ERP software for Six Sigma is a powerful combination that empowers organizations to optimize processes, enhance quality, and achieve operational excellence. This innovative solution aligns seamlessly with Six Sigma principles, providing a comprehensive platform for data-driven decision-making, process automation, and continuous improvement.
Through its robust capabilities, ERP software empowers Six Sigma teams to collect and analyze data effectively, identify root causes, and implement targeted improvements. It streamlines workflows, automates repetitive tasks, and facilitates collaboration, enabling organizations to achieve significant efficiency gains and quality enhancements.
ERP Software for Six Sigma Overview
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive suite of integrated applications that helps businesses manage their core business processes, such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, and supply chain management. ERP software can provide a number of benefits for Six Sigma initiatives, including:
- Improved data accuracy and consistency
- Reduced process variation
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Improved customer satisfaction
ERP software can also help businesses to identify and eliminate waste, which is a key goal of Six Sigma. By providing a single, integrated view of all of the business’s data, ERP software can help to identify areas where waste is occurring.
This information can then be used to develop and implement process improvements that eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
Key Features and Capabilities of ERP Software for Six Sigma
ERP software for Six Sigma typically includes a number of key features and capabilities, such as:
- Process mapping
- Data analysis
- Process improvement tools
- Project management tools
- Reporting and analytics
These features and capabilities can help businesses to:
- Identify and map their business processes
- Collect and analyze data to identify areas for improvement
- Develop and implement process improvements
- Track the progress of their Six Sigma initiatives
- Report on the results of their Six Sigma initiatives
Six Sigma Principles and ERP Software
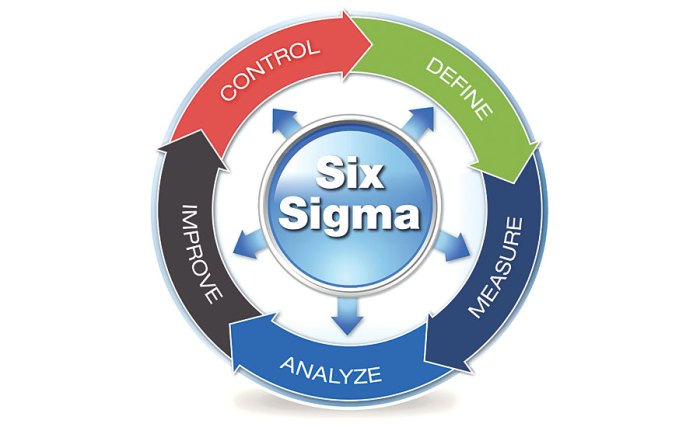
ERP software plays a crucial role in supporting the implementation of Six Sigma principles and methodologies within organizations. By aligning with the DMAIC framework, ERP software provides a comprehensive set of tools and functionalities that facilitate the continuous improvement process.
The DMAIC framework consists of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. ERP software supports each of these phases by providing data, analytics, and automation capabilities that enable organizations to identify and eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and enhance overall performance.
Define Phase
In the Define phase, ERP software helps organizations clearly define the problem or opportunity they are trying to address. By capturing and centralizing data from across the organization, ERP software provides a comprehensive view of business processes and performance metrics.
This data can be used to identify areas for improvement and establish clear goals and objectives for the Six Sigma project.
Data Management and Analysis
ERP software plays a pivotal role in the data-driven Six Sigma methodology. It facilitates efficient data collection, storage, and analysis, enabling organizations to leverage data for continuous process improvement.
ERP systems capture a wealth of operational data from various business functions, including production, supply chain, customer relationship management, and finance. This data provides a comprehensive view of the organization’s processes, allowing for data-driven insights into process performance and improvement opportunities.
Data Collection and Analysis
ERP software enables the automated collection of data from various sources, including production equipment, sensors, and transaction systems. This data is then stored in a central repository, ensuring data integrity and accessibility for Six Sigma analysis.
ERP systems provide robust data analysis tools that allow users to explore, manipulate, and visualize data. These tools facilitate the identification of trends, patterns, and anomalies, enabling teams to pinpoint areas for improvement.
Process Mapping
ERP data can be utilized to create detailed process maps that provide a graphical representation of the steps involved in a process. These maps help identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and other inefficiencies that can hinder process performance.
By analyzing ERP data, teams can gain insights into the flow of materials, information, and resources through the process, enabling them to identify areas for streamlining and optimization.
Root Cause Analysis
ERP data can also be used to perform root cause analysis, which involves identifying the underlying causes of process problems or defects. By examining data from various sources, teams can trace the origin of problems and develop targeted solutions to address them.
ERP systems provide tools for data correlation and regression analysis, enabling teams to identify relationships between variables and pinpoint the root causes of process variation.
Improvement Planning
Once root causes have been identified, ERP data can be used to develop and evaluate improvement plans. By analyzing data on process performance, teams can identify potential solutions and predict their impact on outcomes.
