What is an ERP system and how does it work? This is a question that many businesses ask as they seek to improve their efficiency and effectiveness. ERP systems, or Enterprise Resource Planning systems, are software applications that integrate all aspects of a business into a single, unified system.
This allows businesses to have a complete view of their operations and to make better decisions.
In this article, we will explore what ERP systems are, how they work, and the benefits they can provide to businesses. We will also discuss the challenges of ERP implementation and how to overcome them.
Definition of ERP Systems
ERP is an acronym for Enterprise Resource Planning. It refers to a software system that integrates various business processes and functions into a single, unified system. ERP systems aim to improve operational efficiency, streamline processes, and provide real-time data and insights across the organization.
Core Purpose and Objectives
The core purpose of ERP systems is to provide a centralized platform for managing and integrating key business processes, such as:
- Financial management
- Supply chain management
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Human resource management (HRM)
- Manufacturing and production
By integrating these processes, ERP systems help organizations to:
- Improve communication and collaboration across departments
- Enhance data accuracy and consistency
- Streamline operations and reduce costs
- Gain real-time visibility into business performance
- Make informed decisions based on data-driven insights
Key Components of ERP Systems: What Is An ERP System And How Does It Work?
ERP systems comprise various interconnected modules that perform specialized functions within an organization. These modules enable seamless data integration and communication across different departments, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making.
The key modules commonly found in ERP systems include:
Finance
- General Ledger:Tracks and records financial transactions, providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial health.
- Accounts Payable:Manages payments to vendors, ensuring timely processing and accurate record-keeping.
- Accounts Receivable:Handles customer invoicing, payment tracking, and credit management.
- Fixed Assets:Tracks and depreciates fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment.
Manufacturing
- Production Planning:Schedules and manages production processes, optimizing resource allocation and minimizing waste.
- Material Management:Controls inventory levels, ensures availability of raw materials, and tracks work-in-progress.
- Quality Control:Monitors and maintains product quality standards throughout the manufacturing process.
- Plant Maintenance:Manages equipment maintenance, ensuring uptime and minimizing downtime.
Human Resources
- Payroll:Calculates and processes employee salaries, deductions, and benefits.
- Benefits Administration:Manages employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off.
- Time and Attendance:Tracks employee work hours, overtime, and absences.
- Talent Management:Supports employee recruitment, performance evaluation, and career development.
Sales and Marketing
- Sales Order Management:Processes customer orders, tracks order status, and manages inventory allocation.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM):Stores and manages customer data, tracks interactions, and supports sales and marketing activities.
- Marketing Campaign Management:Plans, executes, and analyzes marketing campaigns to generate leads and drive sales.
- Pricing and Quoting:Automates pricing and quote generation, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
Supply Chain Management
- Procurement:Manages supplier relationships, negotiates contracts, and tracks purchase orders.
- Inventory Management:Optimizes inventory levels, minimizes waste, and ensures product availability.
- Warehouse Management:Controls warehouse operations, including receiving, storing, and shipping of goods.
- Transportation Management:Plans and executes the transportation of goods, optimizing routes and reducing costs.
Business Intelligence and Reporting
- Data Warehouse:Centralizes data from multiple sources, enabling comprehensive analysis and reporting.
- Reporting and Analytics:Generates reports, dashboards, and visualizations to support decision-making and performance monitoring.
- Query and Ad Hoc Reporting:Allows users to create custom reports and queries to access specific data insights.
- Performance Management:Tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) and provides insights into organizational performance.
These modules work together seamlessly to provide a holistic view of an organization’s operations, enabling real-time data sharing, improved communication, and enhanced decision-making. ERP systems play a crucial role in streamlining processes, reducing redundancies, and driving organizational efficiency and growth.
Benefits of ERP Systems
ERP systems offer numerous advantages to businesses, ranging from enhanced efficiency to improved decision-making.
One of the key benefits of ERP systems is their ability to streamline operations. By integrating all business functions into a single platform, ERP systems eliminate the need for manual data entry and reduce the risk of errors. This can lead to significant time and cost savings, as well as improved accuracy.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
ERP systems facilitate collaboration and communication between different departments within a business. By providing a centralized platform for data sharing, ERP systems break down silos and enable teams to work together more effectively. This can lead to improved decision-making, as well as faster and more efficient project completion.
Improved Decision-Making
ERP systems provide businesses with a wealth of data that can be used to make informed decisions. By analyzing data from all areas of the business, ERP systems can help businesses identify trends, spot opportunities, and make better decisions about resource allocation, product development, and marketing strategies.
Challenges of ERP Implementation
ERP implementation projects are complex and challenging, and businesses may encounter various obstacles along the way. These challenges can range from technical difficulties to organizational resistance and can significantly impact the project’s timeline, budget, and overall success.
