ERP software for reporting tools has emerged as a transformative solution, empowering organizations to harness the power of data for informed decision-making. These tools provide a comprehensive suite of capabilities that streamline reporting processes, enhance data visualization, and facilitate real-time insights.
With the increasing complexity of business operations, the need for robust reporting capabilities has become paramount. ERP software for reporting tools addresses this need by integrating seamlessly with core ERP systems, allowing organizations to extract, analyze, and present data from various sources in a cohesive and user-friendly manner.
ERP Software Overview: ERP Software For Reporting Tools
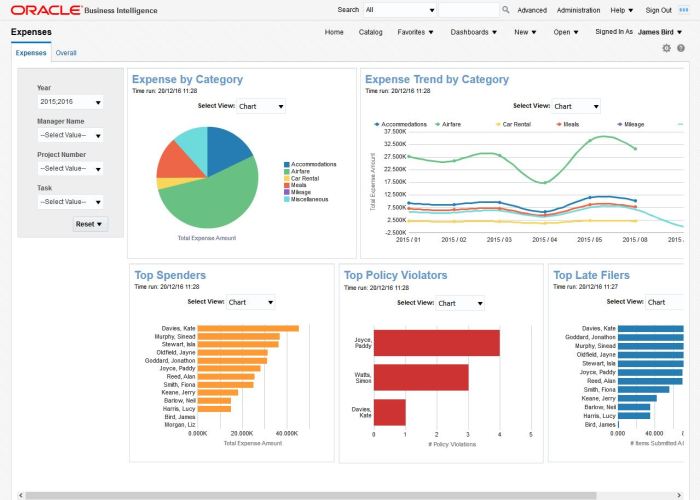
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive business management solution that integrates all facets of an organization’s operations into a single, unified system. It provides a centralized platform for managing core business processes, including finance, supply chain, manufacturing, human resources, and customer relationship management.
ERP systems offer numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy and consistency, streamlined business processes, increased operational efficiency, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. They enable organizations to gain a holistic view of their operations, identify areas for improvement, and respond more effectively to changing market conditions.
Key Modules in ERP Systems
ERP systems typically comprise several key modules, each designed to address specific functional areas of an organization:
- Financial Management:Manages financial transactions, including accounts payable, accounts receivable, general ledger, and financial reporting.
- Supply Chain Management:Optimizes the flow of goods and services throughout the supply chain, including procurement, inventory management, and logistics.
- Manufacturing:Supports manufacturing operations, including production planning, scheduling, and quality control.
- Human Resources:Manages employee information, including payroll, benefits, and performance management.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):Manages interactions with customers, including sales, marketing, and customer service.
Reporting Tools in ERP Systems
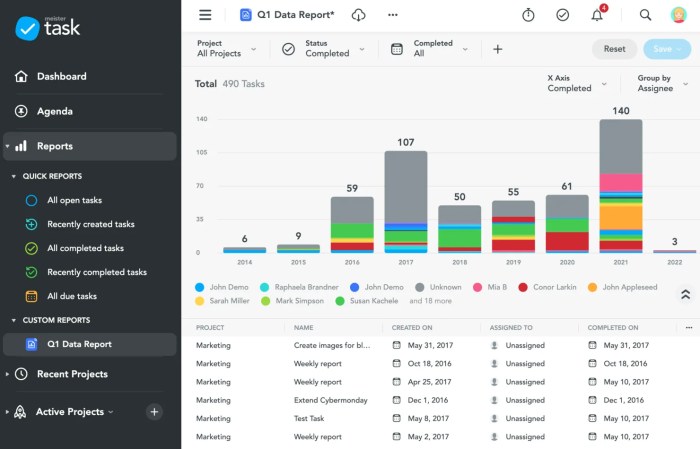
Reporting tools are an essential component of ERP software, enabling businesses to generate insightful reports that provide valuable information for decision-making. These tools allow users to extract, analyze, and present data from various modules within the ERP system, providing a comprehensive view of the organization’s operations.
ERP reporting tools offer a wide range of reporting capabilities, including:
Types of Reports
- Financial reports:Provide insights into the financial performance of the organization, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Operational reports:Track and analyze key operational metrics, such as production output, inventory levels, and customer orders.
- Compliance reports:Help businesses comply with regulatory requirements by generating reports on specific metrics or data points.
- Ad hoc reports:Allow users to create custom reports based on specific criteria or data sources.
Benefits of Using ERP Software for Reporting
ERP software provides numerous advantages for reporting purposes, streamlining the process and enhancing its effectiveness. These benefits include:
ERP reporting tools offer significant advantages over other methods, including:
Centralized Data
- Eliminates data duplication and inconsistencies by providing a single source of truth for all business data.
- Provides a comprehensive view of all aspects of the business, enabling informed decision-making.
Automated Reporting
- Saves time and effort by automating the generation of reports, freeing up resources for other tasks.
- Ensures accuracy and consistency by eliminating manual errors.
Real-Time Reporting
- Provides up-to-date information, allowing businesses to make timely decisions.
- Helps identify trends and patterns, enabling proactive planning.
