As ERP software for government agencies takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with scientific precision and analytical rigor. Prepare to delve into a realm where knowledge reigns supreme, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
ERP software, a cornerstone of modern government operations, empowers agencies to streamline processes, enhance transparency, and achieve significant cost savings. Its comprehensive suite of modules, tailored specifically for the public sector, offers a transformative solution for managing complex operations and delivering exceptional services.
ERP Software for Government Agencies: Definition and Overview
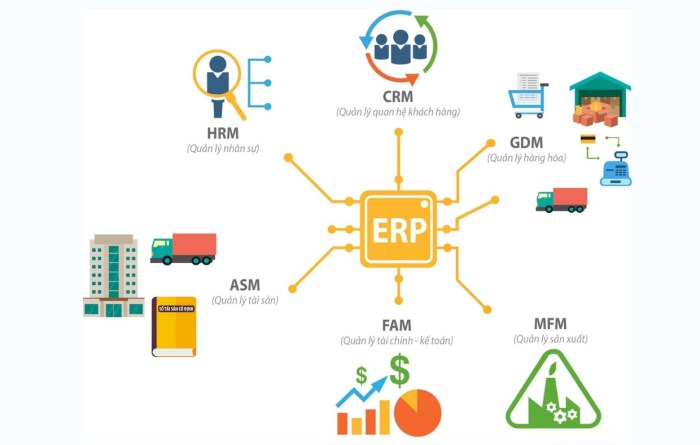
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a comprehensive suite of integrated applications designed to streamline and automate core business processes within an organization. In the context of government agencies, ERP systems play a crucial role in managing complex operations and delivering efficient public services.
Key functionalities and modules commonly found in ERP systems for government include:
- Financial Management:Tracks and manages government funds, including budgeting, accounting, and financial reporting.
- Human Capital Management:Automates HR processes such as payroll, benefits administration, and employee self-service.
- Procurement and Supply Chain Management:Streamlines procurement processes, vendor management, and inventory control.
- Project Management:Facilitates project planning, execution, and tracking.
- Citizen Relationship Management (CRM):Manages interactions with citizens, including service requests, complaints, and feedback.
- Reporting and Analytics:Provides real-time insights into agency performance and enables data-driven decision-making.
li> Asset Management:Tracks and manages government assets, including vehicles, equipment, and facilities.
Benefits of ERP Implementation for Government Agencies

ERP implementation in government agencies offers a range of potential benefits, including:
- Improved efficiency: ERP systems can streamline and automate many government processes, reducing the time and effort required to complete tasks. This can lead to significant cost savings and improved productivity.
- Increased transparency: ERP systems provide a single, centralized repository for all government data, making it easier to track and manage information. This can improve transparency and accountability, and make it easier for citizens to access government information.
- Enhanced decision-making: ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics that can help government agencies make better decisions. This can lead to improved service delivery, reduced costs, and increased efficiency.
There are numerous real-world examples of successful ERP implementations in government organizations. For example, the city of San Francisco implemented an ERP system in 2004 that resulted in significant cost savings and improved efficiency. The system streamlined many city processes, including budgeting, procurement, and human resources.
As a result, the city was able to save millions of dollars and improve the delivery of services to its citizens.
Key Considerations for ERP Selection and Implementation
Selecting and implementing an ERP system for government agencies requires careful consideration of several key factors. These factors include budget, timeline, and stakeholder involvement, among others. By considering these factors and following best practices, government agencies can ensure a smooth and successful ERP implementation process.
Critical Factors to Consider
- Budget:ERP systems can be expensive, so it is important to have a realistic budget in place before beginning the selection process.
- Timeline:ERP implementations can be complex and time-consuming, so it is important to establish a realistic timeline for the project.
- Stakeholder involvement:It is important to involve all stakeholders in the ERP selection and implementation process, from the project team to the end-users.
Best Practices for ERP Implementation
- Create a clear project plan:A clear project plan will help to keep the ERP implementation on track and on budget.
- Communicate regularly with stakeholders:Regular communication will help to keep stakeholders informed about the progress of the ERP implementation and to address any concerns.
- Test the system thoroughly:Before going live with the new ERP system, it is important to test it thoroughly to ensure that it is working properly.
Integration with Existing Systems and Data

Integrating ERP software with existing systems and data sources is crucial for government agencies to ensure seamless data flow, improve data accuracy, and eliminate redundancies. Effective integration enables agencies to consolidate data from multiple sources, creating a centralized and comprehensive view of their operations.
