ERP software for dashboards tools empowers businesses with the ability to harness the power of data for informed decision-making. These tools provide a comprehensive overview of key performance indicators (KPIs), allowing users to visualize, analyze, and monitor critical business metrics in real-time.
With ERP software for dashboards tools, organizations can gain actionable insights into their operations, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions that drive growth and efficiency.
ERP Software Overview
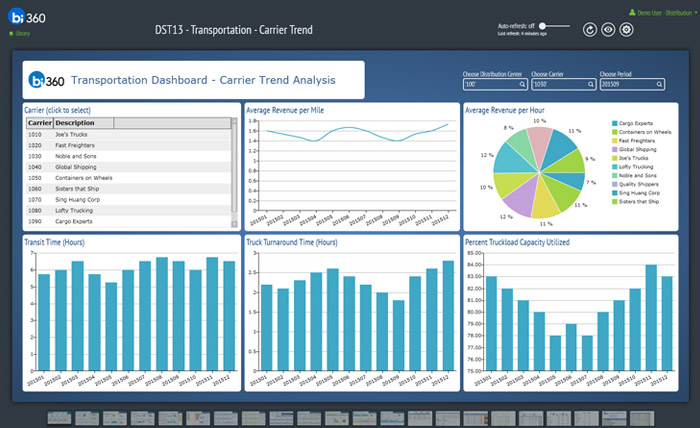
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive business management system that integrates various aspects of an organization’s operations, including finance, accounting, supply chain management, manufacturing, and human resources.
ERP systems provide a centralized platform for managing and accessing data, streamlining processes, and improving efficiency. By eliminating data silos and automating tasks, ERP software helps organizations gain a comprehensive view of their operations, make informed decisions, and respond quickly to changing market demands.
Key Benefits of ERP Systems
ERP systems offer numerous benefits to organizations, including:
- Improved operational efficiency:ERP systems automate many manual tasks, reduce data entry errors, and streamline workflows, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
- Enhanced data visibility and accessibility:ERP systems provide a single source of truth for all business data, making it easier for users to access and analyze information from across the organization.
- Improved decision-making:ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics that help managers make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
- Increased agility and responsiveness:ERP systems enable organizations to respond quickly to changes in the market or customer demands by providing a flexible and adaptable platform for managing operations.
- Enhanced customer service:ERP systems provide a centralized view of customer interactions, enabling organizations to provide personalized and efficient customer support.
Challenges and Considerations of ERP Implementations
While ERP systems offer significant benefits, their implementation can be complex and challenging. Some of the key challenges and considerations include:
- High cost and complexity:ERP systems can be expensive to purchase and implement, and they require significant time and resources to configure and customize.
- Data migration and integration:Migrating data from legacy systems to an ERP system can be complex and time-consuming, and it is crucial to ensure data accuracy and integrity throughout the process.
- Change management:ERP implementations often require significant changes to business processes and workflows, which can be disruptive to employees and require effective change management strategies.
- Vendor selection and partnership:Choosing the right ERP vendor and establishing a strong partnership is essential for successful implementation and ongoing support.
- Ongoing maintenance and upgrades:ERP systems require regular maintenance and upgrades to ensure optimal performance and security, which can add to the overall cost of ownership.
Dashboards in ERP Systems
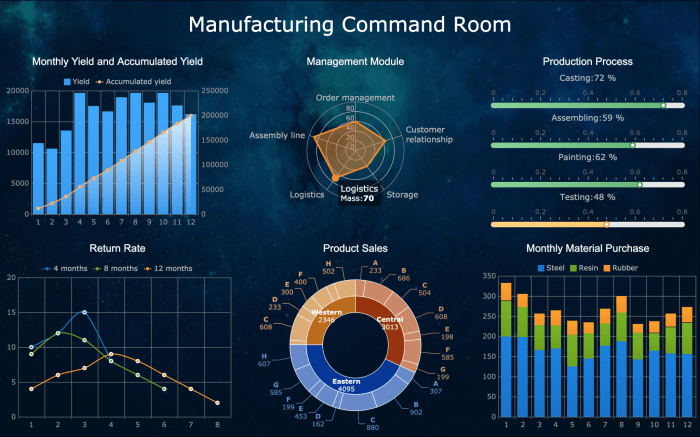
Dashboards are graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that provide real-time data visualization and analysis capabilities within ERP systems. They enable users to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track progress towards goals, and identify areas for improvement.Dashboards in ERP systems can be customized to meet the specific needs of different users and roles within an organization.
