Embark on a transformative journey with ERP software for growth, a powerful tool that empowers businesses to streamline operations, optimize decision-making, and propel their expansion to new heights. Join us as we delve into the world of ERP software, unlocking its potential to drive your business to unprecedented success.
ERP software seamlessly integrates core business processes, providing a centralized platform for managing everything from supply chain to customer relationships. By eliminating data silos and automating workflows, ERP systems streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and free up valuable resources for strategic initiatives.
Benefits of ERP Software for Business Growth

ERP software offers numerous advantages for businesses seeking growth. It streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and provides a comprehensive view of business processes. By integrating various departments and functions, ERP software eliminates data silos, improves communication, and reduces manual errors.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
ERP software automates repetitive tasks, such as order processing, inventory management, and customer relationship management. This frees up employees to focus on higher-value activities, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs. For instance, a manufacturing company implemented an ERP system and experienced a 20% reduction in order processing time and a 15% increase in production output.
Improved Decision-Making
ERP software provides real-time data and analytics that enable businesses to make informed decisions. By accessing accurate and up-to-date information, managers can identify trends, optimize processes, and anticipate market changes. For example, a retail chain used ERP software to analyze sales data and identify underperforming products, resulting in a 10% increase in sales revenue.
Increased Collaboration
ERP software fosters collaboration among different departments by providing a central platform for data sharing and communication. This eliminates information gaps, improves coordination, and ensures that all stakeholders are working towards the same goals. For instance, a healthcare provider implemented an ERP system that enabled seamless communication between doctors, nurses, and administrative staff, leading to improved patient care and reduced wait times.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
ERP software helps businesses provide better customer service by providing a 360-degree view of customer interactions. By tracking customer orders, complaints, and preferences, businesses can personalize their services and respond quickly to inquiries. For example, an online retailer used ERP software to streamline its order fulfillment process, resulting in a 15% increase in customer satisfaction and a 10% reduction in customer complaints.
Key Features to Consider

Selecting ERP software for growth requires evaluating essential features that align with business objectives and support future expansion.
ERP systems offer a comprehensive suite of modules, each addressing specific business functions. The core modules include:
Core ERP Modules
| Module | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Financial Management | Centralizes financial data, streamlines accounting processes, and enhances financial reporting. |
| Supply Chain Management | Optimizes inventory levels, improves supplier relationships, and enhances logistics efficiency. |
| Customer Relationship Management (CRM) | Manages customer interactions, tracks sales pipelines, and provides personalized customer service. |
| Human Capital Management (HCM) | Automates HR processes, including payroll, benefits administration, and talent management. |
| Business Intelligence (BI) | Provides real-time insights, enabling data-driven decision-making and performance monitoring. |
Integration with Existing Systems
ERP software integration with existing business systems is paramount for streamlined operations and growth. It enables seamless data flow, eliminates redundancies, and enhances overall efficiency.
To ensure a successful integration, best practices include thorough planning, mapping of data fields, and phased migration. Regular testing and monitoring post-implementation are crucial to avoid disruptions and maintain system stability.
Data Migration and Disruption Avoidance
- Plan a phased migration to minimize downtime and maintain business continuity.
- Establish a comprehensive data mapping strategy to ensure accurate transfer of data between systems.
- Thoroughly test the integrated system before deployment to identify and resolve any potential issues.
- Provide adequate training to users on the new system to minimize disruptions during the transition.
- Monitor the system closely post-implementation and make necessary adjustments to optimize performance.
Scalability and Flexibility
ERP software should be able to adapt to changing business requirements. As a business grows, its needs will change. The ERP software should be able to accommodate these changes without requiring a complete overhaul. For example, if a business expands into new markets, the ERP software should be able to handle the increased volume of transactions and the different currencies.
Integration with Existing Systems
ERP software should be able to integrate with existing systems, such as accounting software, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and supply chain management (SCM) software. This integration will allow businesses to share data between different systems, which can improve efficiency and reduce errors.
For example, if a business uses an accounting software to track its finances, the ERP software should be able to import data from the accounting software so that the business can have a complete view of its financial performance.
Return on Investment (ROI)

ERP software offers numerous financial benefits, making it a worthwhile investment for businesses. It streamlines processes, reduces operational costs, improves efficiency, and enhances decision-making, ultimately contributing to increased profitability and revenue.
Case Studies
Company A
A manufacturing firm implemented an ERP system, leading to a 15% reduction in production costs due to optimized inventory management and improved production planning.
Company B
A retail chain experienced a 10% increase in sales after implementing an ERP system, thanks to improved customer relationship management and targeted marketing campaigns.
