ERP system pricing is a crucial consideration for businesses embarking on digital transformation journeys. Understanding the different pricing models, influencing factors, and potential hidden costs is essential for making informed decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the complexities of ERP system pricing, providing insights and strategies for optimizing costs and maximizing value.
As organizations strive to enhance efficiency, streamline operations, and gain a competitive edge, ERP systems have become indispensable tools. However, navigating the pricing landscape can be challenging, with various factors influencing the overall cost of implementation and ownership. This guide will equip readers with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions and achieve optimal ROI from their ERP investments.
ERP System Pricing Models
ERP systems are priced using various models, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The most common pricing models include:
Per-user pricing
This model charges a fixed fee for each user who accesses the ERP system. It is simple to implement and provides predictable costs. However, it can be expensive for organizations with a large number of users.
Per-module pricing
This model charges a fee for each module or functionality that is used. It allows organizations to pay only for the features they need. However, it can be complex to manage and can lead to unexpected costs if additional modules are required.
Tiered pricing
This model offers different pricing tiers based on the size and complexity of the organization. It provides flexibility and can be cost-effective for small organizations. However, it can be difficult to determine which tier is the best fit for an organization.
Subscription pricing
This model charges a monthly or annual fee for access to the ERP system. It provides predictable costs and eliminates the need for upfront capital investment. However, it can be more expensive than other pricing models over the long term.
Factors Influencing ERP System Pricing
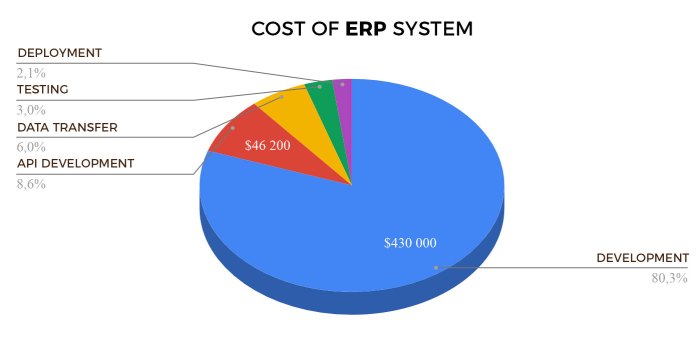
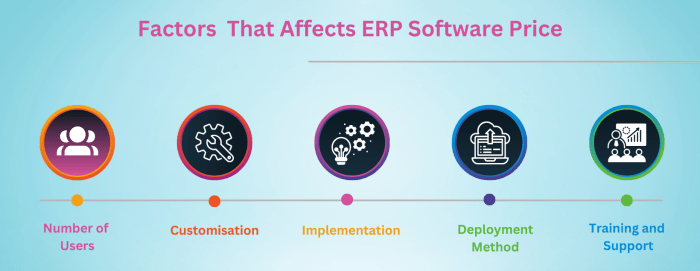
The pricing of ERP systems is influenced by a multitude of factors, ranging from industry-specific requirements to the complexity of the implementation. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses seeking to make informed decisions regarding their ERP investments.
One of the primary factors influencing ERP pricing is the size of the business. Larger enterprises with complex operations and extensive data requirements typically incur higher costs compared to smaller businesses with simpler needs. This is because larger organizations require more comprehensive systems with advanced functionality and scalability, which in turn drives up the overall price.
Industry-Specific Requirements
The industry in which a business operates also plays a significant role in determining ERP pricing. Industries with highly regulated environments, such as healthcare or finance, often require specialized ERP systems that adhere to industry-specific compliance standards. These systems typically involve additional features and customization, leading to higher costs.
Implementation Complexity, ERP system pricing
The complexity of the ERP implementation process can significantly impact the overall pricing. Businesses with complex business processes, multiple locations, or a large number of users may require extensive customization and integration, which can add to the cost of implementation.
Factors such as the need for data migration, training, and ongoing support can also contribute to the overall expense.