Customizable Reporting
- Allows businesses to create reports tailored to their specific needs, ensuring relevance and usefulness.
- Provides flexibility to adjust reports as business requirements change.
Improved Collaboration
- Facilitates collaboration by providing a shared platform for reporting and analysis.
- Improves communication and alignment between different departments.
Increased Efficiency
- Streamlines reporting processes, reducing time and effort required for data collection, analysis, and presentation.
- Improves productivity by providing easy access to relevant information.
Enhanced Decision-Making
- Provides accurate and timely information, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Helps identify areas for improvement and optimize business processes.
Challenges of Using ERP Software for Reporting
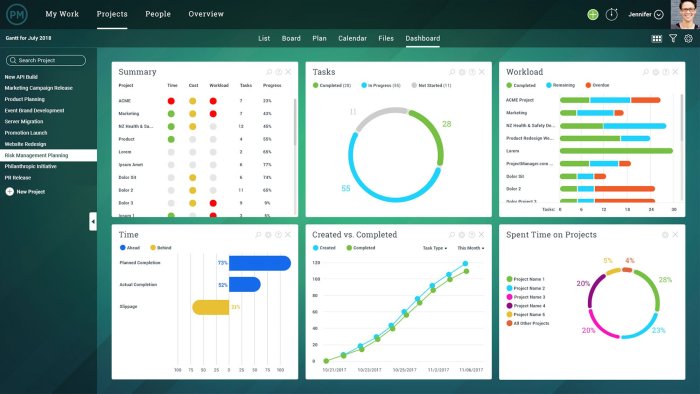
Implementing ERP software for reporting purposes presents several potential challenges for organizations. These include:
- Data Integration:ERP systems often integrate data from multiple sources, which can lead to data inconsistencies and inaccuracies. Ensuring data quality and consistency is crucial for accurate reporting.
- Data Security:ERP systems store sensitive financial and operational data, making data security a top concern. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- User Adoption:Successful implementation of ERP software for reporting requires user adoption. Training users on the new system and ensuring they understand its benefits are essential for maximizing its effectiveness.
- Cost and Complexity:ERP software can be expensive to implement and maintain. Organizations should carefully evaluate the costs and complexity of the implementation process before making a decision.
- Reporting Flexibility:ERP systems may not provide the level of reporting flexibility required by some organizations. Customizing reports or creating new ones may require additional resources and expertise.
Overcoming Challenges
Organizations can overcome these challenges by implementing the following strategies:
- Data Management:Establish clear data management policies and procedures to ensure data quality and consistency. Implement data validation and cleansing processes to identify and correct errors.
- Security Measures:Implement robust security measures such as access controls, encryption, and regular security audits to protect data from unauthorized access.
- User Training and Support:Provide comprehensive user training and support to ensure users understand the system’s functionality and benefits. Foster a culture of user adoption and feedback.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis:Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the potential return on investment before implementing ERP software for reporting.
- Customization Options:Explore customization options to enhance reporting flexibility. Consider third-party reporting tools or custom development to meet specific reporting requirements.
Best Practices for Using ERP Software for Reporting
Effective reporting using ERP software requires careful design and execution. Here are some best practices to ensure optimal results:
Design Considerations:
- Define Report Objectives:Clearly identify the purpose and audience for each report.
- Use Appropriate Data Sources:Ensure that reports are based on accurate and relevant data from the ERP system.
- Design User-Friendly Reports:Create reports that are visually appealing, easy to navigate, and present data in a concise and meaningful way.
Performance and Usability Optimization:
- Optimize Report Queries:Use efficient database queries to minimize report generation time.
- Use Caching Mechanisms:Implement caching to improve report performance for frequently accessed reports.
- Provide Interactive Features:Allow users to filter, sort, and drill down into data to enhance usability.
Comparison of ERP Software for Reporting
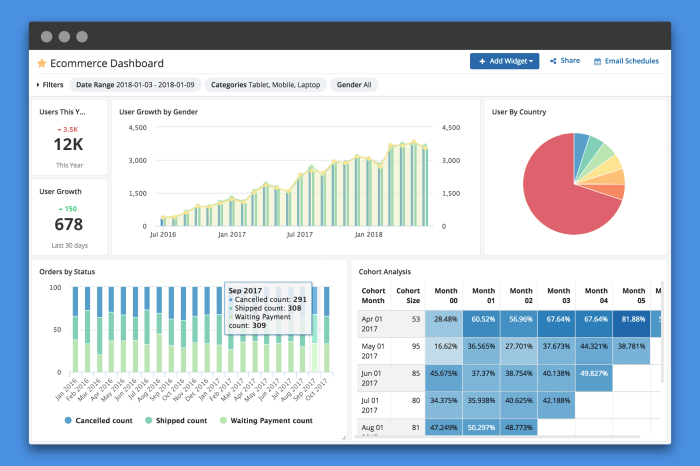
ERP systems provide a range of reporting capabilities to support decision-making and improve business performance. However, the specific features and strengths of these capabilities vary across different vendors. The following table compares several ERP software vendors based on their reporting capabilities:
| Vendor | Key Features | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP | – Comprehensive reporting suite
|
– Market leader with a wide range of reporting capabilities
|
|
| Oracle NetSuite | – Cloud-based reporting platform
|
– Scalable solution for small to mid-sized businesses
|
|
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | – Integration with Microsoft Office Suite
|
– Strong integration with other Microsoft products
|
|
| Infor | – Industry-specific reporting templates
|
– Strong focus on industry-specific reporting needs
|
|
| Epicor | – Cloud-based and on-premise deployment options
|
– Flexible reporting solution for various industries
|
The choice of ERP software for reporting depends on the specific requirements and budget of the organization. It is important to evaluate the key features, strengths, and weaknesses of different vendors to select the solution that best meets the business needs.
