ERP software for affordability opens the door to a world of cost-effective solutions, operational efficiency, and enhanced decision-making. As businesses navigate the ever-changing landscape, this software empowers them to streamline processes, optimize resources, and gain a competitive edge.
ERP software not only reduces operational costs but also provides a substantial return on investment. Its scalability and flexibility adapt to growing businesses and evolving industry trends. By seamlessly integrating with existing systems, ERP software centralizes data, improves decision-making, and automates processes, minimizing errors and maximizing efficiency.
Affordability and Cost-Effectiveness
ERP software is designed to be affordable and cost-effective for businesses of all sizes. The key factors that contribute to the affordability of ERP software include:
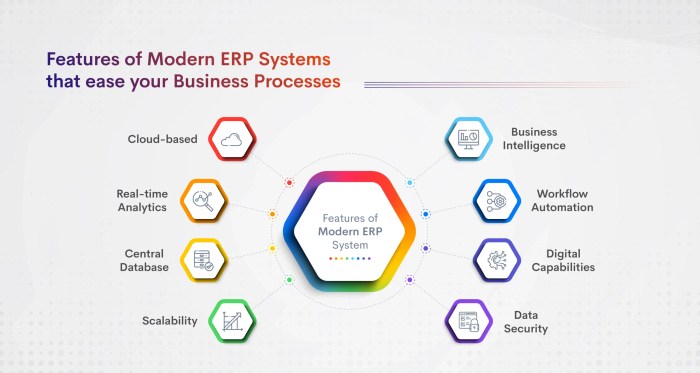
- Cloud-based deployment: Cloud-based ERP software is hosted on a remote server, eliminating the need for businesses to invest in expensive hardware and IT infrastructure.
- Subscription-based pricing: ERP software is typically offered on a subscription basis, which allows businesses to pay a monthly or annual fee rather than a large upfront cost.
- Scalability: ERP software can be scaled up or down to meet the changing needs of a business, ensuring that businesses only pay for the features and functionality they need.
ERP software can help businesses reduce operational costs and improve efficiency in a number of ways. For example, ERP software can:
- Automate tasks: ERP software can automate many of the repetitive tasks that are typically performed manually, such as data entry, order processing, and inventory management. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Improve communication and collaboration: ERP software can provide a central platform for communication and collaboration between different departments within a business. This can help to improve coordination and reduce errors.
- Provide real-time data: ERP software can provide businesses with real-time data on their operations, which can help them to make better decisions and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
The potential return on investment (ROI) associated with implementing ERP software can be significant. A study by Aberdeen Group found that businesses that implemented ERP software saw an average ROI of 18%. The ROI can be even higher for businesses that are able to successfully integrate ERP software with their other business systems.
Scalability and Flexibility
ERP software is designed to adapt to changing business needs and industry trends. Its scalability allows businesses to expand their operations without outgrowing their software, while its flexibility enables customization to meet specific industry requirements.
Scalability is crucial for future growth and expansion. As businesses grow, their ERP software must be able to handle increased data volumes, users, and transactions without compromising performance. ERP software can scale vertically (adding more resources to existing servers) or horizontally (distributing workload across multiple servers), ensuring seamless operation during growth spurts.
Customization for Industry-Specific Needs
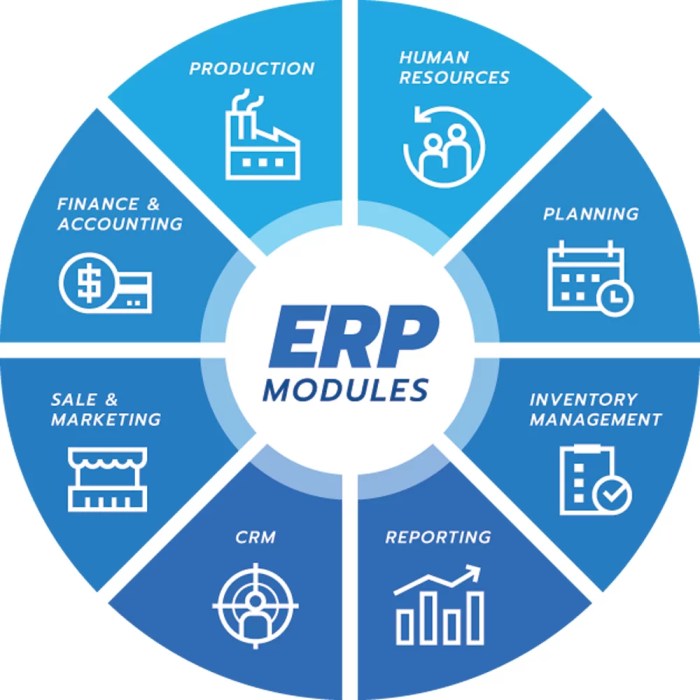
ERP software can be customized to meet the unique requirements of different industries. For example, manufacturers may require modules for production planning and inventory management, while healthcare providers need functionality for patient records and billing. By tailoring the software to industry-specific needs, businesses can optimize their operations and gain a competitive advantage.
