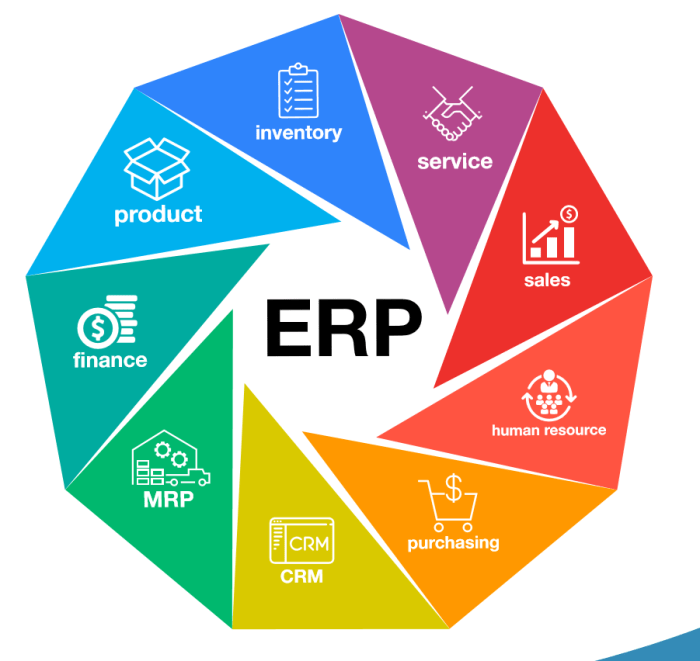
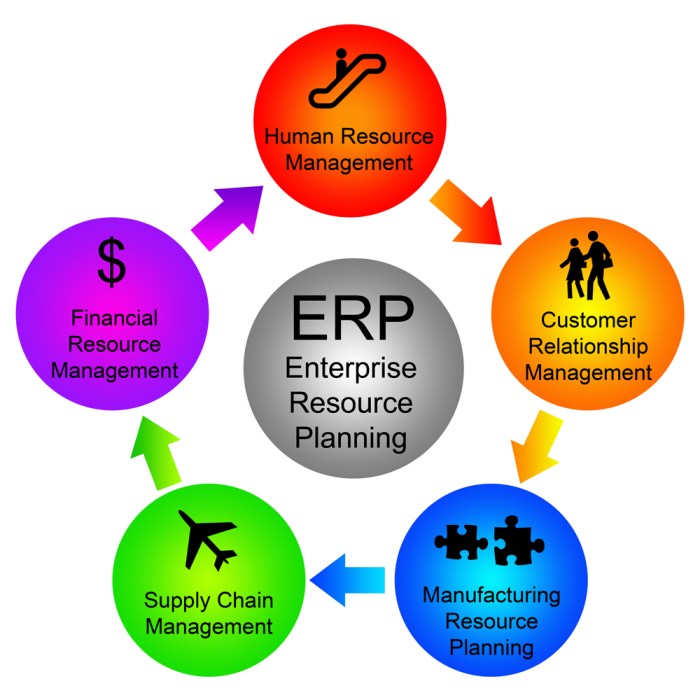
EntERPrise resource planning software implementation – EntERPrise resource planning (ERP) software implementation is a transformative undertaking that can revolutionize the way organizations manage their operations. By integrating various business functions into a single, unified system, ERP software streamlines processes, improves efficiency, and provides valuable insights for informed decision-making.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of ERP implementation, providing a detailed overview of the process, its benefits, challenges, and best practices. We will also explore key considerations for selecting the right ERP software and strategies for ensuring successful user adoption.