It is crucial for businesses to be aware of these potential challenges and develop strategies to mitigate their impact. By addressing these challenges proactively, businesses can increase their chances of a successful ERP implementation.
Technical Challenges
- Data Integration:ERP systems require the integration of data from multiple sources, which can be complex and time-consuming. Data inconsistencies, redundancies, and errors can arise during this process, leading to inaccurate reporting and decision-making.
- System Complexity:ERP systems are comprehensive and complex, requiring extensive customization and configuration to meet specific business needs. This complexity can make it difficult to implement and maintain the system effectively.
- Compatibility Issues:ERP systems may not be compatible with existing legacy systems, leading to integration challenges and data loss. Compatibility issues can also arise when integrating with third-party applications.
Organizational Challenges
- Resistance to Change:ERP implementation often requires significant changes in business processes and workflows. Employees may resist these changes due to fear of the unknown or disruption to their daily routines.
- Lack of User Adoption:If users do not understand or embrace the new ERP system, its adoption and utilization may be low. This can hinder the realization of the system’s full benefits.
- Inadequate Training:Proper training is essential for users to effectively utilize the ERP system. Insufficient training can lead to errors, inefficiencies, and frustration among users.
Strategies for Mitigating Challenges
- Thorough Planning:Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the organization’s needs, processes, and resources before embarking on the ERP implementation. This will help identify potential challenges and develop strategies to address them.
- Data Management:Establish a robust data management strategy to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and integrity throughout the implementation process.
- Change Management:Develop a comprehensive change management plan to address resistance to change and ensure a smooth transition to the new ERP system.
- User Training:Provide comprehensive training to all users, ensuring they understand the system’s functionality and benefits. Address their concerns and provide ongoing support to foster adoption.
- Phased Implementation:Implement the ERP system in phases to minimize disruption and allow for gradual adaptation by users.
Types of ERP Systems
ERP systems can be categorized into three main types based on their deployment model: on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid.
Each type offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial for businesses to carefully consider their specific needs and requirements when selecting an ERP system.
On-Premise ERP Systems
- Deployed and managed on the company’s own servers within their physical infrastructure.
- Provides complete control and customization over the system, allowing businesses to tailor it to their unique requirements.
- Requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and IT resources for implementation and maintenance.
- Offers higher security and data privacy as the data is stored locally within the company’s network.
Cloud-Based ERP Systems
- Hosted and managed by a third-party provider over the internet, eliminating the need for on-premise infrastructure.
- Typically offered as a subscription-based service, providing flexibility and scalability.
- Lower upfront costs compared to on-premise systems, with ongoing subscription fees.
- May have limited customization options and data security concerns, as data is stored on the provider’s servers.
Hybrid ERP Systems
- A combination of on-premise and cloud-based components, allowing businesses to customize and integrate specific modules on-premise while leveraging cloud-based services for others.
- Offers flexibility and scalability while maintaining control over critical data and processes.
- Requires careful planning and integration to ensure seamless operation and data security.
- May involve higher implementation costs and ongoing maintenance efforts.
Integration with Other Systems
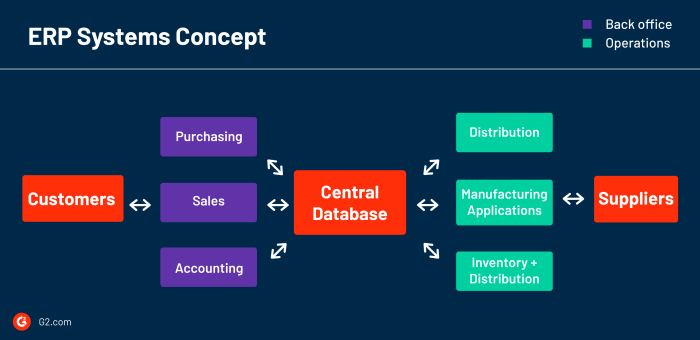
ERP systems are designed to integrate with other business systems, such as customer relationship management (CRM) and supply chain management (SCM) systems. This integration allows businesses to have a single, centralized view of their data, which can improve efficiency and decision-making.
There are many benefits to ERP integration. For example, integrated ERP systems can:
- Improve customer service by providing a complete view of customer interactions.
- Increase efficiency by eliminating duplicate data entry and streamlining processes.
- Improve decision-making by providing real-time data on business performance.
However, there are also some considerations to keep in mind when integrating ERP systems. For example, it is important to ensure that the systems are compatible and that the data is accurate and consistent. Additionally, it is important to have a plan for managing the integration process and for training employees on the new system.
