ERP system vendors are at the forefront of the digital transformation revolution, providing businesses with the tools they need to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. This guide delves into the landscape of ERP vendors, exploring their functionalities, deployment options, pricing models, and more to help organizations make informed decisions about their ERP investments.
The ERP industry is constantly evolving, with vendors introducing innovative solutions to meet the changing needs of businesses. From cloud-based deployments to AI-powered analytics, ERP systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling organizations to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and productivity.
Overview of ERP System Vendors
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are software suites that integrate various business processes, such as finance, supply chain management, human resources, and customer relationship management, into a unified system. They provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s operations and enable efficient data sharing and communication across different departments.The ERP system vendor landscape is diverse, ranging from established players with decades of experience to emerging vendors offering innovative solutions.
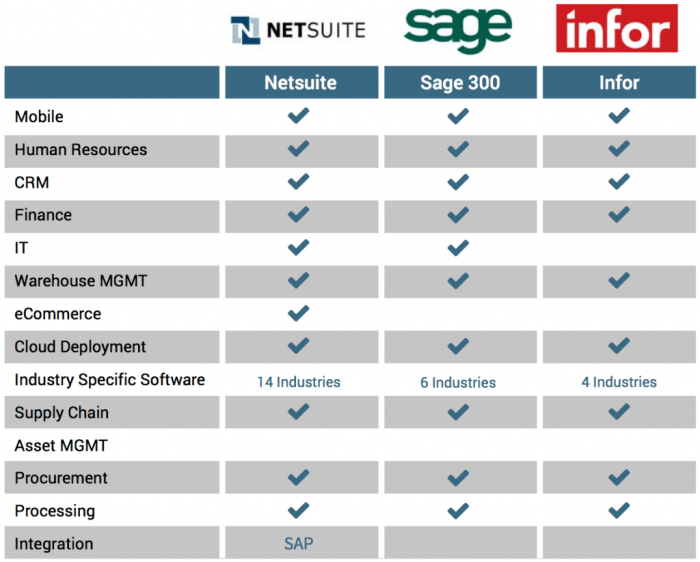
Key vendors include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Infor, and NetSuite. These vendors offer a wide range of ERP solutions tailored to different industries and business sizes.The ERP industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Key trends include the adoption of cloud-based ERP solutions, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), and the rise of industry-specific ERP solutions.
Market Share and Competitive Analysis

The ERP software market is highly competitive, with a diverse range of vendors vying for market share. Market share data reveals the dominance of a few leading vendors, while smaller players compete for niche markets.
Key factors influencing competitive strengths and weaknesses include product functionality, industry expertise, implementation capabilities, and customer support. Vendors differentiate themselves by focusing on specific industry verticals, offering specialized solutions tailored to the unique requirements of different industries.
Market Share Data
According to industry reports, the leading ERP vendors in terms of market share are:
- SAP: Holding a significant market share, SAP is a global leader in ERP software, known for its comprehensive suite of enterprise applications.
- Oracle: Oracle’s ERP solutions are widely used in large enterprises, offering a robust platform for managing complex business processes.
- Microsoft: Microsoft Dynamics ERP is a popular choice for mid-sized businesses, providing a scalable and cost-effective solution.
- Infor: Infor specializes in industry-specific ERP solutions, serving various verticals such as manufacturing, healthcare, and distribution.
- NetSuite: NetSuite offers a cloud-based ERP solution, catering to the needs of small and medium-sized businesses.
Competitive Strengths and Weaknesses
Each vendor possesses unique strengths and weaknesses that shape their competitive position in the market:
- SAP:Strengths include a comprehensive product suite, strong brand recognition, and global reach. Weaknesses may include high implementation costs and complexity.
- Oracle:Strengths include a robust database platform, scalability, and a wide range of industry-specific solutions. Weaknesses may include licensing costs and a complex user interface.
- Microsoft:Strengths include ease of use, affordability, and integration with other Microsoft products. Weaknesses may include limited functionality compared to larger vendors.
- Infor:Strengths include industry expertise, specialized solutions, and flexible deployment options. Weaknesses may include a smaller market share and less brand recognition.
