ERP software for discrete manufacturing is a powerful tool that can help businesses streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. With its comprehensive suite of features, ERP software can manage every aspect of a discrete manufacturing business, from product design and engineering to production planning and scheduling, inventory management, and customer relationship management.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of ERP software for discrete manufacturing, discuss the different types of ERP software available, and provide guidance on selecting and implementing the right ERP software for your business.
Overview of ERP Software for Discrete Manufacturing

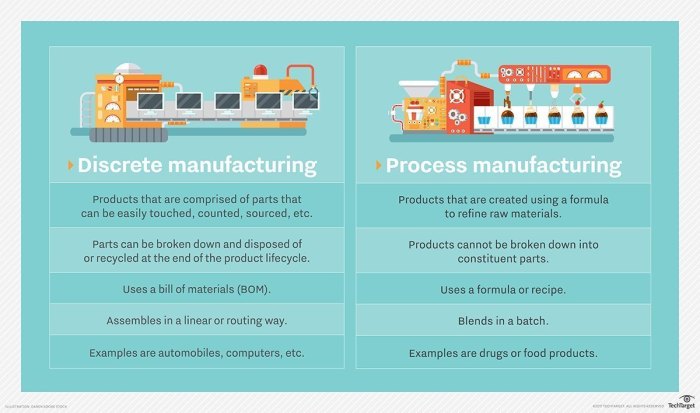
ERP software is designed to streamline and integrate various business processes within a discrete manufacturing organization. It provides a centralized platform for managing operations, from product design and planning to production, inventory control, and customer relationship management.
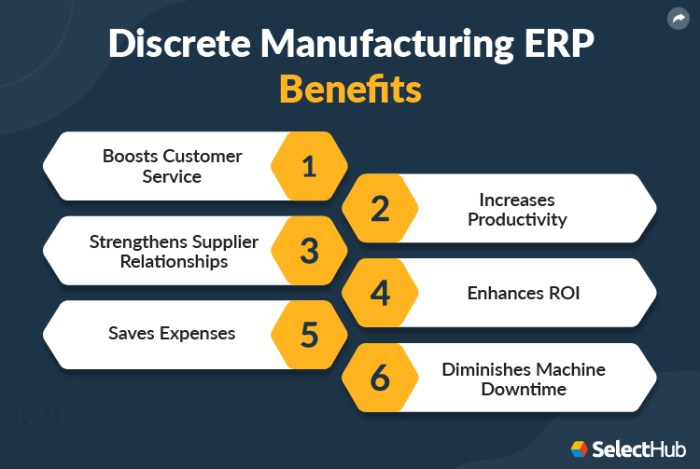
Key benefits of ERP software for discrete manufacturing include:
- Improved efficiency and productivity through automated processes and streamlined workflows.
- Enhanced collaboration and communication among different departments, fostering cross-functional alignment.
- Increased visibility and control over operations, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Improved customer satisfaction through enhanced order fulfillment and support.
li>Reduced costs and improved resource utilization through optimized planning and scheduling.
Key Features and Functionalities
ERP software for discrete manufacturing typically includes the following key features and functionalities:
- Product lifecycle management (PLM):Supports product design, engineering, and manufacturing processes.
- Production planning and scheduling:Optimizes production processes, including capacity planning, scheduling, and material requirements planning (MRP).
- Inventory management:Tracks and controls inventory levels, including raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
- Customer relationship management (CRM):Manages customer interactions, including sales, marketing, and support.
- Financial management:Integrates accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Business intelligence (BI):Provides data analysis and reporting capabilities for informed decision-making.
Types of ERP Software
ERP software for discrete manufacturing can be classified into various types, each tailored to specific requirements and industry practices. Understanding the different types and their respective advantages and disadvantages is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions.
The primary types of ERP software for discrete manufacturing include:
On-Premise ERP
- Advantages:
- Complete control over data and infrastructure
- Enhanced security and privacy
- Potentially lower long-term costs
- Disadvantages:
- Significant upfront investment
- Requires dedicated IT resources for maintenance
- Limited scalability and flexibility
Cloud-Based ERP
- Advantages:
- Lower upfront costs and subscription-based pricing
- Automatic software updates and maintenance
- Enhanced scalability and flexibility
- Disadvantages:
- Limited control over data and infrastructure
- Potential security and privacy concerns
- Ongoing subscription fees
Hybrid ERP
- Advantages:
- Combination of on-premise and cloud-based capabilities
- Allows for customization and control of critical processes
- Provides flexibility and scalability
- Disadvantages:
- Can be more complex to implement and manage
- May require additional IT resources
- Potential for data security and privacy issues
Key Considerations for ERP Selection
Selecting the right ERP software for discrete manufacturing is crucial for optimizing operations and achieving business goals. Several key factors must be considered to ensure a successful implementation and maximize the software’s benefits.