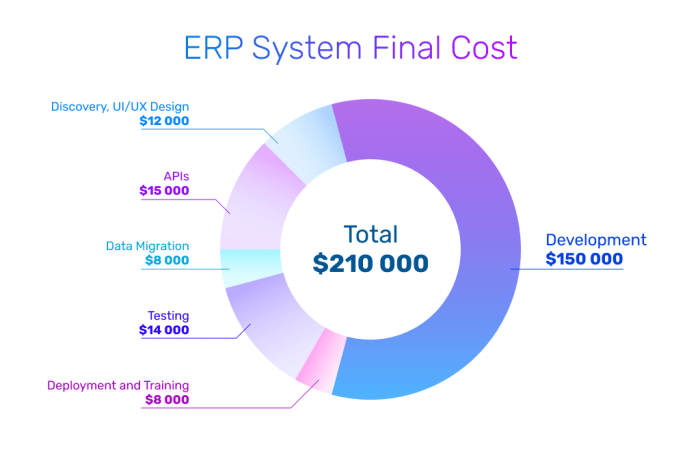
Cost Breakdown of ERP Systems
Implementing an ERP system involves significant costs, encompassing various components that contribute to the overall investment. Understanding this cost breakdown is crucial for organizations to make informed decisions and allocate resources effectively.
The major cost categories associated with ERP system implementation include:
Hardware Costs
- Servers: High-performance servers are required to support the ERP system’s data processing and storage needs.
- Networking equipment: Routers, switches, and firewalls ensure seamless communication and data transfer within the organization.
- Workstations: Each user requires a workstation equipped with appropriate hardware and software to access the ERP system.
Software Costs
- ERP software license: The core ERP software package incurs a licensing fee based on the number of users, modules, and functionality.
- Additional modules: Organizations may require additional modules to extend the ERP system’s capabilities, such as CRM, supply chain management, or business intelligence.
- Customization: Tailoring the ERP system to meet specific business requirements often involves customization costs.
Consulting Costs
- Implementation consulting: Experts guide organizations through the ERP implementation process, ensuring smooth deployment and user adoption.
- Data migration consulting: Converting and transferring existing data into the new ERP system requires specialized consulting services.
- Training consulting: Consultants provide training to users on the ERP system’s functionality and best practices.
Training Costs
- User training: End-users require comprehensive training to effectively utilize the ERP system and maximize its benefits.
- Train-the-trainer programs: Empowering internal staff to train new users or provide ongoing support reduces long-term training costs.
Maintenance Costs
- Software updates: Regular software updates ensure the ERP system remains current with industry standards and security patches.
- Hardware maintenance: Ongoing maintenance contracts for servers and workstations ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Support and troubleshooting: Organizations may require ongoing support from the ERP vendor or a third-party provider for troubleshooting and problem resolution.
Comparison of ERP System Pricing
ERP systems vary significantly in terms of pricing, depending on factors such as vendor reputation, system complexity, and licensing terms. To help organizations make informed decisions, it’s essential to compare the pricing of different ERP systems from leading vendors.
The following table provides a summary of the key features, pricing, and licensing terms of several popular ERP systems:
Pricing Comparison Table
| ERP System | Key Features | Pricing Model | Licensing Terms |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP S/4HANA |
|
Subscription-based | Per-user, per-month |
| Oracle NetSuite |
|
Subscription-based | Per-user, per-month |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 |
|
Subscription-based | Per-user, per-month or per-app |
| Epicor ERP |
|
Perpetual license | One-time fee, with ongoing maintenance costs |
| Infor CloudSuite |
|
Subscription-based | Per-user, per-month |
Negotiating ERP System Pricing
Negotiating ERP system pricing can be a complex process, but it is essential to get the best possible price for your organization. Here are a few tips and strategies to help you negotiate the best possible price for an ERP system:
Before you begin negotiating, it is important to understand your needs and what you are willing to pay. This will help you to set realistic expectations and avoid overpaying for features that you do not need.