- NetSuite:Strengths include cloud-based deployment, scalability, and ease of use. Weaknesses may include limited customization options and higher costs for larger organizations.
Market Strategies and Positioning
ERP vendors employ various market strategies to differentiate themselves and gain competitive advantage:
- Product Innovation:Vendors invest heavily in research and development to enhance product functionality and stay ahead of the competition.
- Industry Specialization:Focusing on specific industries allows vendors to develop tailored solutions that meet the unique needs of different sectors.
- Partnerships and Alliances:Collaborating with other technology providers and consulting firms extends vendors’ reach and offers complementary solutions.
- Cloud Deployment:Cloud-based ERP solutions offer flexibility, scalability, and reduced infrastructure costs, attracting many businesses.
- Pricing Strategies:Vendors adopt different pricing models, including subscription-based, perpetual licensing, and tiered pricing, to cater to diverse customer needs.
Functionality and Features
ERP systems offer a wide range of core functionalities, including financial management, supply chain management, customer relationship management, and human capital management. Different vendors provide varying levels of depth and sophistication within each of these core areas.
In addition to core functionalities, many vendors also offer specialized modules that address the specific needs of particular industries. For example, some vendors offer modules for healthcare, manufacturing, and retail.
When evaluating ERP systems, it is important to consider the user experience and ease of use. The system should be intuitive and easy to navigate, with minimal training required.
Core Functionalities
- Financial management: Includes functions such as general ledger, accounts payable, accounts receivable, and financial reporting.
- Supply chain management: Includes functions such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation management.
- Customer relationship management: Includes functions such as sales force automation, marketing automation, and customer service.
- Human capital management: Includes functions such as payroll, benefits administration, and talent management.
Specialized Modules
- Healthcare: Includes functions such as patient management, medical billing, and electronic health records.
- Manufacturing: Includes functions such as production planning, inventory management, and quality control.
- Retail: Includes functions such as point-of-sale, inventory management, and customer loyalty.
User Experience and Ease of Use
The user experience and ease of use of an ERP system are critical factors to consider when making a purchase decision. The system should be intuitive and easy to navigate, with minimal training required.
Some of the factors that contribute to a positive user experience include:
- A clean and uncluttered interface
- Well-organized menus and navigation
- Context-sensitive help
- Easy access to data and reports
- Customization options to tailor the system to the specific needs of the organization
Deployment Options and Implementation

ERP systems can be deployed in various ways, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these deployment options and selecting the most appropriate one is crucial for successful ERP implementation.
Cloud Deployment
Cloud deployment involves hosting the ERP system on a remote server managed by a third-party provider. This option eliminates the need for on-premises infrastructure and provides scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud ERP solutions are typically accessed through a web browser or mobile app.
On-Premises Deployment
On-premises deployment involves installing the ERP system on the organization’s own servers and hardware. This option provides greater control over the system and data, but requires significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance costs. On-premises ERP systems offer higher levels of security and customization.
Hybrid Deployment
Hybrid deployment combines elements of both cloud and on-premises deployment. In this approach, certain ERP modules or functions are hosted on the cloud while others remain on-premises. Hybrid deployment offers flexibility, scalability, and cost savings while maintaining control over critical data.
Implementation Methodologies
ERP implementation involves several methodologies to ensure successful adoption. These methodologies provide a structured approach to planning, executing, and managing the implementation process.
- Waterfall Methodology:A traditional approach that follows a sequential, step-by-step process, with each phase completed before moving to the next.
- Agile Methodology:An iterative approach that involves frequent feedback and collaboration between stakeholders, allowing for flexibility and rapid development.
- Phased Implementation:A gradual approach that deploys the ERP system in phases, allowing organizations to manage the transition more effectively.
Integration Capabilities
ERP systems must integrate with other business applications to provide a comprehensive view of operations. Integration capabilities enable the exchange of data and processes between ERP and other systems, such as CRM, supply chain management, and financial applications.
Data Migration Strategies
Data migration is a critical aspect of ERP implementation, involving the transfer of data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. Effective data migration strategies ensure data accuracy, completeness, and integrity, minimizing disruptions during the transition.