Vendor Evaluation, ERP software for discrete manufacturing
Thoroughly evaluate potential vendors based on their industry experience, financial stability, and customer support capabilities. Assess their implementation methodology, training programs, and ongoing maintenance and support services.
Software Capabilities
Identify the specific functional requirements for your discrete manufacturing operations. Evaluate software capabilities in areas such as:
- Production planning and scheduling
- Inventory management
- Supply chain management
- Financial management
li>Quality control
Ensure that the software aligns with your current and future business needs, considering scalability, flexibility, and ease of use.
Benefits of ERP Software for Discrete Manufacturing
ERP software offers a range of benefits specifically tailored to the needs of discrete manufacturing businesses. These benefits include improved efficiency, enhanced collaboration, and increased profitability.
One of the key benefits of ERP software is its ability to streamline and automate many of the complex processes involved in discrete manufacturing. This can lead to significant time and cost savings, as well as improved accuracy and efficiency.
For example, ERP software can automate tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and production scheduling.
ERP software can also enhance collaboration between different departments within a discrete manufacturing business. By providing a single, centralized platform for data and information, ERP software can help to break down silos and improve communication between departments. This can lead to better decision-making and improved coordination of activities.
In addition, ERP software can help discrete manufacturing businesses to increase their profitability. By providing real-time data and insights into the business, ERP software can help businesses to identify areas where they can improve efficiency and reduce costs. ERP software can also help businesses to better manage their inventory, which can lead to reduced waste and improved cash flow.
Case Study
One example of a successful ERP implementation in discrete manufacturing is the case of John Deere. John Deere is a leading manufacturer of agricultural and construction equipment. In 2004, John Deere implemented an ERP system from SAP. The implementation was a success, and John Deere has since reported significant benefits, including:
- Reduced inventory costs by 15%
- Improved customer service by 10%
- Increased productivity by 5%
Challenges of ERP Implementation
ERP implementation in discrete manufacturing presents unique challenges due to the industry’s complex processes and diverse requirements. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for successful implementation.Common challenges include:
Data Integration
Integrating data from disparate systems into a single ERP platform can be complex and time-consuming.
Process Disruptions
ERP implementation can disrupt existing processes, leading to operational inefficiencies and potential downtime.
Employee Resistance
Employees may resist change and require extensive training and support to adapt to the new system.
Cost and Time
ERP implementation can be costly and time-intensive, requiring significant investment and resources.
Customization
Discrete manufacturers often have unique requirements that necessitate customization of the ERP system, which can add complexity and increase implementation time.
Overcoming Challenges
To overcome these challenges, manufacturers should:
- Plan thoroughly and involve key stakeholders in the implementation process.
- Conduct a comprehensive data audit to ensure data accuracy and completeness.
- Provide comprehensive training and support to employees to facilitate adoption.
- Allocate sufficient resources and establish realistic timelines for implementation.
- Partner with an experienced ERP vendor or consultant to guide the process and provide expertise.
- Continuously monitor and evaluate the implementation to identify and address any issues promptly.
Best Practices for ERP Implementation
Implementing ERP software in discrete manufacturing requires careful planning, project management, and user adoption strategies. Best practices can help organizations minimize disruptions, maximize value, and ensure a successful implementation.
Effective planning involves defining clear goals, timelines, and resource allocation. Project management should include robust communication, risk assessment, and change management processes. User adoption is crucial and can be achieved through training, support, and involving users in the implementation process.
Planning
- Define specific business objectives and align them with ERP capabilities.
- Establish a clear implementation timeline with milestones and deadlines.
- Identify and allocate necessary resources, including personnel, budget, and infrastructure.
Project Management
- Establish a dedicated project team with clear roles and responsibilities.
- Implement a robust communication plan to keep stakeholders informed and engaged.
- Conduct regular risk assessments and develop mitigation strategies.
- Establish change management processes to handle unexpected challenges.
User Adoption
- Provide comprehensive training to users on ERP functionality and business processes.
- Offer ongoing support and assistance to ensure user proficiency.
- Involve users in the implementation process to gather feedback and address concerns.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement to encourage user engagement and feedback.
Integration with Other Systems
Integrating ERP software with other business systems is crucial for streamlining operations and maximizing efficiency. It eliminates data silos, reduces errors, and improves collaboration across departments.For instance, integrating ERP with CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems allows for seamless customer data management, providing a comprehensive view of customer interactions and preferences.
This enhances customer service and sales effectiveness.
Examples of Successful Integrations
Manufacturing
ERP integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) enables real-time monitoring of production processes, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
Supply Chain
Integration with SCM (Supply Chain Management) systems optimizes inventory management, reduces lead times, and improves supplier collaboration.
Finance
ERP integration with accounting software automates financial processes, reduces errors, and provides real-time financial data for informed decision-making.
