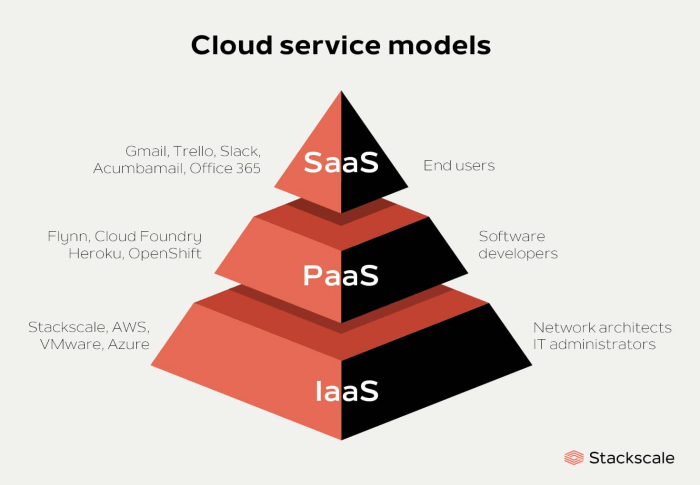
ERP software for PaaS is revolutionizing business operations, offering unparalleled efficiency, cost reduction, and scalability. By seamlessly integrating key business processes onto a cloud-based platform, ERP software for PaaS empowers organizations to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and drive growth.
From financial management to supply chain optimization and customer relationship management, ERP software for PaaS provides a comprehensive suite of tools that cater to the unique needs of modern businesses. Its flexibility and adaptability make it an ideal solution for organizations of all sizes, enabling them to adapt to changing market dynamics and stay ahead of the competition.
Overview of ERP Software for PaaS
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software is a comprehensive business management solution that integrates various aspects of an organization’s operations, including finance, supply chain, manufacturing, and human resources.
ERP software for PaaS (Platform as a Service) is a cloud-based ERP solution that is hosted and managed by a third-party provider. This eliminates the need for organizations to purchase and maintain their own hardware and software, reducing IT costs and complexity.
Popular ERP Software for PaaS
- SAP Business ByDesign
- Oracle NetSuite
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Salesforce
- Workday
Benefits of Using ERP Software for PaaS
ERP software for PaaS offers numerous advantages to businesses. It streamlines operations, reduces costs, and provides scalability to support business growth.
Improved Efficiency: ERP software for PaaS automates and integrates various business processes, eliminating manual tasks and reducing errors. This enhances productivity and frees up employees to focus on strategic initiatives.
Cost Reduction
ERP software for PaaS eliminates the need for multiple software solutions and expensive on-premises infrastructure. The pay-as-you-go model of PaaS reduces capital expenditure and provides cost predictability.
Scalability
ERP software for PaaS is designed to scale with the changing needs of a business. It can easily handle increased transaction volumes and support business expansion without significant investments in infrastructure.
Case Studies
Company A, a manufacturing firm, implemented ERP software for PaaS and achieved a 20% reduction in operating costs. The software automated inventory management and improved supply chain visibility, resulting in reduced waste and improved customer service.
Company B, a healthcare provider, implemented ERP software for PaaS and experienced a 15% increase in patient satisfaction. The software streamlined patient scheduling and medical record management, improving patient experience and reducing wait times.
Key Features of ERP Software for PaaS
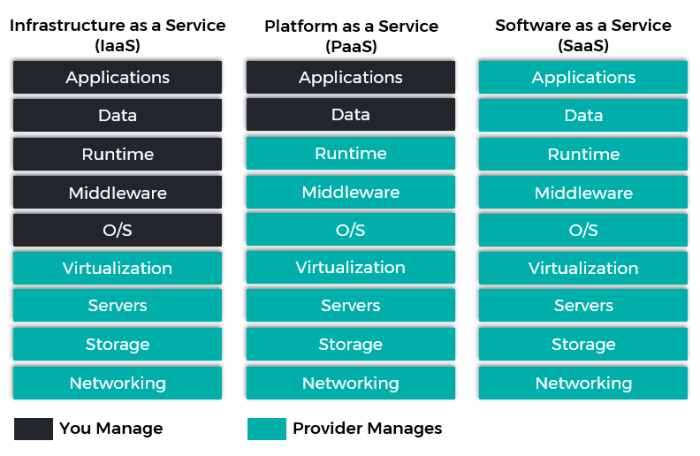
ERP software for PaaS offers a comprehensive suite of features designed to streamline business processes and enhance operational efficiency. These features include:
Financial Management
ERP software for PaaS provides robust financial management capabilities, including:
- General ledger accounting: Track financial transactions, generate financial statements, and manage budgets.
