ERP software for analytics tools has emerged as a transformative solution for businesses seeking to leverage their data for informed decision-making. This powerful combination empowers organizations to seamlessly integrate data from various sources, perform robust data analysis, and generate insightful reports that drive strategic planning and operational efficiency.
With advanced data management capabilities, ERP software ensures the accuracy, consistency, and security of data, providing a reliable foundation for meaningful analysis. By harnessing the power of ERP software for analytics, businesses can gain a competitive edge, optimize their operations, and achieve data-driven success.
Introduction to ERP Software for Analytics Tools
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a comprehensive business management system that integrates various functional areas of an organization, including finance, supply chain management, manufacturing, and human resources. In the context of data analysis, ERP software plays a crucial role by providing a centralized repository of data from across the organization.
This data can then be leveraged for analytics purposes, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights into their operations and make informed decisions.
Benefits of Using ERP Software for Analytics
- Improved Data Accuracy and Consistency:ERP systems enforce data integrity and consistency by ensuring that data is entered and stored in a standardized format. This eliminates data inconsistencies and errors, resulting in more accurate and reliable data for analysis.
- Real-Time Data Access:ERP software provides real-time access to operational data, allowing businesses to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and make timely adjustments as needed. This real-time visibility enables businesses to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer demands.
- Comprehensive Data Analysis:ERP systems offer a wide range of analytical tools and reporting capabilities that enable businesses to perform in-depth data analysis. These tools allow businesses to explore data from multiple perspectives, identify trends, and uncover hidden patterns.
- Enhanced Decision-Making:By providing access to accurate, real-time, and comprehensive data, ERP software empowers businesses to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. This leads to improved operational efficiency, increased profitability, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Key Features of ERP Software for Analytics

ERP software for analytics offers a comprehensive suite of features that empower businesses to harness data and derive actionable insights. These features include:
Data Integration and Management: ERP systems seamlessly integrate data from disparate sources, providing a unified view of business operations. This eliminates data silos and ensures consistency and accuracy for analytics.
Advanced Reporting and Visualization
- ERP software provides robust reporting capabilities, enabling businesses to create customized reports and dashboards. These reports can be easily filtered and manipulated to extract meaningful insights.
- Advanced visualization tools, such as charts, graphs, and maps, help users quickly identify trends, patterns, and outliers in data.
Predictive Analytics
ERP systems incorporate predictive analytics capabilities, leveraging historical data and statistical models to forecast future outcomes. This enables businesses to anticipate trends, optimize operations, and make informed decisions.
Data Mining
ERP software includes data mining tools that allow businesses to uncover hidden patterns and relationships within large datasets. This helps identify new opportunities, optimize processes, and gain a competitive edge.
Real-Time Analytics, ERP software for analytics tools
Modern ERP systems offer real-time analytics capabilities, providing businesses with up-to-date insights into their operations. This enables quick decision-making and proactive response to changing market conditions.
These key features of ERP software for analytics empower businesses to leverage data effectively, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive advantage in today’s data-driven market.
Data Integration and Management
ERP software acts as a central repository for data from various sources, including disparate business systems, spreadsheets, and external data sources. This data integration capability enables businesses to have a comprehensive view of their operations and make informed decisions based on real-time information.The data management capabilities of ERP software include data cleansing, transformation, and standardization.
Data cleansing involves removing duplicate or inaccurate data, while data transformation converts data into a consistent format that can be easily analyzed. Data standardization ensures that data from different sources is represented using the same units, formats, and definitions, enabling seamless integration and analysis.
Data Warehousing
ERP software often includes a data warehousing component that stores historical data for analysis and reporting purposes. Data warehousing allows businesses to track trends, identify patterns, and perform predictive analytics. The data warehouse is typically separate from the operational database, ensuring that the performance of the ERP system is not affected by data analysis activities.
Data Analysis and Reporting
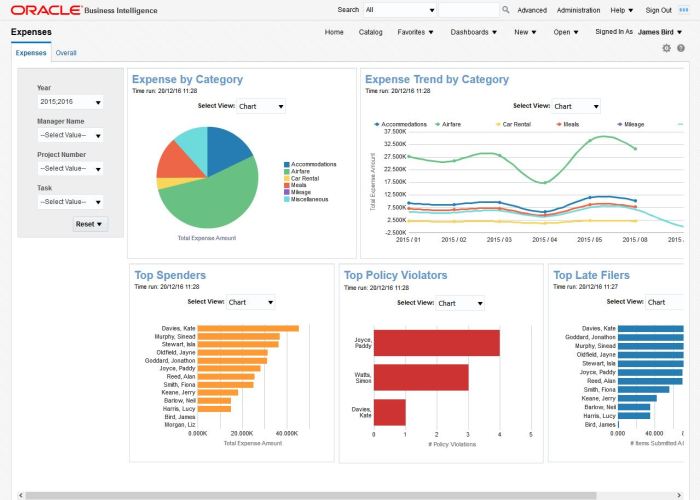
ERP software provides comprehensive data analysis capabilities, enabling businesses to extract meaningful insights from their data. This empowers them to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive advantage.