Integration with CRM Systems
ERP systems can integrate with CRM systems to provide a complete view of customer interactions. This integration can help businesses to:
- Track customer interactions across all channels.
- Identify and target potential customers.
- Provide personalized customer service.
Integration with SCM Systems
ERP systems can integrate with SCM systems to provide a complete view of the supply chain. This integration can help businesses to:
- Track inventory levels.
- Manage supplier relationships.
- Optimize logistics and transportation.
Customization and Scalability
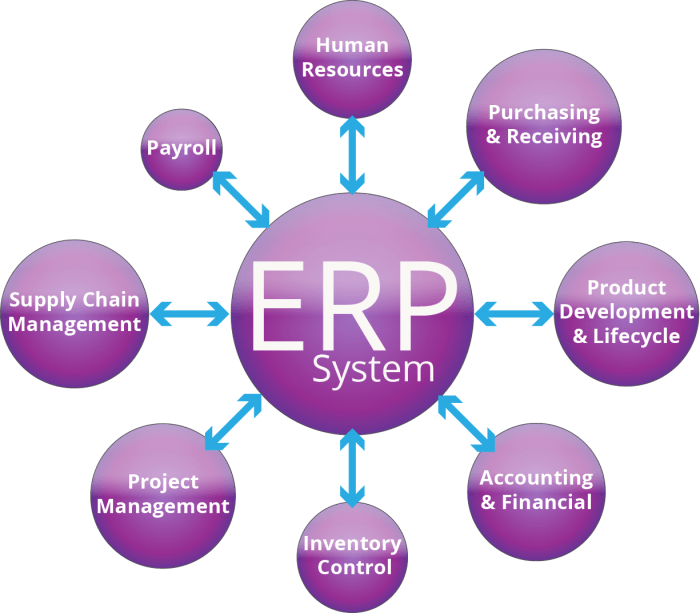
ERP systems offer customization options to tailor them to specific business needs. Businesses can modify data fields, workflows, and user interfaces to align with their unique processes and requirements. This customization ensures that the ERP system effectively supports the organization’s operations and meets its specific goals.ERP systems are designed to be scalable, allowing businesses to accommodate growth and changing requirements.
As the business expands, the ERP system can be scaled up to handle increased data volumes, users, and transactions. This scalability ensures that the ERP system remains a valuable tool throughout the business’s growth journey, adapting to evolving needs and providing a solid foundation for future expansion.
Customization Options
* Data fields can be customized to capture and store data specific to the business, such as industry-specific attributes or unique product characteristics.
- Workflows can be tailored to automate business processes, streamline operations, and enforce business rules.
- User interfaces can be personalized to provide tailored views, easy access to relevant information, and role-based dashboards.
Scalability Features
* Modular architecture allows businesses to add or remove modules as needed, providing flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
- Cloud-based ERP systems offer scalability on demand, enabling businesses to adjust their system capacity based on usage and growth.
- Open APIs facilitate integration with other systems and applications, allowing businesses to extend the functionality of their ERP system as needed.
Return on Investment (ROI)
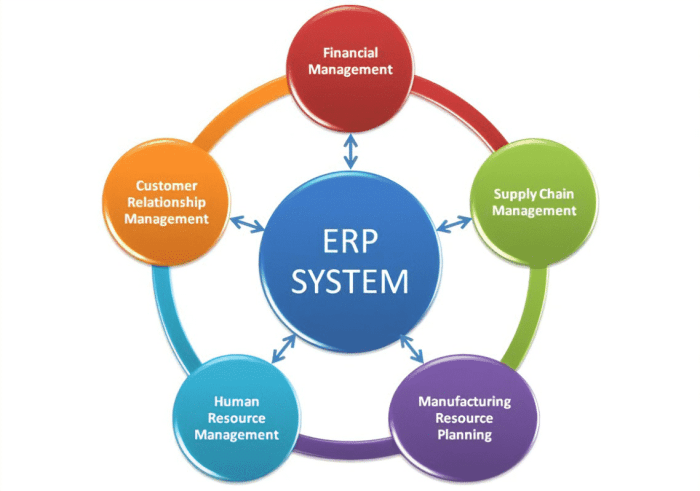
ERP systems can deliver a substantial return on investment (ROI) for businesses. The benefits of ERP systems, such as improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased profitability, can lead to a positive ROI within a relatively short period of time.One of the most significant benefits of ERP systems is their ability to improve operational efficiency.
By streamlining processes and eliminating redundancies, ERP systems can help businesses reduce their operating costs. For example, a study by Aberdeen Group found that businesses that implemented ERP systems experienced a 20% reduction in operating costs.ERP systems can also help businesses increase their profitability by improving sales and marketing efforts.
