ERP software for business process management is a comprehensive solution that empowers organizations to streamline operations, optimize decision-making, and achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency. By integrating key business processes into a single platform, ERP systems provide a holistic view of an organization’s operations, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and respond to market demands with agility.
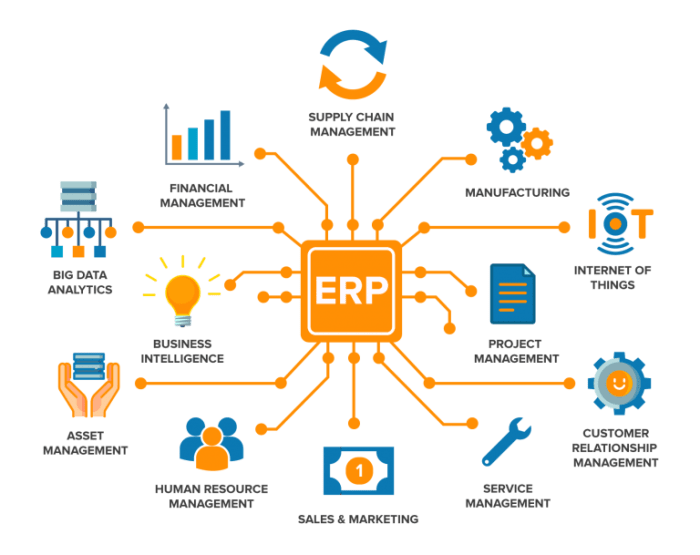
ERP systems offer a wide range of core modules, including finance, supply chain management, human resources, customer relationship management, and manufacturing. These modules seamlessly integrate with each other, eliminating data silos and automating manual processes. By centralizing data and automating tasks, ERP systems reduce errors, improve productivity, and free up valuable time for employees to focus on strategic initiatives.
ERP Software Overview
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive business management solution that integrates various functional areas of an organization into a unified system. It streamlines operations, enhances data accuracy, and improves decision-making by providing a centralized platform for managing core business processes.
ERP systems offer numerous benefits for business process management, including:
- Improved efficiency:ERP software automates tasks, eliminates manual processes, and reduces data redundancy, leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
- Enhanced data accuracy:By centralizing data in a single system, ERP ensures data consistency and integrity, eliminating errors and inconsistencies that arise from using multiple disparate systems.
- Better decision-making:ERP provides real-time data and insights into various aspects of the business, enabling managers to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
Core modules typically included in ERP systems include:
- Financial management:Manages accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Human capital management:Handles payroll, benefits, and employee data.
- Supply chain management:Optimizes inventory, purchasing, and logistics.
- Customer relationship management (CRM):Manages customer interactions, sales, and marketing.
- Manufacturing management:Supports production planning, scheduling, and quality control.
ERP systems play a crucial role in streamlining business operations by:
- Breaking down departmental silos:ERP integrates data and processes across departments, fostering collaboration and improving communication.
- Eliminating data redundancy:By centralizing data in a single system, ERP reduces the risk of data duplication and ensures consistency.
- Automating workflows:ERP automates repetitive tasks, such as order processing and invoice generation, freeing up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
Process Optimization with ERP
ERP software empowers businesses to optimize key processes, streamline operations, and enhance overall efficiency. It automates routine tasks, eliminates manual processes, and provides real-time visibility into business operations. By leveraging ERP, organizations can identify bottlenecks, eliminate redundancies, and improve process flow, leading to increased productivity and cost savings.
Automating Tasks and Eliminating Manual Processes, ERP software for business process management
ERP software automates repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. It automates processes such as data entry, order processing, inventory management, and financial transactions. By eliminating manual processes, ERP reduces the risk of errors, improves data accuracy, and increases overall efficiency.
Case Study: Process Optimization with ERP at ABC Company
ABC Company, a leading manufacturer, implemented an ERP system to streamline its production processes. The ERP system automated tasks such as inventory tracking, production scheduling, and quality control. As a result, ABC Company experienced a 20% increase in production efficiency, a 15% reduction in inventory costs, and a significant improvement in product quality.
Data Management and Reporting
ERP systems play a pivotal role in centralizing and managing data across various business functions. This consolidation provides a unified view of information, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on accurate and real-time data.
ERP systems offer a comprehensive suite of reports and analytics capabilities that allow users to extract meaningful insights from their data. These reports provide visibility into key performance indicators (KPIs), operational metrics, and financial performance, empowering decision-makers with the necessary information to drive growth and optimize processes.
Data Integrity and Security
Data integrity and security are paramount in ERP systems. The centralized nature of ERP data makes it vulnerable to unauthorized access or data breaches. To mitigate these risks, ERP systems employ robust security measures, including:
- Access controls to restrict user permissions and prevent unauthorized data modification.