ERP software facilitates the reporting and visualization of data, making it easy for users to understand complex information. This can include interactive dashboards, customizable reports, and drill-down capabilities that allow users to explore data in detail.
Types of Data Analysis
- Descriptive Analytics:Summarizes historical data to provide insights into past performance.
- Diagnostic Analytics:Examines data to identify the root causes of issues and trends.
- Predictive Analytics:Uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to forecast future outcomes.
- Prescriptive Analytics:Provides recommendations and actions based on data analysis, enabling businesses to make optimal decisions.
Industry-Specific Analytics
ERP software for analytics offers valuable insights for various industries, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and improve their operations.Industries that particularly benefit from ERP software for analytics include:
- Manufacturing:Track production efficiency, optimize supply chain management, and predict demand.
- Retail:Analyze customer behavior, manage inventory levels, and forecast sales trends.
- Healthcare:Monitor patient outcomes, streamline administrative processes, and improve resource allocation.
- Financial Services:Assess risk, manage compliance, and optimize investment strategies.
- Education:Track student performance, identify learning gaps, and improve curriculum development.
Integration with Business Intelligence (BI) Tools
ERP software can be integrated with BI tools to provide a comprehensive view of business data. BI tools allow users to analyze data from multiple sources, create reports, and identify trends. By integrating ERP software with BI tools, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their operations and make more informed decisions.
Benefits of Integrating ERP Software with BI Tools
- Improved data visibility and accessibility
- Enhanced data analysis capabilities
- Increased operational efficiency
- Improved decision-making
- Competitive advantage
Data Security and Compliance

ERP software places a high priority on data security to protect sensitive business information from unauthorized access, theft, or misuse. It implements robust security measures to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
ERP software also assists businesses in complying with various data regulations and standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). It provides features that enable businesses to track data usage, manage user permissions, and implement data encryption to meet compliance requirements.
Data Encryption
ERP software utilizes encryption algorithms to protect data at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Access Controls
ERP software allows businesses to define user roles and permissions, restricting access to sensitive data only to authorized personnel. It also provides audit trails to track user activities and identify any suspicious or unauthorized access attempts.
Data Backup and Recovery
ERP software typically includes data backup and recovery mechanisms to protect against data loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. It ensures that data can be quickly restored in the event of an incident.
Cloud-Based ERP Software for Analytics

Cloud-based ERP software for analytics offers several advantages over on-premises solutions. These benefits include:
- Reduced costs: Cloud-based ERP software is typically more affordable than on-premises solutions, as there is no need to purchase and maintain hardware or software.
- Increased flexibility: Cloud-based ERP software can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it ideal for businesses with remote employees or multiple locations.
- Improved scalability: Cloud-based ERP software can be easily scaled up or down to meet the changing needs of a business.
- Enhanced security: Cloud-based ERP software providers typically have robust security measures in place to protect data.
When choosing a cloud-based ERP solution for analytics, businesses should consider the following factors:
- The size of the business
- The industry in which the business operates
- The specific analytics needs of the business
- The budget of the business
Implementation and Best Practices
Implementing ERP software for analytics requires careful planning and execution. Follow these steps to ensure a successful implementation:
- Define clear objectives: Determine the specific goals you want to achieve with ERP software analytics, such as improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, or enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Choose the right software: Select an ERP software solution that aligns with your business needs and provides robust analytics capabilities. Consider factors such as industry-specific features, scalability, and integration options.
- Establish a data governance framework: Implement policies and procedures for data collection, storage, and usage to ensure data integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Train users: Provide comprehensive training to users on how to use the ERP software analytics tools effectively. This includes data analysis techniques, report generation, and interpretation of results.
- Monitor and evaluate performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your ERP software analytics system and make adjustments as needed to optimize data analysis and reporting.
In addition to these implementation steps, follow these best practices to optimize data analysis with ERP software:
- Use a data-driven approach: Base your analysis on accurate and reliable data from your ERP system. This ensures that your insights are grounded in real-time business information.
- Leverage advanced analytics techniques: Utilize advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and predictive modeling, to uncover hidden patterns and trends in your data. This enables you to make more informed decisions and improve business outcomes.
- Foster a culture of data-driven decision-making: Encourage employees to use data and analytics to inform their decisions. This creates a data-centric culture that drives continuous improvement and innovation.