Common types of dashboards include:
- Executive dashboardsprovide a high-level overview of key business metrics, such as revenue, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
- Operational dashboardsprovide detailed information on specific business processes, such as production, inventory management, and order fulfillment.
- Analytical dashboardsallow users to drill down into data and perform ad-hoc analysis to identify trends and patterns.
Dashboards offer several benefits for data visualization and analysis:
- Improved visibility: Dashboards provide a centralized view of key data, making it easier for users to monitor performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Increased efficiency: Dashboards eliminate the need for manual data collection and analysis, saving time and resources.
- Enhanced decision-making: Dashboards provide real-time insights that can help users make informed decisions based on data.
Tools for Dashboard Creation
Dashboards in ERP systems can be created using various tools. The choice of tool depends on factors such as the size and complexity of the organization, the skillset of the users, and the budget. Common tools used for creating dashboards in ERP systems include:
- Native ERP Dashboarding Tools:Many ERP vendors offer native dashboarding tools that are integrated with the ERP system. These tools are typically easy to use and require minimal technical expertise. However, they may not offer the same level of customization and flexibility as third-party tools.
- Third-Party Dashboarding Tools:There are a number of third-party dashboarding tools available that can be integrated with ERP systems. These tools offer a wider range of features and capabilities than native ERP dashboarding tools, including advanced data visualization, customization, and integration with other systems.
- Open-Source Dashboarding Tools:Open-source dashboarding tools are free to use and can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization. However, they require more technical expertise to implement and maintain than native or third-party tools.
Comparison of Dashboard Creation Tools
The following table compares the features and capabilities of different dashboard creation tools:
| Feature | Native ERP Dashboarding Tools | Third-Party Dashboarding Tools | Open-Source Dashboarding Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Easy | Moderate | Difficult |
| Customization | Limited | Extensive | Unlimited |
| Integration with ERP | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Cost | Included with ERP | Additional cost | Free |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Specific Tools, ERP software for dashboards tools
The choice of dashboard creation tool depends on the specific needs of an organization. Native ERP dashboarding tools are a good option for organizations that want a simple and easy-to-use tool that is tightly integrated with the ERP system. Third-party dashboarding tools offer a wider range of features and capabilities, but they may require more technical expertise to implement and maintain.
Open-source dashboarding tools are free to use and can be customized to meet the specific needs of an organization, but they require more technical expertise to implement and maintain than native or third-party tools.
Data Integration for Dashboards
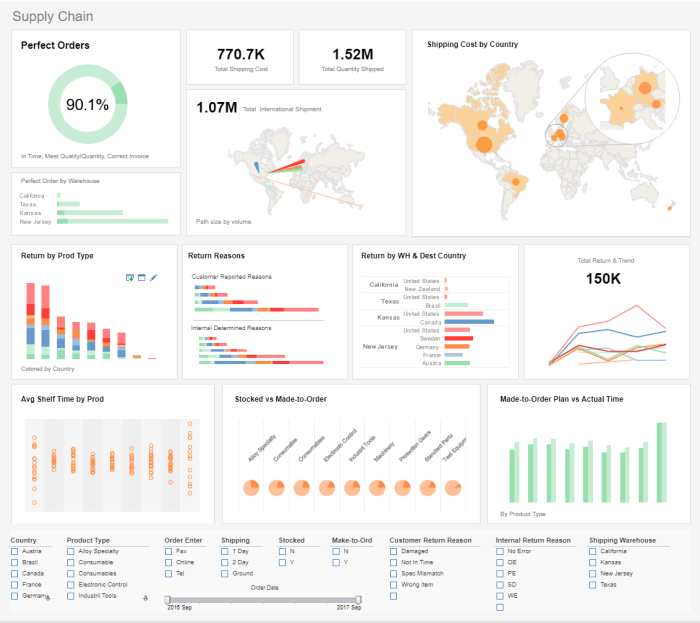
Data integration is crucial for creating effective dashboards. It allows businesses to combine data from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive view of their operations and enabling data-driven decision-making.