ERP Software Implementation Process
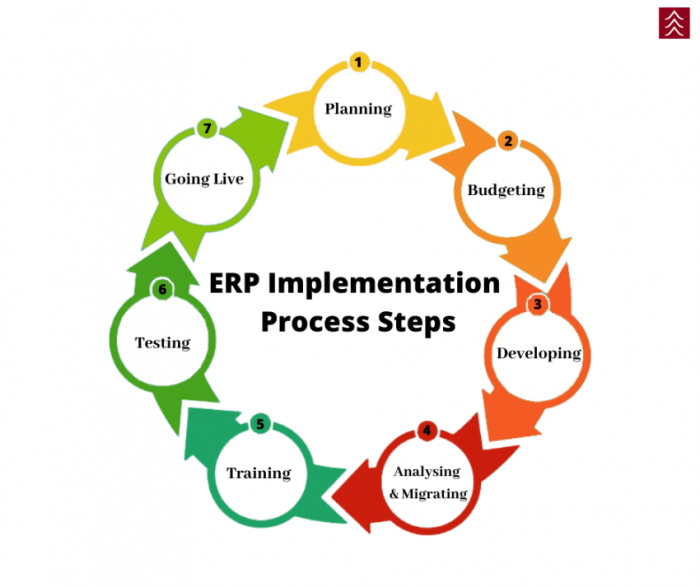
ERP software implementation is a complex process that involves planning, analysis, design, development, testing, and deployment. It is important to carefully follow each step to ensure a successful implementation.
Planning, EntERPrise resource planning software implementation
The planning phase is the first step in ERP software implementation. During this phase, the organization will need to define the scope of the project, establish a budget, and create a timeline. It is also important to identify the key stakeholders who will be involved in the implementation process.
Analysis
The analysis phase is used to gather information about the organization’s current business processes. This information will be used to design the new ERP system. During the analysis phase, the organization will need to identify the key business processes that will be affected by the new ERP system.
Design
The design phase is used to create the new ERP system. During this phase, the organization will need to define the system’s architecture, data structures, and user interfaces. It is also important to develop a testing plan to ensure that the new system meets the organization’s requirements.
Development
The development phase is used to develop the new ERP system. During this phase, the organization will need to code the system and create the necessary documentation. It is also important to conduct unit testing to ensure that the system is functioning properly.
Testing
The testing phase is used to test the new ERP system. During this phase, the organization will need to conduct system testing and user acceptance testing. System testing is used to ensure that the system meets the organization’s requirements. User acceptance testing is used to ensure that the system is easy to use and meets the needs of the users.
Deployment
The deployment phase is used to deploy the new ERP system. During this phase, the organization will need to install the system and train the users. It is also important to develop a support plan to ensure that the system is running smoothly.
Benefits of ERP Implementation: EntERPrise Resource Planning Software Implementation
ERP implementation offers numerous benefits to organizations, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced data integration.ERP systems streamline business processes, eliminating redundant tasks and automating manual processes. This automation reduces the time and effort required to complete tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.ERP systems also help organizations reduce costs by optimizing resource allocation and identifying areas for cost savings.
The centralized data repository provides real-time visibility into all aspects of the business, enabling managers to make informed decisions about resource allocation and cost reduction strategies.Finally, ERP systems enhance data integration by providing a single, unified platform for all business data.
This eliminates data silos and ensures that all departments have access to the same, up-to-date information. This improved data integration leads to better decision-making and increased operational efficiency.
Improved Efficiency
* Reduced time and effort required to complete tasks
- Automated manual processes
- Streamlined business processes
- Increased employee productivity
Cost Reduction
* Optimized resource allocation
- Identified areas for cost savings
- Real-time visibility into all aspects of the business
- Informed decision-making about cost reduction strategies
Data Integration
* Eliminated data silos
- Single, unified platform for all business data
- Access to same, up-to-date information for all departments
- Better decision-making and increased operational efficiency
Challenges of ERP Implementation
ERP implementation projects often encounter various challenges that can hinder their successful execution. These challenges can arise from different aspects of the implementation process, such as data migration, user adoption, and change management.
Data Migration
Data migration is a crucial aspect of ERP implementation, involving the transfer of data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. However, this process can be complex and time-consuming, especially for organizations with large volumes of data. Challenges related to data migration include:
Data accuracy and integrity
Ensuring the accuracy and integrity of data during migration is essential to maintain data quality in the new ERP system. Inconsistent or incomplete data can lead to errors and inefficiencies in the system.
Data mapping
Mapping data from legacy systems to the new ERP system requires careful planning and analysis to ensure data compatibility and consistency. Mismatched data structures or formats can cause data loss or errors.
Data conversion
Converting data from legacy systems to the new ERP system’s format can be a complex and time-consuming process, especially for organizations with customized legacy systems.
