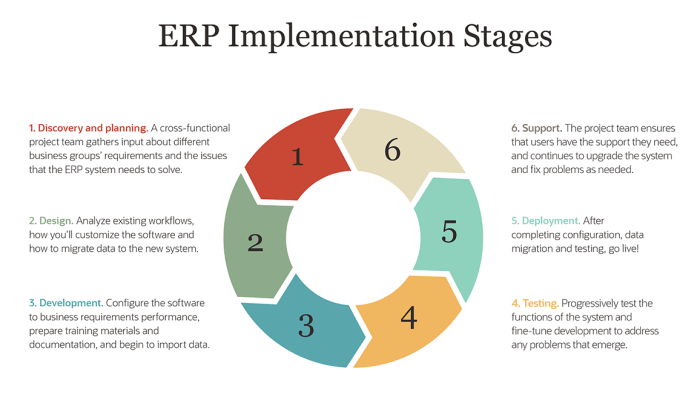
ERP software integration involves connecting various business systems and applications to enhance data sharing and streamline processes. It is crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and improve efficiency.
Methods for Integrating ERP Software
There are several methods for integrating ERP software, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. These include:
- Point-to-Point Integration:Involves direct connections between ERP software and individual systems, enabling data exchange on a limited basis.
- Enterprise Service Bus (ESB):Acts as a central hub for message routing and transformation, facilitating communication between multiple systems and ERP software.
- Application Programming Interface (API):Provides a standardized set of routines and protocols for integrating ERP software with other applications, enabling data exchange and functionality sharing.
- Cloud-Based Integration:Leverages cloud platforms and services to connect ERP software with other systems, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Integration Approaches
| Integration Approach | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Point-to-Point Integration | Simple to implement; low initial cost | Limited scalability; maintenance can be complex |
| Enterprise Service Bus | Supports complex integration scenarios; provides central control | Can be expensive to implement; requires specialized expertise |
| Application Programming Interface | Flexible and customizable; supports a wide range of applications | Can be complex to implement; requires developer expertise |
| Cloud-Based Integration | Scalable and cost-effective; easy to implement | May not be suitable for all applications; security concerns |
ERP Software Training and Support
ERP software training and support are crucial for successful implementation and user adoption. Effective training empowers users with the knowledge and skills to navigate the software efficiently, ensuring optimal utilization and maximizing return on investment.
Training Types
Various training options are available, including:
- Instructor-led training:Classroom-based sessions with a trainer providing hands-on guidance and answering questions.
- Online training:Web-based modules with interactive simulations and assessments.
- On-the-job training:Practical experience under the supervision of an experienced user.
Vendor Support
Vendor support plays a vital role in ERP implementation and maintenance. They provide:
- Technical assistance:Troubleshooting and resolving software issues.
- Product updates:Information on new features and enhancements.
- Documentation:User manuals, training materials, and reference guides.
Ongoing support ensures that users can leverage the software effectively, address challenges promptly, and stay updated with the latest advancements.
ERP Software ROI
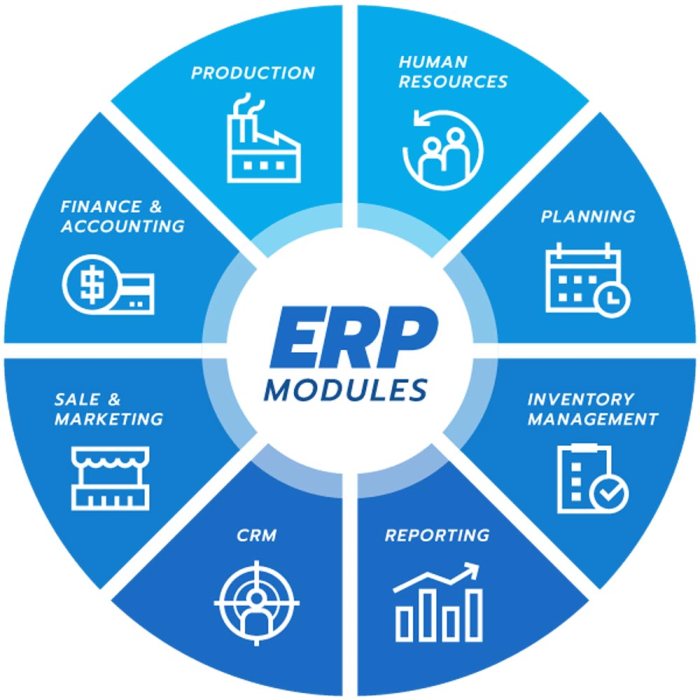
ERP software implementation can bring significant return on investment (ROI) for businesses. To calculate the potential ROI, consider factors such as increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced decision-making.