- Accounts payable: Automate invoice processing, vendor payments, and expense management.
- Accounts receivable: Manage customer invoices, track payments, and handle collections.
- Cash management: Monitor cash flow, forecast cash needs, and manage bank accounts.
- Fixed asset management: Track and manage fixed assets, including depreciation and maintenance.
Supply Chain Management
ERP software for PaaS streamlines supply chain processes, including:
- Inventory management: Track inventory levels, manage stock, and optimize inventory replenishment.
- Procurement: Manage supplier relationships, automate purchase orders, and track vendor performance.
- Warehouse management: Optimize warehouse operations, including receiving, storage, and shipping.
- Transportation management: Plan and execute transportation schedules, manage logistics, and track shipments.
- Demand planning: Forecast demand, optimize production planning, and manage inventory levels.
Customer Relationship Management
ERP software for PaaS enhances customer relationships through:
- Sales management: Manage sales opportunities, track customer interactions, and generate sales orders.
- Marketing automation: Create and execute marketing campaigns, track customer engagement, and generate leads.
- Customer service: Manage customer inquiries, resolve issues, and track customer satisfaction.
- Contact management: Store and manage customer contact information, track interactions, and segment customers.
- Loyalty programs: Create and manage loyalty programs, track customer purchases, and reward repeat business.
Implementation and Integration of ERP Software for PaaS
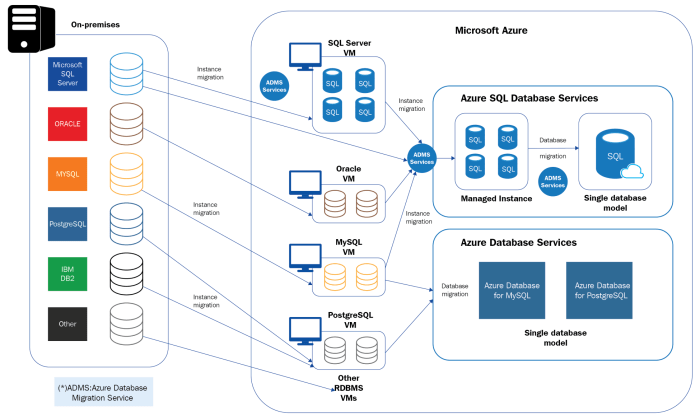
Implementing and integrating ERP software for PaaS involves several key steps. These steps should be followed carefully to ensure a successful implementation.
A step-by-step guide to implementing and integrating ERP software for PaaS:
- Plan and Prepare:Define the project scope, objectives, and timeline. Gather requirements from stakeholders and assess the current IT infrastructure.
- Select a Vendor and Solution:Evaluate different ERP vendors and their offerings. Choose a solution that aligns with the organization’s specific needs and goals.
- Configure and Customize:Tailor the ERP software to meet the organization’s unique requirements. This may involve customizing workflows, creating custom reports, and integrating with other systems.
- Test and Deploy:Conduct thorough testing to ensure the ERP software is functioning correctly. Deploy the software to the production environment and monitor its performance.
- Train and Support:Provide training to users on how to use the ERP software effectively. Offer ongoing support to ensure smooth adoption and address any issues that may arise.
Challenges associated with ERP software implementation:
- Complexity:ERP systems are complex and require significant planning and effort to implement.
- Data Migration:Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP software can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Change Management:Implementing an ERP system can disrupt existing workflows and require significant change management efforts.
- Cost:ERP software can be expensive to purchase and implement.
- Involve stakeholders:Engage key stakeholders throughout the implementation process to ensure their needs are met.
- Use a phased approach:Implement the ERP software in phases to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition.
- Communicate effectively:Keep stakeholders informed about the project progress and any changes that may occur.
- Test thoroughly:Conduct thorough testing to ensure the ERP software is functioning correctly before deploying it to the production environment.
- Provide ongoing support:Offer ongoing support to users to ensure they can use the ERP software effectively.
- A healthcare organization customized its ERP software to manage patient records, automate appointment scheduling, and generate insurance claims.
- A retail business customized its ERP software to integrate with its e-commerce platform, enabling seamless order fulfillment and inventory management.
- Subscription-based pricing is typically the most affordable option for small businesses, as it allows them to pay for the software on a monthly or annual basis. However, subscription-based pricing can be more expensive in the long run than perpetual licensing, as businesses will need to continue to pay the subscription fee to access the software.