ERP systems provide simulation and forecasting tools that allow teams to test different improvement scenarios and assess their potential benefits, ensuring that improvement plans are based on data-driven insights.
Process Optimization and Automation

ERP software plays a pivotal role in optimizing and automating processes within the framework of Six Sigma. It streamlines workflows, enhances data integration, and provides analytical tools to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, leading to significant cycle time reduction and improved operational performance.
One key aspect of process optimization is the automation of repetitive tasks. ERP software automates manual processes, such as data entry, order processing, and inventory management, freeing up resources for more value-added activities. This automation not only reduces the risk of human error but also accelerates cycle times and improves overall efficiency.
ERP Workflows and Integrations
ERP software enables the creation and implementation of standardized workflows that guide users through complex processes, ensuring consistency and adherence to Six Sigma principles. These workflows can be customized to meet specific organizational requirements and can be integrated with other systems, such as CRM and SCM, to create a seamless and efficient process landscape.
For instance, an ERP system can be integrated with a customer relationship management (CRM) system to automate the process of lead generation, qualification, and conversion. This integration eliminates manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors, while also providing a centralized view of customer interactions and preferences.
Quality Control and Assurance
ERP software plays a vital role in quality control and assurance within Six Sigma by providing a centralized platform for tracking defects, monitoring performance, and ensuring compliance.
One of the key capabilities of ERP software is its ability to track defects throughout the production process. This allows manufacturers to identify the root causes of defects and take corrective action to prevent them from recurring. ERP software can also be used to monitor performance against quality standards and identify areas for improvement.
Compliance Management
ERP software can also help manufacturers ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. By automating the tracking of quality data, ERP software can help manufacturers create a comprehensive audit trail that can be used to demonstrate compliance with ISO 9001 and other quality standards.
Collaboration and Communication
Effective collaboration and communication are crucial for Six Sigma teams to achieve their goals. ERP software plays a vital role in facilitating these aspects, fostering teamwork and ensuring efficient project execution.
ERP dashboards provide a centralized platform for team members to access real-time data, track progress, and identify areas for improvement. Reporting tools enable teams to generate customized reports, analyze data, and make informed decisions. Workflow management functionality streamlines communication, assigns tasks, and automates processes, ensuring seamless collaboration among team members.
ERP Dashboards
- Provide real-time data visualization for project tracking.
- Enable teams to monitor progress and identify bottlenecks.
- Facilitate data-driven decision-making by presenting key metrics and trends.
Reporting Tools
- Allow teams to generate customized reports based on specific criteria.
- Provide insights into process performance, defects, and customer feedback.
- Support data analysis and identification of improvement opportunities.
Workflow Management
- Automate task assignments and approvals, streamlining communication.
- Provide visibility into task status and progress.
- Enhance accountability and reduce the risk of errors.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Numerous organizations have achieved remarkable results by implementing ERP software for Six Sigma. These success stories serve as valuable references for companies considering similar initiatives.
ERP implementation empowers organizations to streamline processes, improve data management, and enhance collaboration, leading to significant benefits in quality, efficiency, and cost reduction.
Benefits and Results
- Improved process efficiency and reduced cycle times
- Enhanced data accuracy and integrity
- Increased collaboration and communication among teams
- Improved product and service quality
- Reduced costs and increased profitability
Best Practices and Implementation Strategies
Implementing ERP software for Six Sigma initiatives requires a well-defined strategy and adherence to best practices. By following a structured approach, organizations can ensure a successful deployment and maximize the benefits of the integration.
Effective implementation involves meticulous project planning, engaging key stakeholders, and managing change effectively. A comprehensive project plan Artikels the project scope, timeline, resources, and responsibilities. Stakeholder engagement ensures that all affected parties are informed, consulted, and involved throughout the implementation process.
Change management strategies address the impact of the new system on employees, processes, and the organization as a whole.
Project Planning
- Define clear project objectives, scope, and deliverables.
- Establish a realistic timeline with milestones and deadlines.
- Identify and allocate necessary resources, including personnel, budget, and technology.
- Assign roles and responsibilities to team members.
- Develop a communication plan to keep stakeholders informed.
Stakeholder Engagement
- Identify all stakeholders who will be impacted by the implementation.
- Engage stakeholders early and involve them throughout the process.
- Communicate the benefits and objectives of the ERP software implementation.
- Address concerns and provide training to ensure stakeholder buy-in.
Change Management
- Develop a change management plan to address the impact on employees, processes, and the organization.
- Communicate the changes effectively and provide training to support employees.
- Monitor and evaluate the change management process to ensure successful adoption.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing ERP software for Six Sigma can introduce certain challenges and considerations that need to be addressed for successful deployment. It is crucial to anticipate these potential hurdles and develop appropriate mitigation strategies to ensure smooth implementation and effective utilization.