There are various methods for integrating data into ERP dashboards, including:
Data Warehousing
- Centralizes data from multiple sources into a single repository.
- Provides a consistent and structured view of data, simplifying data analysis and reporting.
- Supports complex data transformations and aggregations.
Data Federation
- Accesses data from multiple sources without physically moving it.
- Provides a virtual view of data, allowing users to query and analyze data as if it were in a single location.
- Requires less technical expertise and resources compared to data warehousing.
Data Virtualization
- Creates a virtual layer over multiple data sources, presenting a unified view of data.
- Enables real-time data access and analysis without the need for physical data integration.
- Supports flexible data access and reduces data redundancy.
Challenges and Best Practices for Data Integration
Data integration can pose challenges, such as:
- Data inconsistency and quality issues.
- Data security and privacy concerns.
- Technical complexities and resource requirements.
Best practices for data integration include:
- Establishing clear data integration goals and requirements.
- Implementing data governance and quality control measures.
- Choosing the appropriate data integration method based on business needs and technical capabilities.
- Ensuring data security and privacy through encryption and access controls.
Dashboard Design Principles
Effective dashboards are designed with user-centric principles that prioritize clarity, usability, and data-driven insights. By adhering to these principles, organizations can create dashboards that empower users to make informed decisions and achieve their goals.
Key design principles for effective dashboards include:
Visual Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy organizes dashboard elements based on their importance and relevance. This is achieved through the use of size, color, placement, and other visual cues to guide users’ attention towards the most critical information.
Color Theory
Color plays a crucial role in dashboard design. Different colors can evoke emotions, convey meanings, and highlight specific data points. A well-chosen color scheme can enhance the readability and comprehension of the dashboard.
Data Organization
Organizing data effectively is essential for creating dashboards that are easy to understand and navigate. Data should be grouped logically and presented in a way that supports the user’s decision-making process.
Optimization for User Roles and Devices
Dashboards should be tailored to the specific needs of different user roles and the devices they use. This may involve customizing the dashboard’s layout, content, and interactivity to ensure optimal usability for each user group.
Customization and Extensibility
Customization and extensibility are crucial for dashboards in ERP systems. Dashboards are most valuable when they can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each business. This means being able to customize the look and feel of the dashboard, as well as the data that is displayed.
Extensibility allows businesses to add custom widgets and reports to their dashboards, further increasing their functionality.
Customization
There are several different ways to customize dashboards in ERP systems. Some systems allow users to change the layout of the dashboard, add or remove widgets, and change the colors and fonts. Others provide more advanced customization options, such as the ability to create custom reports and visualizations.
Extensibility
Extensibility allows businesses to add custom widgets and reports to their dashboards. This can be done through the use of APIs or by developing custom code. Custom widgets can be used to display data from other sources, such as CRM systems or social media feeds.
Custom reports can be used to create more complex visualizations of data.By customizing and extending dashboards, businesses can create a powerful tool that can help them track their performance, make better decisions, and improve their bottom line.
Security and Data Governance: ERP Software For Dashboards Tools
Ensuring the security and integrity of data in ERP dashboards is paramount. Data governance establishes policies and procedures for managing data access, usage, and protection, while access controls restrict who can view or modify sensitive information.
Best Practices for Data Security
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to grant users only the permissions they need.
- Use encryption to protect data at rest and in transit.
- Regularly audit user access and system logs to detect any suspicious activity.
- Establish clear data retention policies to prevent data from being stored indefinitely.
- Train users on data security best practices.
Importance of Data Governance
Data governance ensures that data is accurate, consistent, and used in a manner that aligns with organizational policies. It helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements and mitigate risks associated with data breaches.