Case Studies of ERP Software for Reporting
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented ERP software for reporting, reaping significant benefits. Here are a few case studies highlighting their challenges and achievements:
Acme Corporation, ERP software for reporting tools
Acme Corporation, a manufacturing company, faced challenges with fragmented reporting systems and data inconsistencies. By implementing an ERP system, they centralized their data and streamlined their reporting processes, resulting in improved data accuracy, faster reporting times, and enhanced decision-making.
XYZ Healthcare
XYZ Healthcare, a healthcare provider, struggled with manual reporting processes that were time-consuming and error-prone. With an ERP system, they automated their reporting, saving time and resources. Additionally, they gained real-time visibility into their operations, enabling them to identify and address inefficiencies.
Future Trends in ERP Software for Reporting
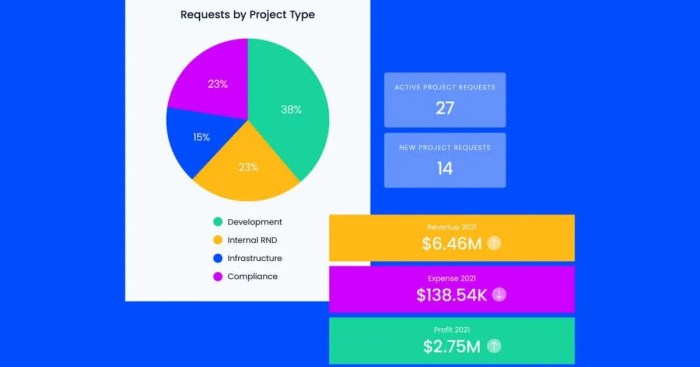
The future of ERP reporting is expected to be shaped by emerging technologies and innovations, such as:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML):AI and ML algorithms can automate many reporting tasks, such as data collection, analysis, and visualization. This can free up time for accountants and other financial professionals to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Cloud computing:Cloud-based ERP systems offer several benefits for reporting, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud-based ERP systems can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, which makes it easy for accountants and other financial professionals to access the data they need, when they need it.
- Real-time reporting:Real-time reporting provides accountants and other financial professionals with up-to-date information on the financial performance of their organization. This information can be used to make better decisions and identify potential problems early on.
- Data visualization:Data visualization tools can help accountants and other financial professionals to understand complex data more easily. Data visualization tools can create charts, graphs, and other visual representations of data, which can make it easier to identify trends and patterns.
Tips for Selecting ERP Software for Reporting
Organizations considering implementing ERP software for reporting should carefully evaluate their specific needs and requirements. Key factors to consider during the selection process include:
- Data integration capabilities:The ERP software should seamlessly integrate with other business systems to ensure accurate and up-to-date reporting.
- Reporting flexibility and customization:The software should provide robust reporting capabilities that allow users to create customized reports based on their specific requirements.
- Real-time reporting capabilities:For organizations that require real-time insights, the ERP software should provide real-time reporting functionality.
- Security and data protection:The ERP software should meet industry-standard security measures to protect sensitive financial and operational data.
- Scalability:The software should be scalable to meet the growing reporting needs of the organization.
- Vendor support and training:The vendor should provide reliable support and training to ensure successful implementation and ongoing use of the ERP software.
Conclusion
ERP software plays a pivotal role in enhancing an organization’s reporting capabilities. It streamlines data integration, automates reporting processes, and provides real-time insights to support informed decision-making.
By leveraging ERP software for reporting, organizations can reap numerous benefits, including improved accuracy and consistency, reduced reporting time and effort, enhanced data security, and the ability to generate comprehensive and customizable reports.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, ERP software for reporting tools has revolutionized the way organizations leverage data for strategic decision-making. By providing comprehensive reporting capabilities, enhanced data visualization, and real-time insights, these tools empower businesses to gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven landscape.
Quick FAQs
What are the key benefits of using ERP software for reporting?
ERP software for reporting offers numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy, enhanced data visualization, streamlined reporting processes, real-time insights, and reduced reporting costs.
What are the common challenges faced when using ERP software for reporting?
Organizations may encounter challenges such as data integration issues, complex report design, and the need for specialized expertise. However, these challenges can be overcome through proper planning, data governance, and training.
How can organizations select the best ERP software for reporting?
Organizations should consider factors such as reporting capabilities, data integration capabilities, ease of use, vendor support, and cost when selecting ERP software for reporting.