Lessons learned from real-world experiences can provide valuable insights into overcoming these challenges.
Data Integration and Compatibility
One significant challenge lies in integrating data from various sources and ensuring compatibility with the ERP system. Six Sigma relies heavily on accurate and consistent data for analysis and improvement initiatives. Integrating data from different systems, such as legacy systems, spreadsheets, and databases, can be complex and time-consuming.
Data compatibility issues can arise due to differences in data formats, data structures, and data definitions.
Change Management and User Adoption
Implementing ERP software for Six Sigma often involves significant changes to existing processes and workflows. This can lead to resistance from users who may be reluctant to adopt new technologies or adapt to new ways of working. Effective change management strategies are essential to address user concerns, provide training, and support users throughout the transition.
Resource Constraints and Costs, ERP software for six sigma
ERP software implementation can require significant resources, including financial investments, IT infrastructure, and skilled personnel. Organizations need to carefully assess their resource constraints and ensure that they have the necessary resources to support the implementation and ongoing maintenance of the ERP system.
Mitigation Strategies
To mitigate these challenges, organizations can adopt the following strategies:
- Conduct thorough data mapping and analysis to identify data sources, formats, and compatibility issues.
- Develop a comprehensive data integration plan that Artikels the steps and processes for data migration and integration.
- Involve users in the implementation process and provide ongoing training and support to facilitate user adoption.
- Establish a change management team to manage the transition and address user concerns.
- Carefully assess resource requirements and develop a realistic implementation plan that aligns with the organization’s capabilities.
10. Future Trends and Innovations
The future of ERP software for Six Sigma is bright, with emerging trends and innovations promising to further enhance its capabilities and impact on businesses. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud computing are at the forefront of these advancements, driving transformative changes in the way Six Sigma initiatives are implemented and executed.
AI and ML algorithms can automate complex data analysis tasks, identify patterns and trends, and make predictions, enabling businesses to gain deeper insights into their processes and make more informed decisions. Cloud computing provides scalable and flexible infrastructure, allowing organizations to access and leverage powerful computing resources without the need for significant upfront investments.
AI and ML in Six Sigma
- Automated data analysis and pattern recognition
- Predictive analytics for risk assessment and process improvement
- Real-time process monitoring and anomaly detection
Cloud Computing for Six Sigma
- Scalable and flexible infrastructure for data storage and processing
- Reduced IT costs and increased accessibility
- Collaboration and data sharing across teams and locations
Conclusion and Recommendations: ERP Software For Six Sigma
ERP software plays a pivotal role in enhancing the effectiveness of Six Sigma initiatives, offering numerous advantages and improvements to organizations. To maximize the benefits, it is crucial for organizations to carefully consider the following recommendations when implementing ERP software for their Six Sigma programs.
It is essential to conduct a thorough assessment of the organization’s current processes, identifying areas where ERP software can add value and contribute to Six Sigma goals. This assessment should involve stakeholders from various departments, including operations, quality, and IT, to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s needs.
Recommendations for Implementation
- Establish clear goals and objectives:Define the specific goals and objectives for implementing ERP software for Six Sigma. This will help guide the selection and implementation process and ensure that the software aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Select the right software:Carefully evaluate different ERP software solutions to identify the one that best meets the organization’s specific requirements and Six Sigma goals. Consider factors such as functionality, scalability, ease of use, and integration capabilities.
- Implement in phases:Implement ERP software in phases to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition. Start with a pilot project in a specific area, such as a single department or process, and gradually expand the implementation to the entire organization.
- Train users thoroughly:Provide comprehensive training to users on the functionality and benefits of the ERP software. This will ensure that users are proficient in using the software and can effectively leverage its capabilities for Six Sigma initiatives.
- Monitor and evaluate progress:Regularly monitor and evaluate the progress of the ERP software implementation. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) and make adjustments as needed to ensure that the software is meeting the organization’s expectations and contributing to Six Sigma goals.
Final Wrap-Up

In conclusion, ERP software for Six Sigma is a transformative solution that empowers organizations to elevate their performance to new heights. By leveraging its advanced capabilities, businesses can streamline processes, enhance quality, and achieve operational excellence, driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Question Bank
What are the key benefits of using ERP software for Six Sigma?
ERP software for Six Sigma provides numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy, streamlined processes, reduced cycle times, enhanced quality control, and increased collaboration.
How does ERP software support the DMAIC phases of Six Sigma?
ERP software aligns with the DMAIC phases by providing tools for data collection (Define), process analysis (Measure), root cause identification (Analyze), improvement implementation (Improve), and control (Control).
What are some examples of how ERP software can be used for process optimization?
ERP software can be used to automate workflows, reduce manual tasks, and eliminate bottlenecks, leading to improved efficiency and reduced cycle times.