However, data integration poses challenges such as data quality issues, compatibility concerns, and security risks. To overcome these challenges, agencies must adopt a comprehensive data integration strategy that includes:
Data Mapping and Standardization
- Establishing clear data mapping rules to define how data from different sources will be aligned and transformed.
- Enforcing data standardization to ensure consistency in data formats, units of measurement, and terminologies.
Data Cleansing and Validation
- Implementing data cleansing processes to identify and correct errors, inconsistencies, and duplicate data.
- Establishing data validation rules to ensure data accuracy and integrity before integration.
Data Security and Governance
- Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Establishing clear data governance policies to define roles, responsibilities, and data usage guidelines.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Government agencies operate in a highly regulated environment and must adhere to strict security and compliance requirements when implementing ERP software. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions.
Implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect sensitive government data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyberattacks. Agencies must also maintain compliance with relevant regulations, such as the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Implementing Robust Security Measures
- Conduct regular security audits and risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities and implement appropriate safeguards.
- Implement multi-factor authentication, encryption, and access controls to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Establish a comprehensive security policy that Artikels roles and responsibilities, incident response procedures, and data retention guidelines.
- Provide regular security awareness training to employees to educate them about cybersecurity best practices.
- Implement a data loss prevention (DLP) solution to monitor and prevent unauthorized data transfers.
Maintaining Compliance with Relevant Regulations
- Conduct a thorough review of applicable regulations to understand the specific requirements and compliance obligations.
- Develop a compliance plan that Artikels the steps necessary to meet regulatory requirements.
- Implement a compliance monitoring program to track progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Obtain necessary certifications, such as ISO 27001 or NIST 800-53, to demonstrate compliance with industry standards.
- Partner with a reputable ERP vendor that provides software and services that meet regulatory requirements.
User Adoption and Training
User adoption and training are critical for the successful implementation of ERP systems in government agencies. When users understand the benefits of the new system and are properly trained, they are more likely to embrace the change and use the system effectively.
There are several strategies that government agencies can use to engage users and ensure successful adoption and training. These include:
Communication and Engagement
- Communicating the benefits of the new ERP system to users in a clear and concise manner.
- Involving users in the planning and implementation process to get their feedback and buy-in.
- Creating a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and use.
Training and Support, ERP software for government agencies
- Providing comprehensive training to users on all aspects of the new ERP system.
- Offering ongoing support to users after the system has been implemented to answer questions and help with any issues.
- Creating user guides and other resources to help users learn and use the system effectively.
Change Management
- Managing the change process effectively to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition to the new ERP system.
- Providing users with support and resources to help them adapt to the new system.
- Monitoring user adoption and usage to identify areas where additional support or training is needed.
By following these strategies, government agencies can increase the likelihood of successful user adoption and training for their ERP systems. This will lead to improved system usage, increased efficiency, and better decision-making.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Deployment Options
Government agencies face a critical decision when selecting an ERP deployment option: cloud-based or on-premise. Both approaches offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the agency’s specific needs and resources.
Cloud-Based Deployment
- Advantages:
- Scalability and flexibility: Cloud-based ERP systems can easily scale up or down to meet changing demands, eliminating the need for costly hardware upgrades.
- Reduced IT costs: Agencies can eliminate the expenses associated with maintaining on-premise infrastructure, including hardware, software, and IT staff.
- Enhanced security: Cloud providers typically offer robust security measures and regular updates to protect data and systems.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited customization: Cloud-based ERP systems may not offer the same level of customization as on-premise solutions.
- Data security concerns: Agencies must trust the cloud provider to ensure the security and privacy of their data.
- Internet connectivity dependence: Cloud-based ERP systems require reliable internet connectivity, which can be a challenge in remote areas.
On-Premise Deployment
- Advantages:
- Full control and customization: Agencies have complete control over their ERP system and can customize it to meet their specific requirements.
- Enhanced data security: Data is stored and managed within the agency’s own infrastructure, providing greater control and security.
- Integration with legacy systems: On-premise ERP systems can be more easily integrated with existing legacy systems.
- Disadvantages:
- High upfront costs: On-premise ERP systems require significant upfront investments in hardware, software, and IT staff.
- Maintenance and upgrades: Agencies are responsible for maintaining and upgrading the ERP system, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Scalability limitations: On-premise ERP systems may not be as scalable as cloud-based solutions, especially during periods of high demand.