Pricing and Licensing Models

ERP systems come with a range of pricing and licensing models that can significantly impact the total cost of ownership. Understanding these models and their implications is crucial for organizations evaluating ERP solutions.
Pricing Models
ERP vendors typically offer a variety of pricing models, including:
- Per-user licensing:This model charges a fixed fee per user, regardless of the number of modules or functionality accessed.
- Concurrent user licensing:Similar to per-user licensing, but it limits the number of users who can access the system simultaneously.
- Module-based pricing:This model charges based on the number and type of modules purchased, allowing organizations to customize their solution and pay only for the functionality they need.
- Tiered pricing:This model offers different pricing levels based on the size of the organization or the number of users.
Licensing Fees
In addition to the pricing model, ERP vendors also charge licensing fees, which can include:
- Initial licensing fee:This is a one-time fee paid at the time of purchase, typically based on the number of users or modules.
- Annual maintenance fee:This is an ongoing fee that covers software updates, support, and technical assistance.
- Implementation fees:These fees cover the cost of customizing and implementing the ERP system, which can vary depending on the complexity of the project.
Factors Influencing Pricing, ERP system vendors
Several factors can influence the pricing of ERP systems, including:
- Industry:Some industries, such as healthcare or manufacturing, may require more specialized modules and functionality, which can increase the cost.
- Organization size:Larger organizations with more users and complex requirements typically pay higher prices.
- Implementation complexity:The cost of implementation can vary depending on the number of modules, integrations, and customizations required.
- Vendor reputation and market share:Well-known vendors with a large market share may charge higher prices.
Subscription-Based Models
Some ERP vendors offer subscription-based models, which provide access to the software on a monthly or annual basis. This model can provide flexibility and reduce upfront costs, but it may result in higher ongoing expenses over time.
Value-Added Services
ERP vendors may offer additional value-added services, such as:
- Training and support:This can include user training, technical support, and consulting services.
- Data migration:This service helps organizations move data from their existing systems to the new ERP system.
- Integration services:This can help organizations integrate the ERP system with other applications and systems.
Understanding the pricing and licensing models of ERP vendors is essential for organizations to make informed decisions and select the solution that best meets their needs and budget.
Customer Support and Services

The quality of customer support provided by ERP vendors is crucial for ensuring smooth implementation and ongoing operations. Different vendors offer varying levels of support, so it’s essential to evaluate their offerings carefully.
Service level agreements (SLAs) define the specific commitments and response times that vendors provide. These SLAs should clearly Artikel the guaranteed levels of support, including response times, resolution times, and availability of support channels.
Training and Consulting Services
Many ERP vendors offer training and consulting services to help customers implement and use their systems effectively. These services can range from basic training to in-depth consulting on complex customization and integration projects.
- Basic training:Covers the fundamentals of the ERP system, including navigation, data entry, and reporting.
- Advanced training:Focuses on specific modules or functionalities of the ERP system, such as finance, supply chain management, or manufacturing.
- Consulting services:Provide guidance on system implementation, customization, integration, and optimization.
Case Studies and Success Stories
ERP systems have been successfully implemented in various industries, leading to significant benefits for organizations. Case studies and success stories showcase the positive outcomes achieved through effective ERP implementation, highlighting the advantages and challenges faced during the process.
These case studies provide valuable insights into the practical aspects of ERP implementation, offering a better understanding of the potential benefits and challenges involved.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
ERP systems offer industry-specific solutions tailored to the unique requirements of different sectors. For instance, in the manufacturing industry, ERP systems streamline production processes, enhance inventory management, and improve supply chain efficiency.
- Automotive:ERP systems help automotive manufacturers manage complex supply chains, optimize production schedules, and improve quality control.
- Healthcare:ERP systems enable healthcare providers to manage patient records, streamline billing processes, and improve operational efficiency.
- Retail:ERP systems provide retailers with tools for inventory management, sales tracking, and customer relationship management.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
The ERP industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies emerging that are having a major impact on the way that businesses operate. Cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics are three of the most important emerging technologies that are shaping the future of ERP systems.
Cloud computing is making it easier for businesses to access and manage their ERP systems. Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted by a third-party provider, which means that businesses do not have to invest in hardware or software. This can save businesses money and time, and it can also make it easier to scale their ERP systems as needed.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to automate many of the tasks that are traditionally performed by humans. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks, and it can also help businesses to improve their efficiency and accuracy.
