ERP software for consumer products has emerged as a game-changer, enabling businesses to optimize their operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic market.
With its comprehensive capabilities, ERP software seamlessly integrates critical business functions, providing real-time visibility, improved collaboration, and data-driven decision-making for consumer product companies.
Overview of ERP Software for Consumer Products
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a comprehensive business management solution that integrates various functional areas of an organization, such as finance, supply chain management, manufacturing, and customer relationship management (CRM), into a single, unified system.
Key features of ERP software include:
- Centralized database
- Real-time data
- Integrated workflows
- Automated processes
- Reporting and analytics
ERP software provides several benefits for consumer products companies, including:
- Improved efficiency and productivity
- Reduced costs
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
- Increased profitability
Examples of successful ERP implementations in the consumer products industry include:
- Procter & Gamble
- Nestlé
- Unilever
- Coca-Cola
- PepsiCo
Key Considerations for Selecting ERP Software
Choosing the right ERP software for consumer products requires careful consideration of several key factors. These include industry-specific functionality, scalability, and vendor evaluation.
Industry-Specific Functionality
ERP software tailored to the consumer products industry offers specialized features and functionalities that align with the unique requirements of the sector. These may include:
- Product lifecycle management (PLM)
- Demand planning and forecasting
- Supply chain optimization
- Sales and marketing automation
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
Scalability
ERP software should be scalable to accommodate the growth and evolving needs of the business. Consider the following:
- Current and projected business volume
- Number of users and locations
- Complexity of operations
Vendor Evaluation, ERP software for consumer products
Selecting the right ERP vendor is crucial. Evaluate vendors based on the following criteria:
- Industry experience and expertise
- Product functionality and fit
- Implementation and support capabilities
- Customer references and testimonials
- Cost and pricing model
Implementation and Integration Challenges

ERP implementation for consumer products presents unique challenges due to the complexity of the industry and the need for seamless integration with existing systems. These challenges can impact project timelines, costs, and overall success.
Data Migration and Integration
Migrating data from legacy systems to the new ERP can be a complex and time-consuming process. Data accuracy and integrity must be maintained throughout the migration to ensure the smooth functioning of the ERP system. Integration with existing systems, such as CRM, supply chain management, and e-commerce platforms, is crucial to ensure data consistency and avoid data silos.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
To mitigate risks and ensure a successful ERP implementation, several strategies can be employed:
- Phased Approach:Implementing the ERP in phases allows for a more controlled and manageable rollout, reducing the risk of disruptions to business operations.
- Data Validation and Cleansing:Before migration, data should be thoroughly validated and cleansed to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Testing and User Acceptance:Rigorous testing and user acceptance testing should be conducted to identify and resolve any issues before go-live.
- Change Management:Effective change management is essential to ensure user adoption and minimize resistance to the new system.
Functional Requirements for ERP Software
ERP software for consumer products requires specific functional modules to cater to the industry’s unique needs. These modules streamline business processes, enhance collaboration, and provide real-time insights into operations.