Best Practices for ERP Implementation
To ensure a successful ERP implementation, adhering to best practices is crucial. These practices provide a structured approach, ensuring that the implementation aligns with the organization’s objectives, maximizes benefits, and minimizes disruptions.
Key best practices include:
Project Planning
- Define clear project objectives, scope, and timelines.
- Establish a dedicated project team with cross-functional expertise.
- Conduct a thorough needs assessment to identify specific requirements.
- Create a detailed implementation plan outlining milestones, tasks, and dependencies.
Stakeholder Engagement
- Identify and involve key stakeholders throughout the implementation process.
- Communicate regularly to keep stakeholders informed and address concerns.
- Seek feedback and buy-in from stakeholders to ensure alignment.
- Train stakeholders on the new ERP system to ensure successful adoption.
Ongoing Support
- Provide ongoing technical support and maintenance to ensure system stability.
- Monitor system usage and performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Regularly review and update the ERP system to align with evolving business needs.
- Establish a process for ongoing user training and support.
ERP Software Selection
ERP software selection is a critical decision that can impact the success of an ERP implementation. Key factors to consider when selecting ERP software include:
- Business needs:The software should align with the organization’s specific business processes and requirements.
- Industry expertise:The software should be designed for the organization’s industry and have specific functionality for that industry.
- Scalability:The software should be able to accommodate the organization’s growth and expansion plans.
- Cost:The software should fit within the organization’s budget, including both the initial purchase price and the ongoing maintenance and support costs.
- Vendor support:The vendor should provide comprehensive support and services, including implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance.
ERP Vendor Comparison
The following table compares different ERP vendors based on features, functionality, and cost:
| Vendor | Features | Functionality | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP | Comprehensive suite of ERP modules | High | High |
| Oracle | Strong financials and supply chain management modules | Medium | Medium |
| Microsoft Dynamics | Easy to use and affordable | Low | Low |
| Infor | Industry-specific solutions | Medium | Medium |
| Epicor | Focus on manufacturing and distribution | Medium | Medium |
ERP Implementation Timeline
ERP implementation timelines vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization, the ERP system being implemented, and the resources available. However, a typical timeline for a medium-sized organization implementing a mid-sized ERP system is as follows:
Project Planning
- Define project scope and objectives
- Assemble project team
- Develop project plan
Business Process Analysis
- Document current business processes
- Identify areas for improvement
- Design new business processes
System Selection and Configuration
- Evaluate and select ERP system
- Configure ERP system to meet specific needs
- Develop and test customization
Data Migration
- Extract data from legacy systems
- Cleanse and transform data
- Load data into ERP system
User Training and Testing
- Develop training materials
- Train users on new ERP system
- Test ERP system with real-world data
Go-Live
- Launch ERP system into production
- Monitor system performance
- Provide ongoing support to users
Post-Implementation
- Evaluate ERP system performance
- Identify and implement improvements
- Continuously optimize ERP system
It is important to note that this timeline is just a guideline. The actual timeline for your ERP implementation may vary depending on your specific circumstances.
ERP Implementation Team
ERP implementation requires a dedicated team of experts to ensure successful execution. Each team member plays a crucial role in different phases of the project.
The core team typically comprises the following members:
Project Manager
- Oversees the entire implementation process
- Manages the project timeline, budget, and resources
- Communicates with stakeholders and ensures project alignment
Business Analysts
- Analyze business processes and requirements
- Translate business needs into technical specifications
- Work closely with end-users to gather feedback and ensure system alignment
Technical Experts
- Configure and customize the ERP software
- Integrate the ERP system with other applications
- Provide technical support and training to end-users
The project manager ensures coordination among team members, while business analysts bridge the gap between business requirements and technical implementation. Technical experts possess the necessary skills to configure and maintain the ERP system.
Having a dedicated and skilled team is essential for effective ERP implementation, as it allows for efficient collaboration, timely decision-making, and successful project execution.
Data Migration in ERP Implementation

Data migration is a crucial aspect of ERP implementation that involves transferring data from legacy systems to the new ERP system. It ensures data integrity and accuracy throughout the implementation process.
The data migration process typically follows a step-by-step approach:
Data Extraction
Data extraction involves identifying and retrieving relevant data from existing systems. This data can include customer information, inventory records, financial data, and other business-critical information.