Integration and Data Management
ERP software’s seamless integration with existing systems and applications is crucial for efficient data flow and comprehensive business management. It enables data sharing and communication between different departments and software, eliminating data silos and streamlining operations.
ERP software centralizes data from various sources, creating a unified repository that provides a comprehensive view of the business. This centralized data management improves decision-making by providing real-time access to accurate and up-to-date information.
Data Automation and Error Reduction
ERP software automates data processes, reducing manual tasks and minimizing errors. Automated processes include data entry, validation, and updates, ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
User-Friendliness and Accessibility

ERP software should prioritize user-friendliness and intuitive navigation to enhance adoption and productivity. A well-designed interface with clear menus, search functionality, and customizable dashboards empowers users to navigate the system efficiently, reducing training time and improving overall user experience.
Mobile Accessibility and Remote Work Capabilities
In today’s dynamic work environments, mobile accessibility and remote work capabilities are essential. ERP systems that offer mobile apps and web-based interfaces allow users to access data and perform tasks from anywhere, at any time. This flexibility empowers teams to collaborate seamlessly, respond to customer inquiries promptly, and maintain business continuity even when working remotely.
Self-Service Capabilities and Reduced Training Time
Modern ERP software empowers users with self-service capabilities, such as the ability to view reports, update personal information, and submit requests. These features reduce the need for IT support and allow users to take ownership of their data and processes.
By providing intuitive self-service tools, ERP systems can significantly reduce training time and improve user autonomy.
Security and Compliance
Data security and regulatory compliance are crucial aspects of ERP software. ERP systems store and process sensitive business information, including financial data, customer records, and intellectual property. Therefore, it is imperative that ERP software provides robust security measures to protect this data from unauthorized access, cyber threats, and data breaches.ERP software employs various security mechanisms to safeguard data, such as encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems.
These measures ensure that only authorized users can access data, and that any unauthorized attempts to access or modify data are detected and prevented. Additionally, ERP software can help businesses meet industry-specific compliance requirements, such as those mandated by HIPAA, GDPR, and ISO 27001.
By providing tools for data privacy, audit trails, and regulatory reporting, ERP software helps businesses comply with these regulations and avoid potential legal penalties.
Encryption
Encryption is a fundamental security measure used in ERP software to protect data from unauthorized access. Encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, transform data into an unreadable format, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to decipher the information. Encryption is applied to data at rest (stored on servers) and data in transit (transmitted over networks), ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive data even in the event of a security breach.
Access Controls
Access controls are another essential security mechanism in ERP software. These controls define who can access specific data and what actions they can perform on that data. ERP software allows administrators to create user roles and assign appropriate permissions to each role.
This granular control ensures that users only have access to the data and functionality necessary for their job roles, minimizing the risk of unauthorized data access or misuse.
Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) monitor ERP systems for suspicious activities and unauthorized attempts to access or modify data. IDS use advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify potential threats, such as malware, phishing attacks, and brute force attempts. When an IDS detects a suspicious activity, it can trigger alerts, block access, or take other appropriate actions to mitigate the threat.
Vendor Support and Implementation
Vendor support is essential for successful ERP software implementation. Expert vendors provide guidance, training, and ongoing maintenance to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of the software.
Vendor Training and Documentation
Vendor training empowers users with the knowledge and skills necessary to operate the ERP system effectively. Comprehensive documentation provides clear instructions and reference materials, reducing the learning curve and ensuring consistent usage.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support
Ongoing maintenance and support ensure the ERP system remains up-to-date and functioning optimally. Vendors provide regular updates, patches, and technical assistance to address issues promptly and maintain system performance.
