ERP software for compliance has emerged as a transformative solution for businesses seeking to navigate the complexities of regulatory landscapes. With its robust capabilities, ERP software empowers organizations to streamline compliance efforts, reduce risks, and achieve operational excellence.
ERP software for compliance integrates seamlessly with core business processes, enabling organizations to automate compliance-related tasks, such as risk assessments, regulatory reporting, and data management. This automation streamlines compliance processes, reduces manual errors, and enhances the accuracy and timeliness of compliance reporting.
Compliance Requirements for ERP Software
ERP software must comply with various regulations to ensure data accuracy, security, and adherence to industry standards. These regulations include data protection laws, financial reporting standards, and industry-specific requirements.
Data Protection Regulations
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation):Protects personal data of EU citizens, requiring organizations to implement appropriate security measures and obtain consent for data processing.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act):Grants California residents the right to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of their personal information.
Financial Reporting Standards
- IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards):A set of accounting standards used by companies in over 140 countries, ensuring consistent and transparent financial reporting.
- US GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles):Accounting standards used by companies in the United States, providing guidance on financial reporting and disclosure.
Industry-Specific Compliance Standards
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act):Protects the privacy and security of health information in the United States.
- ISO 27001 (Information Security Management System):An international standard that provides a framework for organizations to implement and maintain an information security management system.
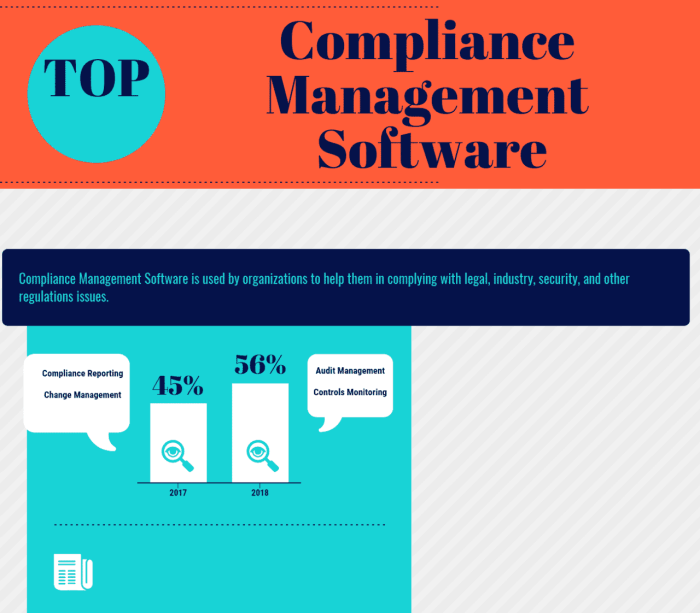
Features of ERP Software for Compliance
ERP software for compliance provides a comprehensive suite of features and modules that enable organizations to streamline their compliance efforts, automate processes, and improve overall compliance posture.
These features include:
Compliance Management Module
- Centralized repository for compliance policies, procedures, and documentation
- Automated tracking and monitoring of compliance activities
- Generation of compliance reports and alerts
Risk Management Module, ERP software for compliance
- Identification and assessment of compliance risks
- Development and implementation of risk mitigation strategies
- Continuous monitoring of risks and risk mitigation efforts
Internal Controls Module
- Documentation and testing of internal controls
- Automated monitoring of internal controls
- Generation of internal control reports and alerts
Audit Management Module
- Planning and execution of internal and external audits
- Management of audit findings and corrective actions
- Generation of audit reports and summaries
Data Management Module
- Centralized storage and management of compliance-related data
- Data integration from multiple sources
- Data analytics and reporting
Implementation and Configuration

ERP software implementation for compliance involves careful planning and execution. Best practices include:
- Engaging a skilled implementation team with compliance expertise.
- Establishing clear project objectives and timelines.
- Thoroughly understanding compliance requirements and mapping them to software functionalities.
- Customizing workflows and processes to align with compliance regulations.
- Conducting thorough testing and validation to ensure compliance adherence.
Compliance-Related Workflows and Processes
Compliance-related workflows and processes should be integrated into ERP software to automate tasks, streamline operations, and improve efficiency. These may include:
- Risk assessments and mitigation plans.
- Internal control documentation and monitoring.
- Regulatory reporting and disclosures.
- Data security and privacy management.
- Incident and investigation management.
Data Management and Security
Data management and security are critical aspects of compliance for ERP software. Organizations must ensure that sensitive data is protected from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
ERP software can help organizations protect sensitive data by providing robust data encryption, access controls, and audit trails. These features help organizations comply with data privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Data Encryption
ERP software should encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that data is protected from unauthorized access even if it is intercepted.