Real-Time Data and Analytics
Real-time data and analytics provide significant advantages for ERP dashboards, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
The integration of real-time data into dashboards allows businesses to:
- Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) in real time, providing immediate insights into business performance.
- Identify trends and patterns as they occur, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Respond quickly to changing market conditions or customer demands.
Technologies and Tools for Real-Time Data Integration and Analysis
Various technologies and tools facilitate real-time data integration and analysis for ERP dashboards:
- Streaming Data Platforms:Kafka, Apache Flume, and Amazon Kinesis are examples of streaming data platforms that ingest and process data in real time.
- In-Memory Databases:Redis, Memcached, and Apache Ignite are in-memory databases that store data in memory, providing extremely fast access and retrieval times.
- Real-Time Analytics Engines:Apache Spark, Apache Flink, and Google Cloud Dataflow are real-time analytics engines that can process large volumes of data in near real time.
Examples of Real-Time Dashboards for Improved Decision-Making
Real-time dashboards can provide valuable insights and improve decision-making in various business areas:
- Supply Chain Management:Real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and delivery schedules enables proactive inventory management and fulfillment.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):Tracking customer interactions, sentiment analysis, and real-time customer feedback can help businesses identify opportunities for improved customer service and engagement.
- Sales and Marketing:Monitoring campaign performance, lead generation, and conversion rates in real time allows businesses to optimize marketing strategies and increase sales.
11. Trends and Innovations
ERP dashboards are continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Emerging trends and innovations are shaping the future of dashboard development and data visualization.
One significant trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP) into ERP dashboards. These technologies enable dashboards to become more intelligent and user-friendly.
AI-Powered Insights
- AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and trends, providing valuable insights that would be difficult to uncover manually.
- ML models can be trained to predict future outcomes, enabling businesses to make more informed decisions.
- NLP allows dashboards to understand and respond to natural language queries, making it easier for users to access information.
The Future of ERP Dashboards
As technology continues to advance, ERP dashboards are expected to become even more sophisticated and integrated.
- Dashboards will become more personalized, tailored to the specific needs of individual users.
- Real-time data and analytics will become even more prevalent, providing businesses with up-to-the-minute insights into their operations.
- Data visualization techniques will continue to evolve, making it easier for users to understand complex data and make informed decisions.
Ending Remarks
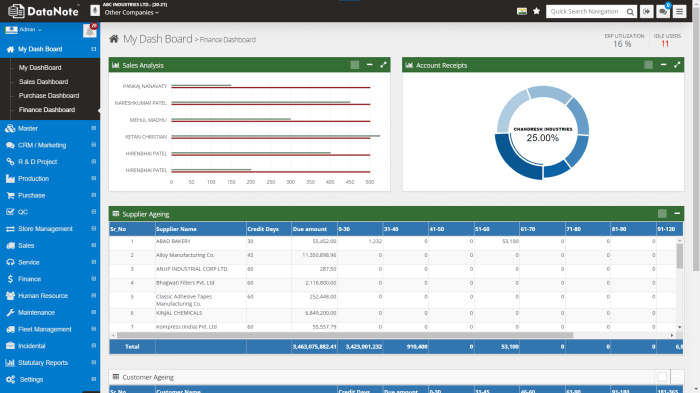
In conclusion, ERP software for dashboards tools has become an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to leverage data for competitive advantage. By providing real-time insights, customizable dashboards, and seamless data integration, these tools empower organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and drive success in today’s data-driven business landscape.
Common Queries
What are the benefits of using ERP software for dashboards tools?
ERP software for dashboards tools offer numerous benefits, including real-time data visualization, customizable dashboards, improved decision-making, enhanced operational efficiency, and increased productivity.
How do ERP software for dashboards tools integrate with other systems?
ERP software for dashboards tools can integrate with various business systems, such as CRM, supply chain management, and financial systems, providing a consolidated view of data from multiple sources.
What are the best practices for designing effective dashboards?
Effective dashboard design involves using visual hierarchy, color theory, and data organization to create dashboards that are easy to read, understand, and act upon.