- Encryption to protect sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
- Regular backups and disaster recovery plans to ensure data availability in the event of system failures or data loss.
Integration and Collaboration
ERP systems offer significant advantages when integrated with other business applications, enabling seamless data flow and streamlined processes across the organization.
ERP integration eliminates data silos, ensuring that all departments have access to the same up-to-date information. This enhances collaboration and communication, as teams can share data, insights, and best practices more effectively.
Improved Data Sharing
- ERP integration allows departments to access and share data in real-time, reducing errors and delays caused by manual data entry.
- Eliminating data silos ensures that all stakeholders have access to the same information, fostering a unified understanding of business operations.
Enhanced Collaboration
- ERP systems facilitate collaboration by providing a central platform for communication and document sharing.
- Teams can access shared calendars, task lists, and project management tools, enabling them to coordinate activities and track progress more effectively.
Successful ERP Integrations
- Case Study:A manufacturing company integrated its ERP system with its customer relationship management (CRM) software, resulting in a 20% increase in sales conversion rates due to improved lead tracking and follow-up.
- Case Study:A retail chain integrated its ERP system with its supply chain management (SCM) software, achieving a 15% reduction in inventory costs through optimized inventory levels and reduced lead times.
Customization and Scalability

ERP systems offer customization capabilities to tailor the software to specific business needs. This flexibility ensures that the ERP system aligns with unique processes, industry-specific requirements, and organizational structures. Customization allows businesses to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage.
Scalability is crucial for ERP systems to accommodate future growth and changing business requirements. Assessing the scalability of an ERP system involves evaluating its ability to handle increased data volumes, user count, and transaction processing without compromising performance. Businesses should consider the potential for expansion and ensure that the ERP system can grow alongside their organization.
Best Practices for ERP Customization
- Identify core business processes:Determine the critical processes that the ERP system will support and prioritize customization efforts accordingly.
- Involve key stakeholders:Engage users, managers, and IT personnel in the customization process to ensure that the system meets their specific needs.
- Test thoroughly:Conduct rigorous testing to verify the functionality and accuracy of customizations before implementation.
- Document changes:Maintain detailed documentation of all customizations, including the rationale, implementation details, and any potential impact on other system components.
- Consider future upgrades:Plan for future ERP upgrades by ensuring that customizations are modular and easy to update.
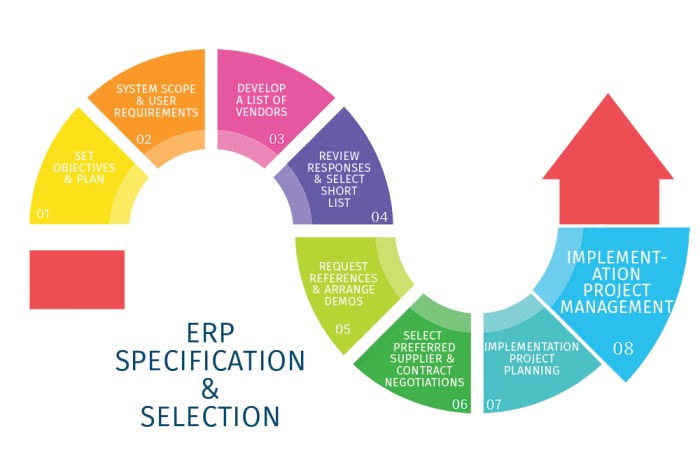
Vendor Selection and Implementation
ERP vendor selection and implementation are crucial for the successful adoption and utilization of ERP software. It involves identifying the right vendor, aligning their capabilities with business requirements, and executing a seamless implementation process.
Key Factors for ERP Vendor Selection
* Business Objectives:Define the specific goals and challenges that the ERP system should address.
Industry Expertise
Evaluate vendors’ experience and track record in the specific industry or domain.
Functional Capabilities
Assess the vendor’s ERP software’s functionality and alignment with business processes.
Technology Infrastructure
Consider the compatibility of the vendor’s software with existing IT systems and infrastructure.
Implementation Experience
Inquire about the vendor’s implementation methodology, timeline, and support capabilities.
Cost and Pricing
Determine the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing support.
Vendor Reputation
Research the vendor’s market reputation, customer reviews, and financial stability.
ERP Implementation Process
* Planning:Define the project scope, goals, and timeline.
Analysis
Conduct a thorough analysis of business processes to identify areas for improvement.
Configuration
Customize the ERP software to align with specific business requirements.
Testing
Perform rigorous testing to ensure the system’s functionality and accuracy.
Training
Provide comprehensive training to users on the new system and processes.
Go-Live
Launch the ERP system and monitor its performance closely.
Optimization
Continuously monitor and adjust the system to improve efficiency and maximize benefits.
Tips for Successful ERP Vendor Selection and Implementation
* Involve Key Stakeholders:Engage key decision-makers and users throughout the process to ensure buy-in and alignment.