Access Controls
ERP software should allow organizations to define fine-grained access controls to restrict who can access sensitive data. This helps prevent unauthorized users from accessing or modifying data.
Audit Trails
ERP software should provide audit trails that track all changes to sensitive data. This helps organizations identify any unauthorized access or modifications to data.
Reporting and Analytics
ERP software can generate comprehensive reports and provide advanced analytics to support compliance audits. These reports and analytics empower organizations to monitor their compliance posture effectively, identify potential risks, and demonstrate compliance to regulatory bodies.
Essential reports for compliance monitoring include:
- Compliance checklists and gap analysis reports: These reports provide a detailed overview of the organization’s compliance status against specific regulations and standards.
- Audit trail reports: These reports track all user activities within the ERP system, providing a comprehensive record of changes made to data and processes.
- Regulatory compliance reports: These reports summarize the organization’s compliance with specific regulations, such as SOX, HIPAA, and GDPR.
In addition to these reports, ERP software also provides analytics that can help organizations identify trends and patterns in their compliance data. This information can be used to improve compliance processes, reduce risks, and ensure ongoing compliance.
Types of Metrics for Compliance Monitoring
Key metrics for compliance monitoring include:
- Number of compliance incidents: This metric tracks the frequency of compliance violations, providing insights into the effectiveness of the organization’s compliance program.
- Time to resolution: This metric measures the average time it takes to resolve compliance incidents, indicating the efficiency of the organization’s response to compliance issues.
- Compliance costs: This metric tracks the financial impact of compliance activities, including the costs of audits, fines, and legal fees.
By monitoring these metrics, organizations can gain a clear understanding of their compliance performance and make informed decisions to improve their compliance posture.
Vendor Selection: ERP Software For Compliance
Selecting the right ERP software vendor is crucial for compliance success. Consider the following factors:
• Compliance Expertise:Assess the vendor’s understanding of industry regulations and their ability to translate them into software solutions.
• Industry Experience:Choose vendors with proven experience in your industry, ensuring they understand your specific compliance challenges.
• Product Capabilities:Evaluate the vendor’s ERP software’s compliance capabilities, including audit trails, automated compliance checks, and reporting tools.
• Customer Support:Ensure the vendor provides reliable support, including compliance-specific assistance and regular software updates.
• Implementation Expertise:Consider the vendor’s experience in implementing ERP software for compliance, ensuring a smooth and successful deployment.
Vendor Evaluation
- Request vendor demonstrations to see their software’s compliance capabilities in action.
- Conduct reference checks with existing customers to gather feedback on the vendor’s compliance expertise and support.
- Review the vendor’s documentation, including white papers and case studies, to assess their knowledge and experience in compliance.
Case Studies and Success Stories

ERP software for compliance has been instrumental in helping organizations achieve and maintain compliance with various regulatory requirements. Let’s delve into case studies of organizations that have successfully implemented ERP software for compliance.
Success Story: XYZ Corporation
XYZ Corporation, a global manufacturer, implemented an ERP system to streamline its compliance processes. The software automated regulatory reporting, improved data accuracy, and enhanced collaboration among compliance teams. As a result, XYZ Corporation reduced its compliance costs by 20% and improved its audit readiness.
Challenge Faced: Data Integration
During the implementation, XYZ Corporation faced challenges in integrating data from multiple legacy systems. The ERP software required a comprehensive data migration strategy to ensure data integrity and accuracy. The organization invested in data cleansing and mapping tools to facilitate a seamless data integration process.
Benefits Achieved: Improved Efficiency and Risk Management
After implementing the ERP software, XYZ Corporation experienced significant benefits. The automated workflows streamlined compliance tasks, freeing up compliance teams to focus on higher-value activities. The improved data accuracy and reporting capabilities enhanced the organization’s risk management processes, enabling proactive identification and mitigation of compliance risks.
Integration with Other Systems
ERP software integration with other systems is critical for comprehensive compliance management. It allows organizations to streamline data sharing, enhance visibility, and improve overall efficiency.Integrating ERP with customer relationship management (CRM) systems enables seamless customer data management. By centralizing customer interactions, organizations can track compliance obligations related to customer data privacy and protection regulations.
Integration with supply chain management systems ensures compliance with regulations governing supplier selection, procurement processes, and inventory management.