Inventory Management
Inventory management is crucial for consumer products companies to maintain optimal stock levels, reduce waste, and meet customer demand. ERP software provides features such as:
- Real-time inventory tracking across multiple warehouses and locations
- Automated inventory replenishment based on demand forecasting
- Lot and serial number tracking for product traceability and quality control
Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management is essential for ensuring timely delivery of products to consumers. ERP software offers modules that:
- Optimize supplier relationships and manage procurement processes
- Track orders, shipments, and deliveries in real-time
- Provide visibility into inventory levels across the supply chain
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
CRM modules in ERP software help consumer products companies manage customer interactions, track sales, and provide personalized experiences. Key features include:
- Centralized customer data repository for a complete view of customer history
- Automated marketing campaigns and personalized communications
- Customer service and support tools for efficient issue resolution
Best Practices for ERP Implementation
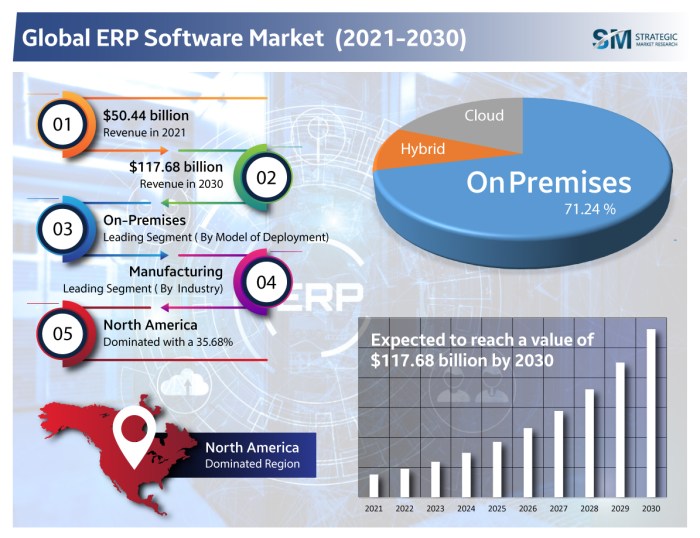
Effective ERP implementation in consumer products demands adherence to industry best practices. These practices encompass stakeholder engagement, change management, and continuous improvement. Optimizing ERP software performance and maximizing its benefits necessitate meticulous attention to these key aspects.
Stakeholder Engagement
Successful ERP implementation hinges upon the active involvement and collaboration of all stakeholders. This includes employees from various departments, senior management, and external partners. Effective communication, transparent information sharing, and regular feedback loops foster stakeholder buy-in and ensure that their needs and concerns are addressed.
Change Management
ERP implementation inevitably brings about significant changes to business processes and workflows. To mitigate resistance and facilitate a smooth transition, organizations must implement a comprehensive change management strategy. This strategy should include clear communication, training and development programs, and support mechanisms to help employees adapt to the new system.
Continuous Improvement
ERP systems are not static entities; they require ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and improvement to maintain optimal performance. Organizations should establish a process for regularly reviewing the system’s effectiveness, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing necessary enhancements. This ensures that the ERP system continues to align with the evolving needs of the business.
Trends and Innovations in ERP Software
ERP software for consumer products is constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. Emerging trends and innovations are shaping the future of ERP systems, enabling businesses to streamline operations, improve customer experience, and drive digital transformation.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is transforming the way businesses access and manage ERP software. Cloud-based ERP systems offer several advantages, including scalability, flexibility, and reduced costs. Businesses can access their ERP system from anywhere with an internet connection, and they can scale their system up or down as needed.
Cloud-based ERP systems also eliminate the need for businesses to purchase and maintain hardware and software, which can save significant costs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is another major trend that is impacting ERP software. AI-powered ERP systems can automate tasks, improve decision-making, and provide insights into data. For example, AI can be used to automate tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and customer service.
AI can also be used to analyze data to identify trends and patterns, which can help businesses make better decisions.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The IoT is connecting devices and sensors to the internet, which is creating new opportunities for ERP systems. ERP systems can be integrated with IoT devices to collect data from the physical world. This data can be used to improve supply chain management, inventory management, and customer service.
For example, ERP systems can be integrated with IoT sensors to track the location of inventory items in real time. This data can be used to improve inventory management and reduce costs.
Case Studies and Success Stories

ERP software has transformed the business landscape for consumer products companies, enabling them to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. Numerous companies have successfully implemented ERP software, reaping significant benefits. This section presents case studies of these success stories, highlighting the challenges they overcame, the solutions they adopted, and the transformative impact ERP software had on their performance.
Success Story: XYZ Corporation
XYZ Corporation, a leading manufacturer of consumer electronics, faced challenges with fragmented data, inefficient supply chain management, and a lack of real-time visibility into operations. They implemented an ERP system that integrated all aspects of their business, from product development to customer service.
The ERP software provided a centralized platform for data management, streamlined workflows, and improved communication across departments. As a result, XYZ Corporation experienced significant improvements in productivity, reduced lead times, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Vendor Landscape and Market Analysis

The ERP software market for consumer products is highly competitive, with a wide range of vendors offering solutions tailored to the specific needs of this industry. To help businesses make informed decisions, we have compiled a comparative analysis of leading ERP vendors in the consumer products space.