Implementation Challenges

ERP implementation can be a complex and challenging process. Businesses may encounter various obstacles during the deployment, which can impact the project’s timeline, budget, and overall success.To ensure a smooth and successful implementation, it is crucial to anticipate and address these challenges proactively.
Common implementation challenges include:
- Lack of clear goals and objectives:Businesses may fail to define clear goals and objectives for their ERP implementation, leading to confusion and misalignment among stakeholders.
- Insufficient stakeholder involvement:Failing to involve key stakeholders, such as users, managers, and IT personnel, in the planning and implementation process can result in resistance to change and poor adoption.
- Data migration issues:Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP system can be complex and time-consuming, often leading to data loss or errors if not managed properly.
- Lack of training and support:Inadequate training and support for users can hinder adoption and impact the system’s efficiency and effectiveness.
- Integration difficulties:Integrating the ERP system with existing business applications and processes can be challenging, leading to data inconsistencies and operational inefficiencies.
- Budget and resource constraints:ERP implementation can be expensive and require significant resources, which can strain budgets and limit the project’s scope.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, effective communication, and a commitment to change management. By addressing these challenges upfront, businesses can increase the likelihood of a successful ERP implementation and maximize the benefits it offers for growth.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premise Solutions
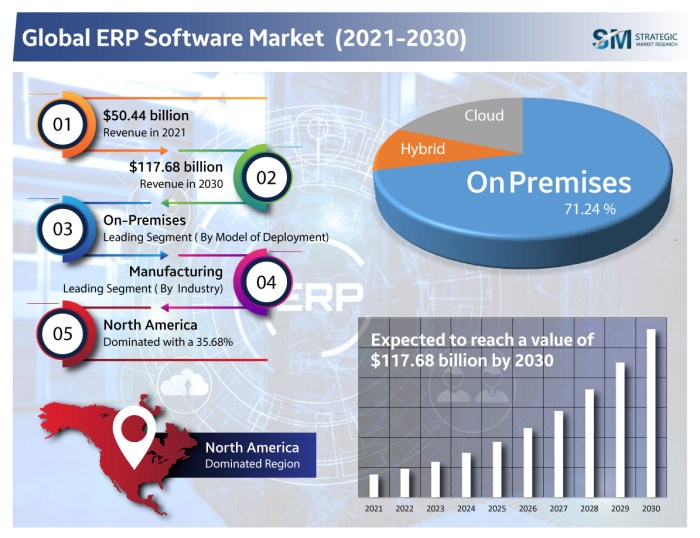
When selecting an ERP software solution, businesses must decide between cloud-based and on-premise options. Each approach offers distinct advantages and drawbacks that can impact growth aspirations.
Cloud-based ERP solutions are hosted by a third-party provider over the internet, while on-premise solutions are installed and maintained on the business’s own servers. Both options have unique strengths and weaknesses that should be carefully considered.
Advantages of Cloud-Based Solutions
- Lower upfront costs:Cloud-based solutions typically require lower upfront investments compared to on-premise systems, as businesses do not need to purchase hardware or software licenses.
- Scalability:Cloud-based solutions can easily scale up or down to meet changing business needs, providing flexibility for growth.
- Accessibility:Cloud-based solutions can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
- Regular updates:Cloud-based solutions are regularly updated by the provider, ensuring access to the latest features and security patches.
Disadvantages of Cloud-Based Solutions
- Internet dependency:Cloud-based solutions require a reliable internet connection, which can be a concern in areas with limited or unstable connectivity.
- Security concerns:Businesses must trust the cloud provider to protect their data, which may raise security concerns.
- Limited customization:Cloud-based solutions may offer less customization options compared to on-premise systems.
Advantages of On-Premise Solutions
- Greater control:On-premise solutions provide businesses with complete control over their data and IT infrastructure.
- Security:On-premise solutions are often considered more secure as they are not accessible over the internet.
- Customization:On-premise solutions can be highly customized to meet specific business requirements.
Disadvantages of On-Premise Solutions
- Higher upfront costs:On-premise solutions typically require significant upfront investments in hardware, software licenses, and implementation.
- Maintenance and upgrades:Businesses are responsible for maintaining and upgrading on-premise solutions, which can be time-consuming and expensive.
- Scalability limitations:On-premise solutions may have scalability limitations, especially during periods of rapid growth.
Which Option is More Suitable for Businesses with Growth Aspirations?
For businesses with growth aspirations, cloud-based ERP solutions may be more suitable due to their lower upfront costs, scalability, and accessibility. Cloud-based solutions allow businesses to focus on growth and innovation without being constrained by IT infrastructure limitations. However, businesses with specific security or customization requirements may prefer on-premise solutions.