Challenges and Benefits of Integration
Challenges:
- Data compatibility and standardization across different systems
- Complexity of integrating legacy systems with modern ERP
- Ensuring data security and integrity during integration
Benefits:
- Improved data accuracy and consistency
- Enhanced visibility into compliance-related data across the organization
- Streamlined compliance processes and reduced manual effort
Future Trends
The future of ERP software for compliance is expected to be shaped by several emerging trends, including:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being increasingly used to automate compliance tasks, such as risk assessments, data analysis, and reporting. This can help organizations to improve the efficiency and accuracy of their compliance programs.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is becoming increasingly popular for ERP software, as it offers several benefits, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. This trend is expected to continue in the future, as more organizations move their ERP systems to the cloud.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way that organizations manage compliance. Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent records of compliance activities, which can help to improve accountability and reduce the risk of fraud.
Data Analytics
Data analytics is becoming increasingly important for compliance, as organizations need to be able to analyze large amounts of data to identify risks and trends. This trend is expected to continue in the future, as organizations invest in data analytics tools and technologies.
Cost and ROI

ERP software for compliance can involve significant upfront costs, but it can also provide substantial return on investment (ROI) over time. The ROI of ERP software for compliance is influenced by several factors, including the size and complexity of the organization, the industry in which it operates, and the specific compliance requirements that must be met.
The costs of implementing ERP software for compliance can be categorized into three main areas: software licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance costs. Software licensing fees vary depending on the size of the organization and the number of users who will be accessing the system.
Implementation costs include the costs of hardware, software installation, data migration, and training. Ongoing maintenance costs include the costs of software updates, support, and technical assistance.
Factors Influencing ROI
- Size and complexity of the organization:Larger organizations with more complex operations are likely to experience a higher ROI from ERP software for compliance, as they have more to gain from the efficiencies and cost savings that the software can provide.
- Industry:Organizations in highly regulated industries, such as healthcare or financial services, are more likely to benefit from ERP software for compliance, as they face more stringent compliance requirements.
- Compliance requirements:The more complex and comprehensive the compliance requirements that an organization must meet, the greater the potential ROI from ERP software for compliance.
- Implementation and ongoing costs:The costs of implementing and maintaining ERP software for compliance can vary significantly, so it is important to carefully evaluate the costs and benefits before making a decision.
Measuring the Benefits
The benefits of ERP software for compliance can be measured in several ways, including:
- Reduced compliance costs:ERP software for compliance can help organizations reduce compliance costs by automating compliance processes, reducing the need for manual labor, and improving the accuracy of compliance reporting.
- Improved compliance:ERP software for compliance can help organizations improve compliance by providing a centralized repository for compliance-related information, automating compliance processes, and providing real-time visibility into compliance status.
- Reduced risk:ERP software for compliance can help organizations reduce risk by providing a comprehensive view of compliance status, identifying and mitigating compliance risks, and providing early warning of potential compliance issues.
- Increased efficiency:ERP software for compliance can help organizations increase efficiency by automating compliance processes, reducing the need for manual labor, and improving the accuracy of compliance reporting.
- Improved decision-making:ERP software for compliance can help organizations make better decisions by providing real-time visibility into compliance status, identifying and mitigating compliance risks, and providing insights into compliance trends.
Table of ERP Software for Compliance
Choosing the right ERP software for compliance can be a daunting task. To help you make an informed decision, we have compiled a table that compares and contrasts different ERP software solutions based on their compliance capabilities.
The table includes columns for features, pricing, and industry focus. We hope this information will help you narrow down your choices and find the best ERP software for your needs.
Features
- Compliance management
- Risk management
- Audit management
- Data security
- Regulatory reporting
Pricing
- Subscription-based
- Perpetual license
- Cloud-based
- On-premise
Industry Focus
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Financial services
- Retail
- Government
Final Wrap-Up
By leveraging ERP software for compliance, organizations can gain a competitive edge in today’s regulatory environment. ERP software not only ensures compliance but also improves operational efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances stakeholder confidence. As businesses navigate the evolving compliance landscape, ERP software will continue to play a pivotal role in enabling organizations to achieve compliance and operational excellence.
FAQ Section
What are the key benefits of using ERP software for compliance?
ERP software for compliance offers numerous benefits, including automated compliance processes, reduced manual errors, improved data accuracy, enhanced stakeholder confidence, and increased operational efficiency.
How does ERP software help organizations comply with industry-specific regulations?
ERP software for compliance is designed to address industry-specific regulations by providing tailored features and modules that support compliance efforts. These features include industry-specific data models, pre-configured compliance workflows, and automated reporting capabilities.
What are the best practices for implementing ERP software for compliance?
Best practices for implementing ERP software for compliance include conducting a thorough needs assessment, selecting a vendor with robust compliance capabilities, and involving key stakeholders throughout the implementation process.