Overcoming Challenges with Vendor Support
Vendor support plays a crucial role in overcoming implementation challenges:
- Data Migration:Vendors assist with data conversion and migration, ensuring seamless transfer of existing data into the new system.
- User Adoption:Training and support help users adapt to the new system, minimizing resistance and maximizing adoption.
- Integration:Vendors facilitate integration with existing systems, ensuring data flows seamlessly and eliminating redundancies.
Cloud-Based ERP and Deployment Options

Cloud-based ERP and on-premises ERP are two main deployment options for ERP systems. Each option has its own set of benefits and considerations, which organizations should carefully evaluate before making a decision.
Cloud-based ERP is hosted on a remote server and accessed over the internet. On-premises ERP, on the other hand, is installed and managed on an organization’s own servers.
Benefits of Cloud-Based ERP
- Cost savings: Cloud-based ERP can offer significant cost savings compared to on-premises ERP. Organizations do not need to invest in hardware, software, and IT staff to manage the system. They also do not need to pay for maintenance and upgrades.
- Scalability: Cloud-based ERP is highly scalable, which means that it can easily be expanded or contracted to meet the changing needs of an organization. This is especially beneficial for organizations that are experiencing rapid growth or that have fluctuating business demands.
- Accessibility: Cloud-based ERP can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This gives employees the flexibility to work from anywhere, at any time.
Considerations for Choosing Between Cloud and On-Premises ERP
When choosing between cloud-based ERP and on-premises ERP, organizations should consider the following factors:
- Cost: Cloud-based ERP can offer significant cost savings compared to on-premises ERP. However, organizations need to factor in the ongoing cost of cloud services.
- Security: Cloud-based ERP providers typically have robust security measures in place. However, organizations need to ensure that their data is secure and that they have a plan in place for data recovery in the event of a breach.
- Control: With on-premises ERP, organizations have complete control over their system. With cloud-based ERP, organizations share control with the cloud provider.
- Flexibility: Cloud-based ERP is typically more flexible than on-premises ERP. Organizations can easily add or remove users and modules as needed.
Examples of How Cloud-Based ERP Can Offer Cost Savings, Scalability, and Accessibility Advantages
- A small business can save money on IT costs by using cloud-based ERP. They do not need to purchase and maintain hardware and software, and they can pay for the system on a monthly basis.
- A large enterprise can use cloud-based ERP to scale its system to meet the demands of its growing business. They can easily add or remove users and modules as needed.
- A global organization can use cloud-based ERP to give employees access to the system from anywhere in the world. This can improve collaboration and productivity.
Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
Industry-specific ERP software is tailored to meet the unique needs of specific industries. It provides specialized functionality and addresses industry-specific business challenges and regulatory requirements. By leveraging industry-specific ERP solutions, businesses can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive advantage.
Industry-specific ERP solutions are designed to address the unique business processes, data management requirements, and regulatory compliance needs of specific industries. They offer pre-configured industry-specific modules, templates, and best practices that align with industry standards and regulations.
Benefits of Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
- Tailored Functionality:Industry-specific ERP solutions provide specialized features and modules that cater to the specific needs of each industry, such as project management for construction, inventory management for manufacturing, or patient management for healthcare.
- Streamlined Operations:By automating industry-specific processes, businesses can reduce manual tasks, improve data accuracy, and enhance operational efficiency.
- Improved Decision-Making:Industry-specific ERP solutions provide real-time industry-specific data and insights that enable businesses to make informed decisions and respond quickly to market changes.
- Regulatory Compliance:Industry-specific ERP solutions help businesses meet industry-specific regulations and standards, ensuring compliance and mitigating risks.
- Competitive Advantage:By leveraging industry-specific ERP solutions, businesses can gain a competitive advantage by optimizing their operations, improving customer service, and reducing costs.
Examples of Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
Industry-specific ERP solutions are available for a wide range of industries, including:
- Manufacturing:ERP solutions for manufacturing provide features such as production planning, inventory management, quality control, and supply chain management.
- Healthcare:Healthcare ERP solutions offer functionality for patient management, electronic health records, billing, and insurance processing.
- Construction:Construction ERP solutions provide tools for project management, resource planning, and cost control.