Industry-Specific Solutions
ERP software tailored to specific industries can provide significant benefits for businesses. By leveraging industry-specific functionality and best practices, companies can streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge.
For example, manufacturers can choose ERP solutions designed specifically for their industry, which offer features such as inventory management, production planning, and quality control. These solutions are tailored to meet the unique challenges and requirements of manufacturing businesses, helping them to optimize their production processes and reduce costs.
Examples of Industry-Specific ERP Solutions
- Retail:ERP solutions for retail businesses provide features such as point-of-sale (POS) integration, inventory management, and customer relationship management (CRM). These solutions help retailers to manage their inventory effectively, track customer transactions, and improve the overall customer experience.
- Healthcare:Healthcare-specific ERP solutions offer features such as patient management, electronic health records (EHR), and medical billing. These solutions help healthcare providers to streamline their operations, improve patient care, and reduce costs.
- Financial Services:ERP solutions for financial services businesses provide features such as core banking, loan management, and risk management. These solutions help financial institutions to automate their processes, improve customer service, and reduce operational costs.
Mobile Accessibility
In the current business landscape, remote work and collaboration have become increasingly prevalent. Mobile access to ERP software is essential for empowering remote teams and enhancing overall efficiency.
Mobile ERP apps allow employees to access real-time data, collaborate with colleagues, and perform essential tasks from anywhere, at any time. This flexibility enables teams to respond quickly to changing business needs, improve decision-making, and maintain productivity even when working remotely.
Examples of Mobile ERP App Functionality
- Access to real-time data, including inventory levels, sales figures, and customer information
- Approval of purchase orders, invoices, and other business documents
- Collaboration with colleagues through messaging, video conferencing, and document sharing
- Customer relationship management (CRM) and salesforce automation
li>Task management and project tracking
Customer Success Stories
ERP software has enabled numerous businesses to achieve remarkable growth. Let’s explore some compelling success stories that demonstrate the transformative impact of ERP implementation.
Many companies have reported substantial revenue growth, increased operational efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction after adopting ERP systems. These success stories serve as a testament to the transformative power of ERP software in driving business growth.
Case Study: XYZ Corporation
XYZ Corporation, a leading manufacturer of industrial equipment, implemented an ERP system to streamline its operations and improve customer service. The system integrated all aspects of the business, from inventory management to order processing, providing real-time visibility into key performance indicators.
As a result, XYZ Corporation experienced a 25% increase in revenue and a 15% reduction in operational costs within the first year of implementation.
Testimonial: John Smith, CEO of ABC Company
“Our ERP system has been a game-changer for our business. It has allowed us to automate many of our processes, improve communication between departments, and gain a comprehensive view of our operations. We’ve seen a significant increase in efficiency and productivity, which has translated into increased profitability.”
Best Practices for ERP Implementation
Implementing an ERP system effectively is crucial for maximizing its benefits. To ensure a successful implementation, organizations should adhere to a set of best practices that cover various aspects of the project, including planning, change management, and user training.
Project Planning
A comprehensive project plan is the foundation for a successful ERP implementation. It should define the project scope, timelines, budget, and resource allocation. Involving key stakeholders and obtaining their buy-in is essential to ensure alignment and commitment throughout the project lifecycle.
Change Management
ERP implementation involves significant changes to business processes and workflows. Organizations must effectively manage these changes to minimize disruption and gain user acceptance. This includes communicating the changes clearly, providing training and support, and involving users in the decision-making process.
User Training, ERP software for growth
Adequate user training is essential for ensuring that employees can effectively utilize the new ERP system. Training should be tailored to different user roles and responsibilities, and it should cover both technical and functional aspects of the system. Hands-on practice and simulations can help users gain proficiency and confidence in using the system.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, ERP software for growth is an indispensable investment for businesses seeking to scale and thrive in today’s competitive market. Its ability to streamline operations, optimize decision-making, and foster collaboration makes it a cornerstone of successful growth strategies. By embracing ERP software, businesses can unlock a world of possibilities and propel themselves towards sustained growth and prosperity.
Question & Answer Hub: ERP Software For Growth
What are the key benefits of ERP software for growth?
ERP software streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, fosters collaboration, and provides real-time insights, enabling businesses to grow and scale effectively.
How does ERP software help businesses optimize decision-making?
ERP systems provide a centralized platform for accessing real-time data and analytics, allowing businesses to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
What is the importance of scalability in ERP software for growth?
ERP software should be scalable to accommodate business growth and expansion, ensuring that it can adapt to changing needs and support future growth initiatives.