Studies have shown that businesses can achieve ROI of up to 200% within 3-5 years of ERP software implementation. For example, a manufacturing company reduced inventory costs by 25% and increased production efficiency by 15% after implementing an ERP system.
Factors Contributing to Successful ERP Software ROI
- Proper Planning and Implementation:Careful planning, thorough implementation, and user training are crucial for maximizing ROI.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Seamless integration with existing systems ensures data accuracy and eliminates redundancies, enhancing ROI.
- Scalability and Flexibility:Choosing an ERP system that can adapt to changing business needs ensures long-term ROI.
- User Adoption and Training:Effective user training and adoption drive ROI by empowering employees to leverage the system’s capabilities.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance:Regular software updates, maintenance, and technical support ensure optimal performance and maximize ROI.
ERP Software Trends and Future: ERP Software For Implementation Tools
The ERP software industry is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These trends are driven by a number of factors, including the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the growing need for data analytics, and the rise of artificial intelligence (AI).
One of the most significant trends in ERP software is the move to cloud computing. Cloud-based ERP systems offer a number of advantages over on-premise systems, including lower costs, greater flexibility, and easier scalability. As a result, more and more businesses are choosing to implement cloud-based ERP systems.
Another major trend in ERP software is the growing need for data analytics. Businesses are increasingly recognizing the value of data and are looking for ways to use data to improve their decision-making. ERP systems can provide businesses with a wealth of data, and many ERP vendors are now offering tools to help businesses analyze their data and gain insights from it.
Finally, the rise of AI is having a significant impact on ERP software. AI can be used to automate a variety of tasks, from data entry to customer service. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks and can help businesses improve their efficiency and productivity.
The Future of ERP Software
The future of ERP software is bright. As businesses continue to adopt cloud computing, data analytics, and AI, ERP systems will become even more essential to their success. ERP systems will continue to evolve to meet the changing needs of businesses, and new innovations will continue to emerge.
One of the most important trends in the future of ERP software is the convergence of ERP and CRM systems. CRM systems are used to manage customer relationships, and ERP systems are used to manage business operations. As businesses become more customer-centric, they are increasingly looking for ways to integrate their ERP and CRM systems.
This convergence will create a single, unified view of the customer, which will help businesses improve their customer service and sales.
Another important trend in the future of ERP software is the adoption of AI. AI can be used to automate a variety of tasks, from data entry to customer service. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks and can help businesses improve their efficiency and productivity.
ERP software is essential to the success of businesses in the 21st century. As businesses continue to adopt cloud computing, data analytics, and AI, ERP systems will become even more essential to their success.
ERP Software Case Studies
ERP software implementations can be complex and challenging, but they can also deliver significant benefits to organizations. To help you make the most of your ERP implementation, we have compiled a list of real-world case studies of successful ERP software implementations.
These case studies provide valuable insights into the challenges, benefits, and lessons learned from ERP implementations. We encourage you to review these case studies and learn from the experiences of others.
Case Study: ABC Company
ABC Company is a large manufacturing company with over 10,000 employees. The company implemented an ERP system to improve its efficiency and productivity.
The implementation was successful, and ABC Company realized a number of benefits, including:
- Improved inventory management
- Reduced production costs
- Improved customer service
ABC Company also learned a number of valuable lessons during the implementation process, including:
- The importance of planning and preparation
- The need for strong leadership
- The importance of user training and support
Case Study: XYZ Company
XYZ Company is a small retail company with 50 employees. The company implemented an ERP system to improve its financial management and reporting.
The implementation was successful, and XYZ Company realized a number of benefits, including:
- Improved financial reporting
- Reduced accounting costs
- Improved cash flow management
XYZ Company also learned a number of valuable lessons during the implementation process, including:
- The importance of selecting the right ERP system
- The need for a phased implementation approach
- The importance of ongoing support and maintenance
Table of Key Takeaways
The following table summarizes the key takeaways from the ERP software case studies:
| Case Study | Key Takeaways |
|---|---|
| ABC Company |
|
| XYZ Company |
|
Closure
In the ever-evolving landscape of business technology, ERP software remains a cornerstone for organizations seeking to streamline operations and drive growth. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the essential implementation tools, empowering businesses to navigate the complexities of ERP adoption and reap its transformative benefits.
By embracing the insights and strategies Artikeld within these pages, organizations can unlock the full potential of ERP software and position themselves for success in the digital age.
FAQ
What are the key benefits of using ERP software implementation tools?
ERP implementation tools streamline the implementation process, reduce errors, enhance data accuracy, and facilitate seamless integration with existing systems.
What are some common challenges associated with ERP software implementation?
Common challenges include data migration, user adoption, customization complexity, and ensuring compatibility with existing systems.
How can businesses ensure a successful ERP software implementation?
Successful implementation requires careful planning, vendor evaluation, user training, data preparation, and ongoing support.