ERP software for implementation sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the intricate workings of ERP systems, we will uncover the key components, benefits, and challenges associated with their implementation.
Join us on this captivating journey as we explore the nuances of ERP software, empowering businesses to streamline operations and achieve new heights of efficiency.
ERP software has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing a comprehensive suite of tools to manage various aspects of an organization, from supply chain management to customer relationship management. With its ability to integrate disparate systems and automate complex processes, ERP software has become an indispensable asset for businesses seeking to gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market landscape.
ERP Software Overview
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive software suite that integrates all aspects of a business, including finance, supply chain management, human resources, manufacturing, and customer relationship management (CRM). ERP systems provide a single, unified view of all business data, enabling organizations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make better decisions.
ERP software typically consists of the following key components:
- Financial management:This module tracks all financial transactions, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, and general ledger. It provides a comprehensive view of the company’s financial performance.
- Supply chain management:This module manages the flow of goods and services from suppliers to customers. It includes functions such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation management.
- Human resources:This module manages all aspects of human resources, including payroll, benefits, and employee relations. It provides a comprehensive view of the company’s workforce.
- Manufacturing:This module manages all aspects of manufacturing, including production planning, scheduling, and quality control. It provides a comprehensive view of the company’s production process.
- Customer relationship management (CRM):This module manages all aspects of customer relationships, including sales, marketing, and customer service. It provides a comprehensive view of the company’s customers.
ERP software offers a number of benefits to organizations, including:
- Improved efficiency:ERP systems can help organizations improve efficiency by automating tasks, reducing errors, and streamlining processes.
- Reduced costs:ERP systems can help organizations reduce costs by eliminating duplicate processes, improving inventory management, and optimizing supply chain operations.
- Better decision-making:ERP systems provide a single, unified view of all business data, enabling organizations to make better decisions based on accurate and timely information.
There are different types of ERP software available, each designed to meet the specific needs of different organizations. Some of the most common types of ERP software include:
- On-premise ERP:On-premise ERP software is installed on the organization’s own servers. This type of ERP software provides the most control and customization, but it can also be more expensive and complex to implement.
- Cloud ERP:Cloud ERP software is hosted by a third-party provider and accessed over the internet. This type of ERP software is less expensive and complex to implement than on-premise ERP software, but it can also be less customizable.
- Hybrid ERP:Hybrid ERP software is a combination of on-premise and cloud ERP software. This type of ERP software provides the benefits of both on-premise and cloud ERP software, but it can also be more complex to implement.
The type of ERP software that is right for an organization will depend on its specific needs and resources.
ERP Software Implementation

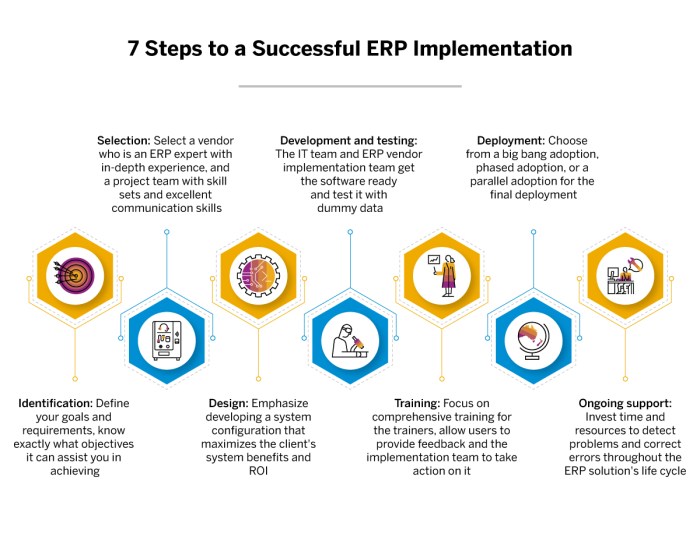
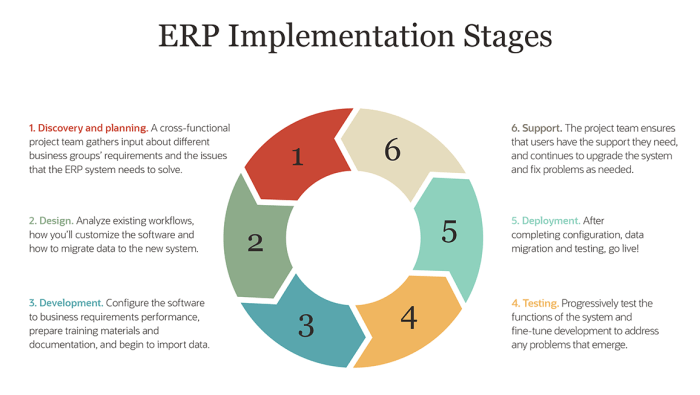
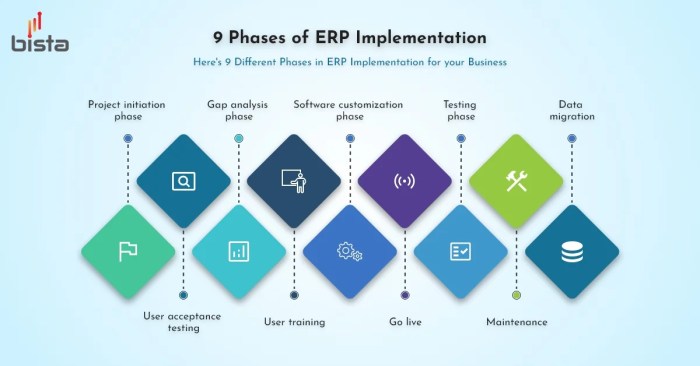
ERP software implementation involves a series of steps to integrate the software into an organization’s business processes. These steps typically include:
- Planning:Defining the project scope, goals, and timeline.