Data analytics is helping businesses to make better use of the data that they collect. Data analytics tools can help businesses to identify trends, patterns, and insights that can be used to improve decision-making.
Impact on the ERP Industry
These emerging technologies are having a major impact on the ERP industry. Cloud computing, AI, and data analytics are making ERP systems more accessible, affordable, and powerful than ever before. This is leading to a growing number of businesses adopting ERP systems, and it is also driving innovation in the ERP industry.
As these technologies continue to evolve, they will continue to have a major impact on the ERP industry. Businesses that are able to adopt these technologies early will be well-positioned to succeed in the future.
Vendor Selection and Evaluation
Selecting and evaluating the right ERP vendor is crucial for successful ERP implementation. This process involves carefully assessing vendors based on their capabilities, experience, and alignment with the organization’s specific needs.
Vendor Selection Process
The vendor selection process typically includes the following steps:
- Define Requirements:Clearly Artikel the organization’s functional, technical, and business requirements for an ERP system.
- Create a Vendor Shortlist:Identify potential vendors based on their industry expertise, product offerings, and customer references.
- Request for Proposal (RFP):Issue an RFP to shortlisted vendors, outlining the organization’s requirements and evaluation criteria.
- Vendor Demonstrations and Presentations:Schedule demonstrations and presentations to evaluate vendors’ solutions and capabilities firsthand.
- Reference Checks:Contact existing customers of potential vendors to gather feedback on their experience and satisfaction.
- Vendor Evaluation:Assess vendors based on their product functionality, technical architecture, implementation approach, pricing, and customer support.
- Vendor Selection:Select the vendor that best meets the organization’s requirements and aligns with its long-term goals.
Vendor Evaluation Criteria
When evaluating ERP vendors, consider the following criteria:
- Functional Capabilities:Ensure the vendor’s ERP system meets the organization’s core business processes and functional requirements.
- Technical Architecture:Assess the system’s scalability, security, and integration capabilities.
- Implementation Approach:Evaluate the vendor’s methodology for implementing the ERP system, including timelines, resources, and risk management.
- Pricing and Licensing:Determine the total cost of ownership, including software licensing, implementation fees, and ongoing maintenance.
- Customer Support:Assess the vendor’s level of support, response times, and availability of technical resources.
- Industry Expertise:Consider the vendor’s experience and knowledge in the organization’s industry.
- Company Stability and Reputation:Evaluate the vendor’s financial stability, market presence, and customer satisfaction ratings.
Contract Negotiation and Vendor Management
Once a vendor is selected, it is important to negotiate a contract that clearly Artikels the terms of the agreement. This includes:
- Scope of Work:Define the specific deliverables and services to be provided by the vendor.
- Pricing and Payment Terms:Establish the total cost of the project and the payment schedule.
- Implementation Timeline:Set clear deadlines for each phase of the implementation process.
- Performance Metrics:Define metrics to measure the success of the ERP implementation.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs):Artikel the vendor’s commitments regarding uptime, response times, and support availability.
Effective vendor management is essential to ensure a successful ERP implementation. This involves:
- Regular Communication:Establish clear communication channels and hold regular meetings to track progress and address any issues.
- Performance Monitoring:Track the vendor’s performance against agreed-upon SLAs and metrics.
- Relationship Building:Foster a positive and collaborative relationship with the vendor to encourage open communication and problem-solving.
Last Point
Selecting the right ERP system vendor is a critical decision for any organization. By carefully evaluating the vendors’ capabilities, pricing, and support offerings, businesses can ensure they choose a solution that aligns with their specific requirements and sets them on the path to success.
Common Queries
What is an ERP system?
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system is a software suite that integrates various business functions, such as finance, supply chain management, manufacturing, and human resources, into a single, unified platform.
What are the benefits of using an ERP system?
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, increased data accuracy, enhanced collaboration, and better decision-making.
How do I choose the right ERP system vendor?
Selecting the right ERP system vendor requires careful evaluation of factors such as functionality, deployment options, pricing, customer support, and industry expertise.