- Retail:Retail ERP solutions offer features such as inventory management, point-of-sale systems, and customer relationship management.
- Nonprofit:Nonprofit ERP solutions provide functionality for donor management, fundraising, and program tracking.
Emerging Technologies and ERP Software: ERP Software For Affordability

The advent of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and automation is revolutionizing the landscape of ERP software. These technologies are being incorporated into ERP systems to enhance data analysis, provide predictive insights, and automate processes, leading to increased efficiency and improved decision-making.
AI and Machine Learning
- AI and ML algorithms enable ERP systems to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions. This allows businesses to gain insights into their operations, customer behavior, and market trends.
- For example, an ERP system with AI capabilities can analyze historical sales data to predict future demand, optimize inventory levels, and suggest personalized product recommendations.
Automation
- Automation capabilities in ERP software reduce manual tasks, streamline processes, and improve accuracy. This frees up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
- For instance, an ERP system with automation features can automatically generate purchase orders, process invoices, and reconcile bank statements.
Integration with Other Technologies
- ERP software is increasingly integrating with other emerging technologies, such as blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT). This enables businesses to connect their ERP systems with their supply chains, manufacturing equipment, and other business applications.
- For example, an ERP system integrated with IoT sensors can monitor production lines in real-time, providing insights into equipment performance and optimizing production schedules.
Best Practices for ERP Software Selection
ERP software selection is a critical decision for businesses seeking to optimize their operations and achieve their strategic goals. By following best practices, organizations can increase the likelihood of choosing the right ERP system for their specific needs.
The key factors to consider when evaluating and selecting ERP software include:
- Business requirements:Clearly define the specific business needs and objectives that the ERP system should address.
- Vendor capabilities:Assess the capabilities of potential vendors to meet the organization’s business requirements, including industry experience, technical expertise, and financial stability.
- Due diligence:Conduct thorough due diligence on potential vendors, including reference checks, site visits, and financial analysis.
A step-by-step guide to ERP software selection includes:
- Vendor evaluation:Identify and evaluate potential vendors based on their capabilities and alignment with the organization’s business requirements.
- RFP creation:Develop a detailed request for proposal (RFP) that Artikels the organization’s specific requirements and evaluation criteria.
- Contract negotiation:Negotiate the terms of the contract with the selected vendor, including pricing, implementation timelines, and support arrangements.
Case Studies and Success Stories
ERP software has transformed businesses of all sizes, enabling them to streamline operations, reduce costs, and gain a competitive edge. Let’s explore some case studies and success stories to illustrate its impact:
Improved Efficiency and Reduced Costs, ERP software for affordability
- A manufacturing company implemented an ERP system that integrated all its business processes, from production planning to inventory management. This led to a 20% reduction in production time and a 15% decrease in inventory costs.
- A healthcare provider implemented an ERP system that automated patient scheduling, billing, and medical record management. This resulted in a 30% increase in patient throughput and a 10% reduction in administrative costs.
Enhanced Customer Service
- A retail company implemented an ERP system that provided a single, real-time view of customer data across all channels. This enabled them to personalize customer interactions, resolve issues faster, and increase customer satisfaction by 15%.
- A logistics company implemented an ERP system that integrated with its transportation management system. This allowed them to track shipments in real-time, improve delivery accuracy, and reduce customer complaints by 25%.
Increased Revenue and Profitability
- A software company implemented an ERP system that streamlined its product development and sales processes. This resulted in a 10% increase in new product releases and a 15% growth in revenue.
- A non-profit organization implemented an ERP system that integrated its fundraising, donor management, and financial reporting. This led to a 20% increase in donations and a 12% improvement in financial efficiency.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, ERP software for affordability is a strategic investment that empowers businesses to thrive in today’s dynamic market. By optimizing operations, reducing costs, and enhancing data management, ERP software sets the stage for sustained growth, innovation, and profitability.
FAQ
What are the key benefits of ERP software for affordability?
ERP software reduces operational costs, improves efficiency, and provides a substantial return on investment.
How does ERP software adapt to changing business needs?
ERP software is scalable and flexible, allowing businesses to customize and expand the system as their needs evolve.
How does ERP software improve data management?
ERP software centralizes data, automates processes, and minimizes errors, leading to better decision-making and operational efficiency.