- Data conversion:Migrating existing data into the new ERP system.
- Configuration:Customizing the ERP software to meet the organization’s specific requirements.
- Testing:Verifying the functionality and accuracy of the ERP system.
- Training:Educating users on how to use the ERP system.
- Go-live:Launching the ERP system and transitioning to its use.
- Post-implementation support:Providing ongoing assistance and maintenance to ensure the smooth operation of the ERP system.
Challenges and Risks
ERP software implementation is a complex and challenging process that can pose several risks to an organization. These include:
- Cost overruns:ERP software implementation projects can be expensive, and costs can easily exceed the initial budget.
- Time delays:ERP software implementation projects often take longer than expected, which can disrupt business operations.
- Data integrity issues:Data conversion errors can lead to inaccurate or incomplete data in the ERP system.
- User resistance:Employees may resist the change to a new ERP system, which can hinder its adoption.
- Business disruption:ERP software implementation can disrupt business operations, especially during the go-live phase.
To mitigate these challenges and risks, organizations should carefully plan and manage their ERP software implementation projects. They should also consider using experienced consultants to assist with the process.
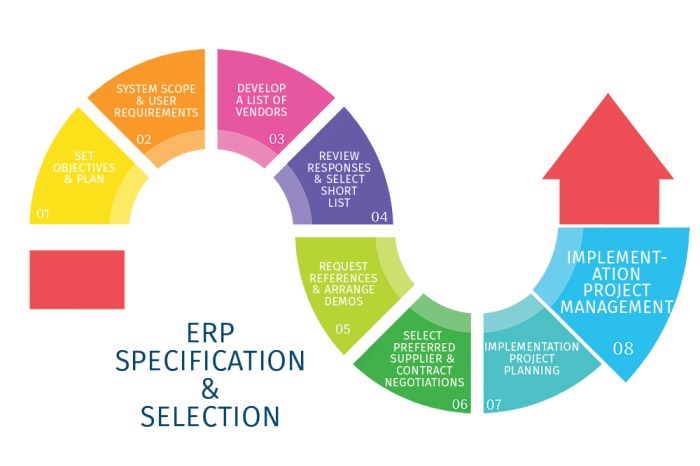
ERP Software Selection
Selecting the right ERP software for a specific organization is a critical step in the implementation process. The software should be aligned with the organization’s unique needs, processes, and industry requirements. A well-chosen ERP system can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide valuable insights to support decision-making.
The ERP software selection process typically involves the following steps:
- Define business requirements:Identify the organization’s specific needs and goals for implementing an ERP system. This includes understanding the current business processes, pain points, and areas for improvement.
- Research and evaluate vendors:Conduct thorough research to identify potential ERP software vendors that meet the organization’s requirements. Evaluate their product offerings, industry experience, customer support, and implementation track record.
- Request for proposal (RFP):Issue an RFP to shortlisted vendors outlining the organization’s requirements and evaluation criteria. This allows vendors to provide detailed proposals that demonstrate how their software meets the specific needs of the organization.
- Vendor demos and evaluations:Conduct demos and evaluations of the shortlisted software solutions. This provides an opportunity to assess the functionality, user interface, and integration capabilities of each system.
- Reference checks and due diligence:Contact references provided by vendors to gather feedback on their experiences with the software and the vendor’s support services.
- Contract negotiation and implementation:Negotiate the terms of the contract with the selected vendor and plan for the implementation of the ERP software. This includes establishing a timeline, budget, and resource allocation.