Industry Trends and Future of ERP: ERP Software For Discrete Manufacturing
The ERP software market for discrete manufacturing is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing industry demands. Here are some of the latest trends and insights into the future of ERP:
Cloud-based ERP systems are becoming increasingly popular, offering benefits such as scalability, flexibility, and reduced IT costs. These systems are hosted by a third-party provider and can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being integrated into ERP systems to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into manufacturing operations. AI-powered ERP systems can analyze large amounts of data to identify patterns, predict demand, and optimize production schedules.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is connecting manufacturing equipment and sensors to ERP systems, providing real-time data on production processes. This data can be used to improve quality control, reduce downtime, and increase overall efficiency.
The future of ERP for discrete manufacturing is bright, with continued advancements in technology and a growing focus on customer-centricity. ERP systems will become even more integrated, intelligent, and personalized, helping manufacturers to achieve greater efficiency, agility, and profitability.
Emerging Technologies
Several emerging technologies have the potential to further transform the ERP landscape for discrete manufacturing, including:
- Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and transparent supply chains, enabling manufacturers to track the movement of goods and materials in real time.
- Digital twin technology creates virtual representations of physical assets, allowing manufacturers to simulate and optimize production processes before implementing them in the real world.
- Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) can be used to provide immersive training experiences for manufacturing employees and to assist with remote maintenance and repair.
Vendor Landscape
The ERP software market for discrete manufacturing is highly competitive, with numerous vendors offering a range of solutions. These vendors vary in terms of their key features, pricing, and customer reviews.
To help you make an informed decision, we have compiled a table comparing some of the leading ERP software vendors for discrete manufacturing.
Key Features
The key features to consider when choosing an ERP software for discrete manufacturing include:
- Manufacturing execution system (MES)
- Product lifecycle management (PLM)
- Supply chain management (SCM)
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Financial management
- Human capital management (HCM)
Pricing
The pricing of ERP software for discrete manufacturing can vary depending on the vendor, the number of users, and the features required. Some vendors offer a subscription-based pricing model, while others offer a perpetual license model.
Customer Reviews
Customer reviews can provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of different ERP software vendors. When reading customer reviews, it is important to consider the size and industry of the companies that have implemented the software.
Implementation Case Studies
ERP implementation in discrete manufacturing companies has a significant impact on their operational efficiency and profitability. Several case studies demonstrate the successful implementation of ERP systems, highlighting the challenges faced and the benefits achieved.
Challenges Faced
Common challenges encountered during ERP implementation in discrete manufacturing include:
- Complex and lengthy implementation process
- Data migration and integration issues
- Resistance to change from employees
- Lack of proper training and support
- Customization and configuration complexities
Benefits Achieved
Despite the challenges, ERP implementation can lead to substantial benefits for discrete manufacturing companies:
- Improved operational efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced data accuracy and visibility
- Reduced costs and improved profitability
- Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Improved supply chain management and inventory control
Glossary of ERP Terms
ERP systems encompass a wide range of terms and acronyms specific to discrete manufacturing. Understanding these terms is crucial for effective implementation and utilization of ERP software.
Common ERP Terms
- Bill of Materials (BOM):A detailed list of components and materials required to manufacture a product.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):A software suite that integrates various business functions into a single system.
- Inventory Management:The process of tracking and managing the flow of goods within a manufacturing facility.
- Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP):A module within ERP that optimizes production planning and scheduling.
- Production Planning:The process of determining the optimal production schedule to meet customer demand.
- Quality Management:The processes and systems used to ensure product quality and compliance.
- Shop Floor Control:The management of production activities on the factory floor.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM):The coordination and optimization of activities throughout the supply chain, from raw materials to finished goods.
Summary
ERP software can provide discrete manufacturing businesses with a number of benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased profitability. By streamlining operations and providing a central repository for all data, ERP software can help businesses improve their decision-making, respond more quickly to customer needs, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
FAQ
What is ERP software?
ERP software is a comprehensive business management software that integrates all aspects of a business, from product design and engineering to production planning and scheduling, inventory management, and customer relationship management.
What are the benefits of ERP software for discrete manufacturing?
ERP software can provide discrete manufacturing businesses with a number of benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased profitability. By streamlining operations and providing a central repository for all data, ERP software can help businesses improve their decision-making, respond more quickly to customer needs, and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
What are the different types of ERP software available?
There are a number of different types of ERP software available, each with its own unique features and benefits. Some of the most common types of ERP software include on-premise ERP, cloud-based ERP, and hybrid ERP.
How do I choose the right ERP software for my business?
There are a number of factors to consider when choosing ERP software for your business, including the size of your business, the industry you are in, and your specific business needs. It is important to do your research and compare different ERP software options before making a decision.
How do I implement ERP software?
ERP software implementation can be a complex and time-consuming process. It is important to plan carefully and work with an experienced ERP implementation partner to ensure a successful implementation.