Establish a Clear Scope
Define a clear project scope to avoid delays and budget overruns.
Conduct Due Diligence
Thoroughly research potential vendors and conduct reference checks.
Set Realistic Expectations
Understand the time, effort, and resources required for a successful implementation.
Communicate Effectively
Keep all stakeholders informed and address concerns promptly.
Seek Expert Assistance
Consider hiring a consultant or integrator to guide the process and provide technical expertise.
Cost and Return on Investment
ERP software implementation involves upfront and ongoing costs. The initial investment covers software licensing, implementation services, hardware upgrades, and training. Ongoing costs include maintenance, support, and upgrades.
Calculating the return on investment (ROI) of ERP systems requires a comprehensive analysis of benefits and costs. Tangible benefits include reduced operational costs, improved efficiency, increased revenue, and enhanced customer satisfaction. Intangible benefits, such as improved decision-making and increased agility, are also considered.
Calculating ROI
Common methods for calculating ROI include:
- Payback period: Measures the time it takes to recoup the initial investment.
- Net present value (NPV): Calculates the present value of future cash flows minus the initial investment.
- Internal rate of return (IRR): Determines the discount rate that makes the NPV equal to zero.
Case Studies
Numerous businesses have achieved significant ROI with ERP:
- Example 1:A manufacturing company reduced production costs by 15% and increased revenue by 10% within two years of ERP implementation.
- Example 2:A retail chain improved inventory management by 20%, leading to reduced stockouts and increased customer satisfaction.
Emerging Trends in ERP
ERP software is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. The latest trends in ERP software include the adoption of emerging technologies, such as AI and cloud computing, which are shaping the future of ERP and have the potential to revolutionize business process management.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. For example, AI-powered ERP systems can be used to automate tasks such as invoice processing, purchase order approvals, and inventory management. AI can also be used to analyze data to identify trends and patterns, which can help businesses make better decisions.
Additionally, AI can be used to provide insights into customer behavior, which can help businesses improve their marketing and sales strategies.
Cloud computing is another emerging trend in ERP software. Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on a remote server, which means that businesses can access their ERP system from anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud-based ERP systems are also more scalable than on-premises ERP systems, which means that businesses can easily add or remove users as needed.
Additionally, cloud-based ERP systems are typically more cost-effective than on-premises ERP systems.
The Potential Impact of Emerging Trends on Business Process Management
The adoption of emerging technologies, such as AI and cloud computing, has the potential to revolutionize business process management. AI can be used to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. Cloud computing can make ERP systems more accessible, scalable, and cost-effective.
These trends have the potential to make businesses more efficient, productive, and profitable.
Industry-Specific ERP Solutions

ERP software tailored to specific industries addresses unique business requirements, processes, and regulations. These solutions streamline operations, improve efficiency, and provide industry-specific insights.
Key industry-specific requirements for ERP software include:
- Compliance with industry regulations and standards
- Support for industry-specific processes and workflows
- Integration with specialized equipment and software
- Reporting and analytics tailored to industry metrics
Examples of Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
- Manufacturing:ERP systems for manufacturing manage production planning, inventory control, quality management, and supply chain operations.
- Healthcare:Healthcare ERP systems handle patient records, medical billing, inventory management, and compliance with HIPAA regulations.
- Retail:Retail ERP systems manage point-of-sale transactions, inventory tracking, customer loyalty programs, and omnichannel operations.
- Financial Services:Financial services ERP systems automate accounting, risk management, compliance, and customer relationship management.
Benefits and Considerations of Industry-Specific ERP Systems
Benefits:
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced compliance and risk management
- Real-time visibility into industry-specific metrics
- Reduced costs and increased profitability
Considerations:
- Higher implementation costs compared to generic ERP systems
- Need for specialized expertise and training
- Potential for vendor lock-in due to industry-specific customization
Conclusion
In conclusion, ERP software for business process management is an essential investment for organizations seeking to optimize operations, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive edge. By leveraging the power of ERP systems, businesses can streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and drive innovation, ultimately positioning themselves for long-term success.
FAQ: ERP Software For Business Process Management
What are the key benefits of ERP software for business process management?
ERP software offers numerous benefits, including improved process efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced data accuracy, increased collaboration, and better decision-making.
How does ERP software optimize business processes?
ERP systems automate tasks, eliminate manual processes, and provide real-time visibility into operations, enabling businesses to identify and address inefficiencies.
What types of reports and analytics are available through ERP systems?
ERP systems provide a wide range of reports and analytics, including financial statements, inventory reports, sales reports, and customer relationship management reports.
How can businesses ensure successful ERP implementation?
Successful ERP implementation requires careful planning, vendor selection, and a commitment to change management. It is crucial to involve stakeholders, define clear goals, and establish a realistic implementation timeline.