Factors to Consider When Making the Deployment Decision
The following factors should be considered when making the cloud-based vs. on-premise deployment decision:
- Agency size and complexity
- Budget constraints
- IT resources and expertise
- Data security requirements
- Integration with existing systems
- Scalability needs
Cost and Budget Planning
Implementing ERP software for government agencies involves several cost components, and it is crucial to plan a realistic budget and secure funding to ensure successful implementation.
The cost of ERP software implementation typically includes the following components:
- Licensing fees:These fees cover the right to use the ERP software for a specific period.
- Maintenance fees:These fees cover ongoing support, updates, and bug fixes for the ERP software.
- Customization costs:These costs cover any modifications or enhancements to the ERP software to meet the specific needs of the government agency.
- Implementation costs:These costs cover the services of consultants and other professionals involved in the ERP implementation process.
- Training costs:These costs cover the training of government agency staff on the use of the ERP software.
Developing a Realistic Budget
To develop a realistic budget for ERP software implementation, government agencies should consider the following tips:
- Estimate the total cost of ownership (TCO):The TCO should include all of the cost components listed above, as well as any other anticipated costs, such as hardware and infrastructure upgrades.
- Identify funding sources:Government agencies should identify potential funding sources for the ERP project, such as federal grants, state or local appropriations, or internal funds.
- Secure funding:Government agencies should work with their financial officers and other stakeholders to secure the necessary funding for the ERP project.
Vendor Selection and Evaluation
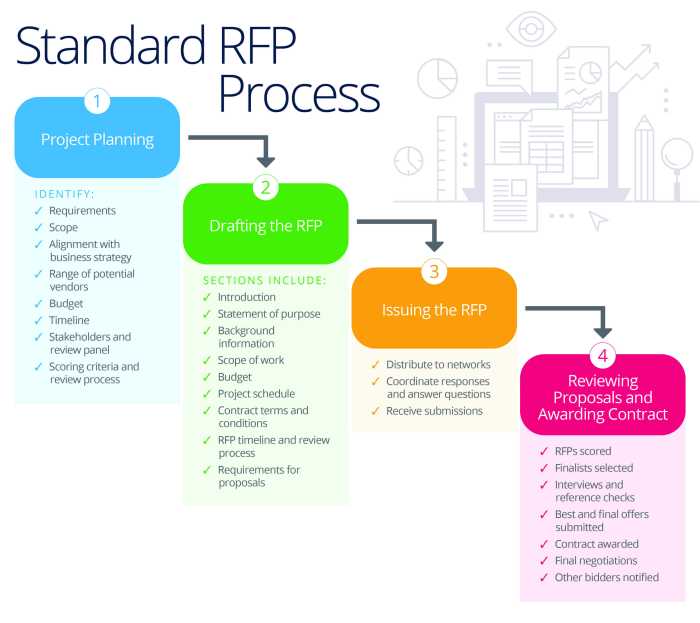
Selecting the right ERP vendor is critical for the success of any ERP implementation. Government agencies must carefully evaluate vendors based on their capabilities, experience, and financial stability.
The vendor selection process typically involves the following steps:
- Develop a Request for Proposal (RFP) that Artikels the agency’s requirements.
- Send the RFP to potential vendors and request proposals.
- Evaluate proposals based on the criteria established in the RFP.
- Conduct due diligence on the shortlisted vendors.
- Select the vendor that best meets the agency’s needs.
Criteria for Assessing Vendor Capabilities
When evaluating ERP vendors, government agencies should consider the following criteria:
- Experience:The vendor should have a proven track record of successful ERP implementations in government agencies.
- Capabilities:The vendor’s ERP solution should meet the agency’s specific requirements.
- Financial stability:The vendor should be financially stable and have the resources to support the implementation and ongoing maintenance of the ERP solution.
Epilogue
In conclusion, ERP software for government agencies stands as a beacon of efficiency, transparency, and fiscal responsibility. By embracing this transformative technology, agencies can unlock a new era of operational excellence, empowering them to serve their communities with greater effectiveness and accountability.
FAQ: ERP Software For Government Agencies
What are the key benefits of ERP software for government agencies?
ERP software offers numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, enhanced transparency, reduced costs, and better decision-making.
How can government agencies ensure a successful ERP implementation?
Successful ERP implementation requires careful planning, stakeholder involvement, and a commitment to user adoption and training.
What are the security considerations for ERP software in government agencies?
Government agencies must adhere to strict security and compliance requirements, necessitating robust security measures and ongoing monitoring.