Data Cleansing
Once data is extracted, it needs to be cleansed to ensure accuracy and consistency. This involves removing duplicate records, correcting errors, and standardizing data formats.
Data Loading
The final step is data loading, where the cleansed data is transferred into the new ERP system. This process requires careful planning and testing to ensure data integrity and minimize disruptions.
User Adoption in ERP Implementation
User adoption is crucial for the success of any ERP implementation. Strategies to ensure successful user adoption include:
- Training:Comprehensive training empowers users with the knowledge and skills to navigate the new ERP system effectively.
- Communication:Clear and consistent communication keeps users informed about the implementation process, timelines, and benefits.
- Change Management:Addressing user concerns, providing support, and managing resistance to change fosters a positive attitude towards the new system.
Training
Effective training programs include:
- Customized training:Tailored to specific user roles and responsibilities.
- Hands-on practice:Allows users to apply their knowledge in a simulated environment.
- User manuals and online resources:Provide ongoing support and reference materials.
Communication
Open and transparent communication channels are essential for:
- Announcing the implementation:Informing users about the project, its objectives, and benefits.
- Regular updates:Keeping users informed about progress, timelines, and changes.
- Addressing concerns:Listening to user feedback, addressing their concerns, and providing timely responses.
Change Management
Change management strategies include:
- Early involvement:Engaging users in the implementation process fosters ownership and buy-in.
- Resistance management:Identifying and addressing user resistance, providing support and guidance.
- Continuous feedback:Gathering user feedback throughout the implementation to make necessary adjustments.
ERP Implementation Success Metrics
ERP implementation success is a complex and multifaceted concept that encompasses various aspects of the project’s performance. Measuring success requires a comprehensive approach that considers both qualitative and quantitative factors. Key metrics used to gauge the success of ERP implementation include:
Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI is a crucial metric that measures the financial benefits of ERP implementation. It calculates the ratio of benefits gained to the costs incurred. A positive ROI indicates that the implementation has generated value for the organization.
User Satisfaction
User satisfaction is a qualitative metric that assesses the level of acceptance and adoption of the ERP system by end-users. It measures the extent to which the system meets their needs and expectations. High user satisfaction contributes to increased productivity and efficiency.
Efficiency Gains
Efficiency gains are measured by comparing the performance of business processes before and after ERP implementation. Key indicators include reduced cycle times, increased throughput, and improved resource utilization. Efficiency gains directly impact operational costs and profitability.
Data Quality
Data quality refers to the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of data in the ERP system. High-quality data is essential for effective decision-making and efficient business operations. Data quality metrics track the percentage of accurate and complete data, as well as the number of data errors and inconsistencies.
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
ERP systems can help organizations meet industry-specific regulations and compliance requirements. Success metrics in this area include the ability to track and manage compliance-related data, generate regulatory reports, and demonstrate adherence to standards.
Scalability and Flexibility
Scalability and flexibility metrics assess the ERP system’s ability to adapt to changing business needs and support future growth. They include the system’s capacity to handle increased data volumes, accommodate new business processes, and integrate with other applications.
Other Success Metrics
In addition to the core metrics mentioned above, other factors can contribute to the success of ERP implementation. These include:
- Timely project completion
- Within-budget implementation
- Reduced risk and disruption
- Improved collaboration and communication
- Enhanced decision-making capabilities
By tracking and analyzing these metrics, organizations can assess the effectiveness of their ERP implementation and identify areas for improvement. Regular monitoring and evaluation ensure that the system continues to meet the evolving needs of the business and deliver sustained value.
Wrap-Up
Embarking on an ERP implementation journey requires careful planning, stakeholder collaboration, and ongoing support. By following the best practices Artikeld in this guide, organizations can harness the full potential of ERP software and achieve significant improvements in their operational efficiency, data management, and overall business performance.
Clarifying Questions
What are the key benefits of ERP implementation?
ERP implementation offers numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced data integration, increased visibility into operations, and improved decision-making capabilities.
What are the common challenges associated with ERP implementation?
ERP implementation projects often face challenges such as data migration complexities, user resistance to change, inadequate training, and lack of stakeholder involvement.
How can organizations ensure successful ERP implementation?
Successful ERP implementation requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement, ongoing support, effective change management, and a dedicated project team with the necessary expertise.