- Perpetual licensing is typically the most expensive option for small businesses, as it requires a one-time payment for the software. However, perpetual licensing can be more affordable in the long run than subscription-based pricing, as businesses will not need to continue to pay the subscription fee to access the software.
- Cloud-based pricing is typically more flexible than subscription-based pricing, as it allows businesses to scale their usage up or down as needed. However, cloud-based pricing can be more expensive than subscription-based pricing, as businesses will need to pay for the software as well as the infrastructure to support it.
- Assess the vendor’s experience in providing ERP solutions for PaaS.
- Inquire about their industry knowledge and understanding of specific business requirements.
- Request references from previous customers to gain insights into the vendor’s track record.
- Evaluate the ERP software’s functionality and alignment with business needs.
- Consider the availability of key features such as financial management, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
- Assess the software’s scalability and ability to support future growth.
- Inquire about the vendor’s technical support capabilities and response times.
- Evaluate the availability of documentation, online resources, and training programs.
- Consider the vendor’s commitment to software updates and security patches.
- Understand the vendor’s pricing structure, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Compare the vendor’s pricing with other providers to ensure competitiveness.
- Negotiate favorable terms that meet business needs and budget constraints.
- Evaluate the vendor’s experience in implementing ERP solutions on PaaS.
- Inquire about their methodology and timeline for implementation.
- Assess the vendor’s ability to integrate with existing systems and applications.
- Research the vendor’s reputation in the industry.
- Read online reviews and testimonials from previous customers.
- Contact references to gather feedback on the vendor’s performance.
- Automate data entry and processing
- Identify and mitigate risks
- Optimize inventory levels
- Predict customer demand
- Identify patterns and trends in data
- Make predictions about future events
- Recommend actions to users
- Scalability: Cloud-based ERP software can be easily scaled up or down to meet the changing needs of your business.
- Reliability: Cloud-based ERP software is hosted in secure data centers, which ensures that your data is always available and protected.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud-based ERP software is typically more cost-effective than on-premises ERP software, as you only pay for the resources you use.
- Encourage user training and support to ensure proficiency.
- Involve users in the implementation process to foster ownership.
- Provide clear documentation and resources for easy reference.
- Establish data governance policies to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
- Implement data integration tools to streamline data flow between systems.
- Regularly monitor data quality to identify and address errors.
- Regularly review and assess ERP performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Incorporate feedback from users and stakeholders to enhance functionality.
- Stay updated with the latest ERP software updates and industry best practices.
Best practices for ERP software implementation:
Security Considerations for ERP Software for PaaS
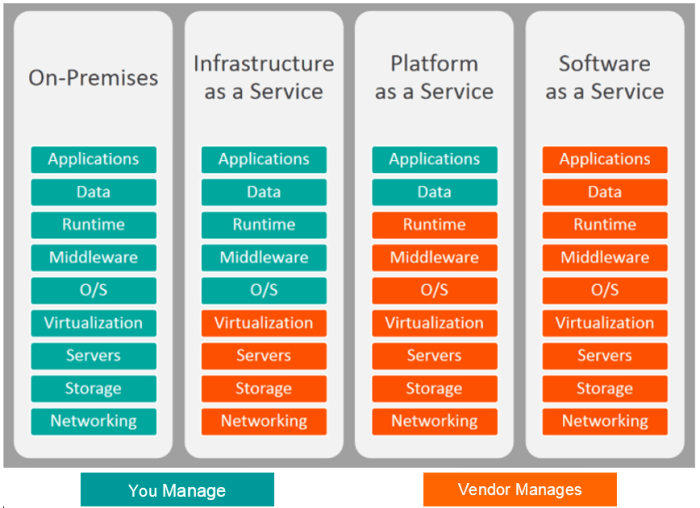
ERP software for PaaS inherits the security features of the underlying PaaS platform, providing a secure foundation for data storage and processing. However, it is crucial to address additional security concerns specific to ERP software deployments in the PaaS environment.
One of the primary security concerns is data protection. ERP systems manage sensitive business data, including financial information, customer records, and operational details. It is essential to implement robust data encryption mechanisms at rest and in transit to safeguard data from unauthorized access or interception.
Data Access Control
Access control mechanisms should be implemented to restrict access to ERP data and functionality based on user roles and permissions. This ensures that only authorized users have access to the data they need to perform their job functions, minimizing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized modifications.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
ERP software for PaaS must comply with relevant industry regulations and data protection laws. This includes adhering to standards such as ISO 27001, GDPR, and HIPAA to ensure data privacy, security, and compliance.