By providing a single, integrated view of customer data, ERP systems can help businesses identify and target new customers. Additionally, ERP systems can help businesses track sales and marketing campaigns, which can help them improve their ROI.
Case Studies
There are numerous case studies of businesses that have achieved positive ROI through ERP implementation. For example, the clothing retailer Gap Inc. implemented an ERP system in 2006. The system helped Gap Inc. to reduce its operating costs by 10% and increase its sales by 5%.Another example is the manufacturing company Caterpillar Inc.
Caterpillar implemented an ERP system in 2000. The system helped Caterpillar to reduce its inventory costs by 20% and increase its production efficiency by 15%.
Trends and Innovations in ERP Systems

The ERP industry is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These advancements are driven by the need for businesses to become more efficient, agile, and data-driven. In this section, we will discuss some of the latest technologies and advancements that are shaping the future of ERP systems.
Cloud-based ERP
Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on a remote server and accessed over the internet. This offers several advantages over on-premises ERP systems, including lower upfront costs, greater flexibility, and easier scalability. Cloud-based ERP systems are also more likely to be updated with the latest features and functionality, ensuring that businesses can always take advantage of the latest advancements.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are being used to automate a variety of tasks within ERP systems, such as data entry, forecasting, and fraud detection. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks, and it can also help businesses to improve their efficiency and accuracy.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that is being used to create secure and transparent supply chains. This can help businesses to track the movement of goods and services, and it can also help to prevent fraud.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT devices are being used to collect data from a variety of sources, such as sensors, machines, and vehicles. This data can be used to improve the efficiency of ERP systems, and it can also help businesses to make better decisions.
Digital twins
Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, such as buildings, factories, and equipment. These digital twins can be used to simulate different scenarios and test new ideas, which can help businesses to reduce risk and improve their operations.
Case Studies and Success Stories
ERP systems have transformed business operations for numerous organizations. To showcase their effectiveness, we present case studies and success stories of businesses that have successfully implemented ERP systems, highlighting the challenges they faced and the benefits they achieved.
Nike
- Challenges:Fragmented data, inefficient supply chain, and lack of real-time visibility.
- Benefits:Improved inventory management, streamlined supply chain, increased sales, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
SAP SE
- Challenges:Complex and diverse business processes, global operations, and need for scalability.
- Benefits:Reduced costs, improved efficiency, increased agility, and enhanced collaboration.
Coca-Cola
- Challenges:Global presence, diverse product portfolio, and complex supply chain.
- Benefits:Improved demand planning, optimized production, enhanced customer service, and increased profitability.
These case studies demonstrate the transformative impact ERP systems can have on businesses, addressing challenges, streamlining operations, and delivering tangible benefits.
Implementation Considerations

ERP implementation can be a complex and challenging process, but it can also be highly rewarding. By following a comprehensive checklist and considering the key steps and factors involved, businesses can increase their chances of success.
Here is a comprehensive checklist for businesses considering ERP implementation:
Assess Business Needs
- Identify the specific business processes that need to be improved.
- Determine the desired outcomes of the ERP implementation.
- Develop a clear understanding of the business’s current IT infrastructure and capabilities.
Select an ERP Vendor, What is an ERP system and how does it work?
- Research different ERP vendors and their products.
- Request demos and references from potential vendors.
- Select a vendor that has a strong track record of success in your industry.
Plan the Implementation
- Develop a detailed implementation plan that includes timelines, budgets, and resources.
- Identify the key stakeholders who will be involved in the implementation.
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders and get their buy-in.
Implement the ERP System
- Follow the implementation plan and make necessary adjustments as needed.
- Train users on the new system and provide ongoing support.
- Monitor the system’s performance and make necessary adjustments.
Evaluate the Implementation
- Track the progress of the implementation and measure the results against the desired outcomes.
- Identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
- Communicate the results of the evaluation to stakeholders.
Final Wrap-Up
ERP systems are a powerful tool that can help businesses improve their efficiency, effectiveness, and profitability. However, it is important to carefully consider the challenges of ERP implementation before making a decision. By understanding the benefits and challenges of ERP systems, businesses can make an informed decision about whether or not an ERP system is right for them.
FAQ Insights
What are the benefits of ERP systems?
ERP systems can provide a number of benefits to businesses, including:
- Improved efficiency
- Increased effectiveness
- Reduced costs
- Improved decision-making
- Increased customer satisfaction
What are the challenges of ERP implementation?
ERP implementation can be a challenging process, but there are a number of steps that businesses can take to overcome these challenges, including:
- Proper planning
- Engaging stakeholders
- Choosing the right ERP system
- Adequate training
- Ongoing support