This analysis considers key factors such as market share, product offerings, industry expertise, strengths, weaknesses, and recommendations based on specific business requirements.
Leading ERP Vendors for Consumer Products
| Vendor | Market Share | Product Offerings | Industry Expertise | Strengths | Weaknesses | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAP | 35% | SAP S/4HANA Cloud, SAP ECC | Strong in large enterprises, manufacturing, and retail | Scalability, robust functionality, industry-specific solutions | High cost, complex implementation | Suitable for large, complex organizations with significant ERP needs |
| Oracle | 25% | Oracle ERP Cloud, Oracle NetSuite | Strong in mid-size to large businesses, supply chain management | Feature-rich, integrated suite, robust analytics | Can be expensive, customization may require additional resources | Ideal for businesses with complex supply chains or those seeking a comprehensive ERP solution |
| Microsoft | 15% | Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, Microsoft Dynamics AX | Strong in small to mid-size businesses, retail, and distribution | Ease of use, affordable, cloud-based options | Limited functionality compared to larger vendors, may require additional customization | Suitable for smaller businesses or those seeking a cost-effective ERP solution |
| Infor | 10% | Infor CloudSuite Industrial, Infor LN | Strong in manufacturing, distribution, and service industries | Industry-specific functionality, robust production planning and scheduling | Can be complex to implement, may require additional customization | Ideal for businesses in manufacturing or distribution sectors seeking industry-specific capabilities |
| Epicor | 5% | Epicor ERP, Epicor Kinetic | Strong in manufacturing, distribution, and retail | Agile, flexible, mobile-friendly solutions | May lack the breadth of functionality of larger vendors | Suitable for businesses seeking a modern, user-friendly ERP solution |
Cost and ROI Considerations
ERP software implementation for consumer products involves significant financial investments and requires careful evaluation of costs and potential return on investment (ROI). Understanding the cost structure and developing a robust ROI framework are crucial for making informed decisions.
Cost Estimation
- Software Licensing:Licensing fees vary depending on the size and complexity of the ERP system, the number of users, and the deployment model (on-premises or cloud-based).
- Implementation Costs:Professional services for implementation, customization, and data migration typically constitute a major portion of the expenses.
- Hardware and Infrastructure:On-premises deployments require investments in servers, storage, and network infrastructure.
- Training and Support:User training and ongoing support services are essential to ensure successful adoption and utilization.
ROI Framework
Calculating ROI involves quantifying the benefits and comparing them to the costs incurred. Benefits may include:
- Operational Efficiencies:Streamlined processes, reduced manual errors, and improved inventory management.
- Enhanced Customer Service:Faster order processing, improved product availability, and personalized experiences.
- Increased Sales and Profitability:Improved demand forecasting, optimized pricing, and better customer retention.
ROI Maximization Strategies
Maximizing ROI requires a holistic approach that includes:
- Thorough Planning and Scope Definition:Clear objectives, well-defined requirements, and a realistic implementation plan.
- Phased Implementation:Breaking down the project into manageable phases to reduce risks and facilitate continuous improvement.
- Change Management and User Adoption:Engaging stakeholders, providing training, and ensuring ongoing support to foster user acceptance.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Seamless integration with other business applications to avoid data silos and ensure data integrity.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, ERP software for consumer products is an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to streamline their operations, improve customer experiences, and drive growth in the ever-evolving consumer products industry.
By embracing the latest innovations and industry best practices, companies can unlock the full potential of ERP software and achieve operational excellence, enhanced profitability, and long-term success.
FAQ
What are the key benefits of using ERP software for consumer products?
ERP software provides numerous benefits, including improved operational efficiency, enhanced collaboration, increased data accuracy, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
What are the critical factors to consider when selecting ERP software for consumer products?
Key considerations include industry-specific functionality, scalability, vendor reputation, implementation costs, and ongoing support.
What are the common challenges faced during ERP implementation for consumer products?
Common challenges include data migration, integration with existing systems, change management, and ensuring user adoption.