Customization and Configuration of ERP Software for PaaS
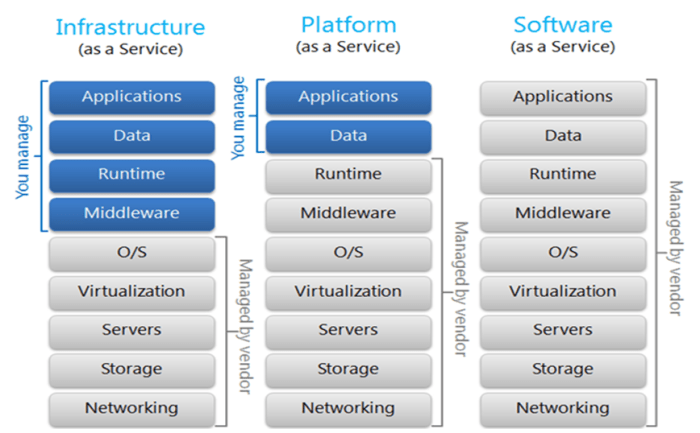
ERP software for PaaS offers extensive options for customization and configuration to tailor it to specific business needs. Businesses can modify various aspects of the software, including workflows, data fields, reports, and user interfaces.
Customization Options
* Workflow Customization:Businesses can create custom workflows to automate business processes, streamlining operations and improving efficiency.
Data Field Customization
ERP software allows businesses to add, remove, or modify data fields to capture and manage specific data relevant to their operations.
Report Customization
Businesses can design custom reports to extract and present data in formats that meet their reporting requirements.
User Interface Customization
The user interface of ERP software can be customized to match the specific preferences and needs of the business, improving user experience and adoption.
Examples of Customization
* A manufacturing company customized its ERP software to track production schedules, manage inventory levels, and generate real-time production reports.
Cost and Pricing Models for ERP Software for PaaS
The cost and pricing models for ERP software for PaaS vary depending on the vendor and the specific features and capabilities of the software. However, there are three main pricing models that are commonly used:
Subscription-based pricing: This model involves paying a monthly or annual fee to access the software. The fee typically includes access to all of the software’s features and capabilities, as well as support and maintenance.
Perpetual licensing: This model involves purchasing a perpetual license to use the software. The license fee is typically a one-time payment, and it gives the purchaser the right to use the software indefinitely. However, perpetual licenses do not typically include access to support and maintenance, which must be purchased separately.
Cloud-based pricing: This model involves paying a monthly or annual fee to access the software over the internet. The fee typically includes access to all of the software’s features and capabilities, as well as support and maintenance. Cloud-based pricing is often more flexible than subscription-based pricing, as it allows businesses to scale their usage up or down as needed.
Comparison of Cost and Pricing Models
Vendor Selection and Evaluation
Choosing the right ERP software vendor for PaaS is crucial for successful implementation and ongoing success. Businesses should consider the following key criteria when evaluating vendors:
Vendor Expertise and Experience
Software Capabilities and Features
Technical Support and Maintenance
Cost and Pricing Model
Implementation and Integration
Reputation and References
Trends and Innovations in ERP Software for PaaS
ERP software for PaaS is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging all the time. These trends are shaping the future of ERP software for PaaS, making it more powerful, efficient, and user-friendly.
Some of the most important trends and innovations in ERP software for PaaS include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is rapidly changing the way businesses operate, and ERP software is no exception. AI-powered ERP software can automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights that were previously unavailable. For example, AI can be used to:
Machine Learning (ML), ERP software for PaaS
ML is a subset of AI that allows computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. ML-powered ERP software can improve its performance over time by learning from the data it processes. For example, ML can be used to:
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing resources over the internet. ERP software for PaaS is increasingly being deployed in the cloud, which offers a number of benefits, including:
Best Practices for Using ERP Software for PaaS
Maximize the benefits of ERP software for PaaS by adopting best practices. These include promoting user adoption, managing data effectively, and pursuing continuous improvement.
User Adoption
Data Management
Continuous Improvement
Last Word
In conclusion, ERP software for PaaS is an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and achieve sustainable growth. Its robust features, scalability, and security make it a valuable investment that can transform business processes and drive success in the digital age.
Clarifying Questions
What are the benefits of using ERP software for PaaS?
ERP software for PaaS offers numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, cost reduction, scalability, enhanced collaboration, and real-time data access.
What are the key features of ERP software for PaaS?
Key features of ERP software for PaaS include financial management, supply chain management, customer relationship management, inventory management, and project management.
How do I choose the right ERP software vendor for PaaS?
When selecting an ERP software vendor for PaaS, consider factors such as industry expertise, customer support, implementation experience, and cost.