- Integrate ERP analytics with other business systems: Connect your ERP software analytics with other business systems, such as CRM and supply chain management, to gain a holistic view of your operations. This enables you to identify cross-functional opportunities and make more informed decisions.
- Stay updated on the latest trends: Keep abreast of the latest advancements in ERP software analytics and data analysis techniques. This ensures that you are leveraging the most effective tools and approaches to optimize your business performance.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Organizations worldwide have leveraged ERP software for analytics to enhance their decision-making capabilities and achieve significant benefits. Here are a few notable case studies:
Manufacturing Company
- Company:XYZ Manufacturing
- Industry:Manufacturing
- Challenge:Lack of real-time data visibility and inefficient reporting
- Solution:Implemented an ERP system with robust analytics capabilities
- Benefits:
- Improved production efficiency by 15%
- Reduced inventory costs by 10%
- Enhanced customer satisfaction through faster order fulfillment
Retail Company
- Company:ABC Retail
- Industry:Retail
- Challenge:Difficulty in analyzing customer behavior and forecasting demand
- Solution:Integrated ERP software with advanced analytics tools
- Benefits:
- Increased sales revenue by 8%
- Optimized inventory levels, reducing stockouts by 20%
- Improved customer loyalty through personalized marketing campaigns
Future Trends and Innovations
ERP software for analytics is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. Some of the emerging trends in this space include:
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML):AI and ML are being used to automate data analysis tasks, such as data cleansing, feature engineering, and model building. This can free up analysts to focus on more strategic tasks, such as interpreting results and making decisions.
- Natural language processing (NLP):NLP is being used to make ERP software more user-friendly. For example, analysts can now use natural language queries to access data and generate reports.
- Cloud-based ERP software:Cloud-based ERP software is becoming increasingly popular because it offers several advantages, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Data visualization:Data visualization tools are becoming more sophisticated, making it easier for analysts to visualize and understand data. This can help analysts to identify trends and patterns that would otherwise be difficult to spot.
- Prescriptive analytics:Prescriptive analytics is a type of analytics that can help businesses to make better decisions. Prescriptive analytics tools use data to identify the best course of action in a given situation.
Innovative Technologies
Several innovative technologies are shaping the future of data analysis with ERP software. These technologies include:
- Blockchain:Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that can be used to create secure and transparent data sharing networks. This can be beneficial for businesses that need to share data with partners or customers.
- Edge computing:Edge computing is a type of computing that takes place at the edge of the network, closer to the devices that are generating data. This can reduce latency and improve performance for data-intensive applications.
- Quantum computing:Quantum computing is a new type of computing that has the potential to revolutionize data analysis. Quantum computers can perform calculations that are impossible for traditional computers, which could lead to new breakthroughs in data analysis.
Last Recap: ERP Software For Analytics Tools
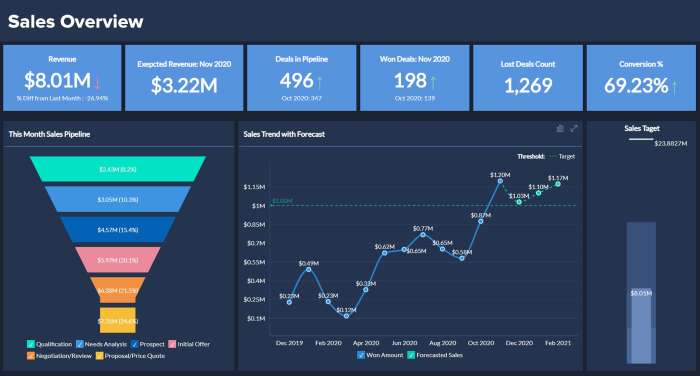
In conclusion, ERP software for analytics tools has revolutionized the way businesses approach data analysis. Its comprehensive features, seamless data integration, robust reporting capabilities, and industry-specific applications make it an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to unlock the full potential of their data.
As the future of data analysis continues to evolve, ERP software will remain at the forefront, empowering businesses with the insights they need to thrive in an increasingly data-driven world.
Top FAQs
What are the benefits of using ERP software for analytics?
ERP software for analytics offers numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy and consistency, enhanced data visibility, streamlined reporting, and support for industry-specific analytics.
How does ERP software integrate data from various sources?
ERP software utilizes data integration tools and connectors to seamlessly extract data from disparate systems, ensuring a comprehensive and consolidated view of all relevant data.
What types of data analysis can be performed with ERP software?
ERP software supports a wide range of data analysis techniques, including descriptive analysis, predictive analysis, and prescriptive analysis, enabling businesses to gain actionable insights from their data.