When evaluating ERP software, it is essential to consider the following key factors:
- Functional requirements:Ensure that the software meets the organization’s specific functional requirements, such as financial management, inventory management, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
- Scalability and flexibility:Choose software that can scale to meet the organization’s future growth and adapt to changing business needs.
- Industry expertise:Consider vendors who have experience in the organization’s industry and understand its specific requirements and best practices.
- Implementation costs and timeline:Factor in the cost of software licenses, implementation services, and ongoing maintenance. Determine the expected timeline for implementation and the resources required.
- Vendor support and services:Evaluate the vendor’s support services, including technical support, training, and ongoing updates. Reliable and responsive support is crucial for successful ERP implementation.
- Integration capabilities:Assess the software’s ability to integrate with existing systems and applications within the organization’s IT landscape.
By carefully considering these factors and following a structured selection process, organizations can choose the right ERP software that aligns with their unique requirements and drives business success.
ERP Software Customization
ERP software can be customized to meet specific business needs. This can involve modifying the software’s functionality, user interface, or data structure. Customization can be done by the software vendor, a third-party consultant, or the business itself.
There are several benefits to customizing ERP software. Customization can improve the software’s fit with the business’s specific processes, improve efficiency, and increase user adoption. However, customization can also be expensive and time-consuming, and it can make it more difficult to upgrade the software in the future.
Benefits of ERP Software Customization
- Improved fit with the business’s specific processes
- Improved efficiency
- Increased user adoption
Drawbacks of ERP Software Customization
- Can be expensive and time-consuming
- Can make it more difficult to upgrade the software in the future
ERP Software Integration
ERP software can be integrated with other business systems to create a more comprehensive and efficient business management solution. This integration can be achieved through the use of application programming interfaces (APIs), which allow different systems to communicate with each other.
There are many benefits to integrating ERP software with other business systems. These benefits include:
- Improved data accuracy and consistency
- Reduced data entry errors
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Improved customer service
- Reduced costs
However, there are also some challenges to integrating ERP software with other business systems. These challenges include:
- The cost of integration
- The complexity of integration
- The need for ongoing maintenance and support
Despite these challenges, the benefits of ERP software integration can often outweigh the costs. By carefully planning and executing an integration project, businesses can achieve significant improvements in their business operations.
Data Integration
One of the most important aspects of ERP software integration is data integration. This involves ensuring that data is shared between different systems in a consistent and accurate manner.
There are a number of different ways to achieve data integration. One common approach is to use a data warehouse. A data warehouse is a central repository of data that is collected from different systems.
Another approach to data integration is to use a data federation. A data federation is a software layer that sits between different systems and allows them to share data without having to be physically integrated.
Process Integration
In addition to data integration, ERP software can also be integrated with other business systems at the process level. This involves automating the flow of information between different systems.
There are a number of different ways to achieve process integration. One common approach is to use a workflow management system. A workflow management system is a software application that automates the flow of tasks and documents between different users.
Another approach to process integration is to use a business process management (BPM) suite. A BPM suite is a software platform that provides a comprehensive set of tools for managing and automating business processes.
Benefits of ERP Software Integration, ERP software for implementation
There are many benefits to integrating ERP software with other business systems. These benefits include:
- Improved data accuracy and consistency
- Reduced data entry errors
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Improved customer service
- Reduced costs
By carefully planning and executing an integration project, businesses can achieve significant improvements in their business operations.
ERP Software Maintenance
ERP software maintenance is crucial for ensuring the smooth and efficient functioning of an ERP system. It involves activities that help keep the software up-to-date, resolve any issues, and enhance its performance.Maintenance activities include:
- Regular updates and patches to address bugs, security vulnerabilities, and new features.
- Monitoring system performance and resolving any performance issues.
- Backing up data regularly to prevent data loss.
- Training users on new features and updates.
- Customizing the software to meet specific business needs.
- Integrating the software with other systems.
Closing Notes: ERP Software For Implementation

In conclusion, ERP software implementation presents a transformative opportunity for businesses to optimize their operations, enhance decision-making, and drive growth. By carefully considering the factors discussed in this guide, organizations can navigate the implementation process successfully and unlock the full potential of ERP software.
As technology continues to advance, ERP systems will undoubtedly evolve, offering even more sophisticated capabilities to empower businesses in the years to come.
Q&A
What is ERP software?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a comprehensive business management solution that integrates various functional areas of an organization, such as finance, supply chain management, manufacturing, and human resources, into a single, unified system.
What are the benefits of implementing ERP software?
ERP software offers numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced data accuracy, better decision-making, and increased customer satisfaction.
What are the challenges associated with ERP implementation?
ERP implementation can be complex and challenging, requiring careful planning, resource allocation, and change management to ensure a successful outcome.