Understanding Your Needs
The first step in negotiating ERP system pricing is to understand your needs. What are the specific requirements of your organization? What are your goals for implementing an ERP system? Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, you can start to evaluate different ERP systems and compare their pricing.
Leveraging Competitive Quotes
Once you have a few ERP systems in mind, it is important to get competitive quotes from each vendor. This will give you a good idea of the market price for ERP systems and help you to negotiate a better price.
When you are negotiating with a vendor, be sure to be prepared to walk away. If you are not satisfied with the price or the terms of the contract, do not be afraid to look for another vendor.
Hidden Costs of ERP Systems
ERP system implementation involves not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing costs that can significantly impact the total cost of ownership. These hidden costs can be categorized into three main areas: customization, integration, and ongoing support.
Customization Costs
ERP systems are often customized to meet the specific needs of an organization. Customization can involve modifying the software’s functionality, adding new features, or integrating with other systems. While customization can enhance the value of the ERP system, it can also increase the overall cost.
The complexity and extent of customization determine the cost, which can range from a few thousand dollars to hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Integration Costs
ERP systems need to be integrated with other systems within an organization, such as CRM, accounting, and supply chain management systems. Integration costs can vary depending on the number of systems being integrated, the complexity of the integration, and the expertise of the integration team.
Integration costs can range from a few thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars.
Ongoing Support Costs
ERP systems require ongoing support to ensure optimal performance and security. Support costs include software updates, bug fixes, technical assistance, and user training. The cost of ongoing support is typically a percentage of the initial purchase price and can range from 15% to 25% per year.Understanding these hidden costs is crucial for organizations considering ERP system implementation.
By carefully considering these costs and factoring them into the total cost of ownership, organizations can make informed decisions and avoid unexpected expenses.
Return on Investment (ROI) of ERP Systems
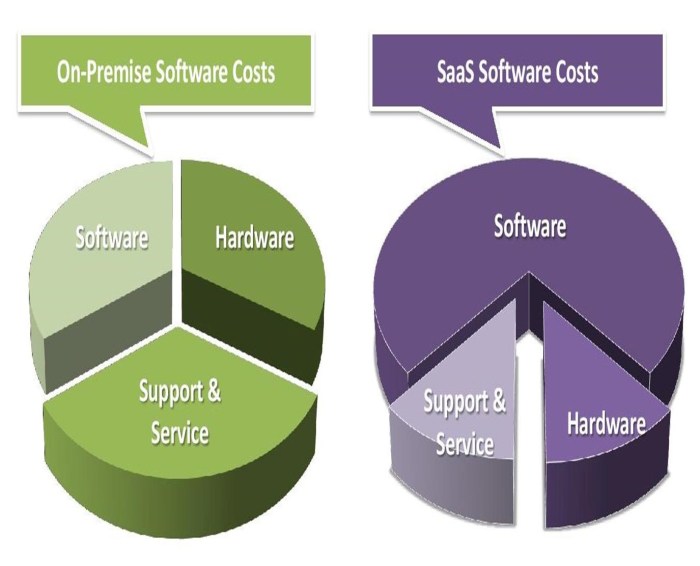
ERP systems can provide significant returns on investment (ROI) for businesses. To calculate the ROI of an ERP system implementation, businesses can compare the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the ERP system to the benefits it provides. The TCO includes the cost of the software, hardware, implementation, maintenance, and support.
The benefits of an ERP system can be both quantifiable and intangible.
Quantifiable Benefits
Quantifiable benefits of ERP systems include:
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Reduced costs
- Improved customer service
- Increased sales
- Improved decision-making
Intangible Value
Intangible benefits of ERP systems include:
- Improved collaboration
- Increased agility
- Enhanced visibility
- Improved risk management
- Increased innovation
The ROI of an ERP system can be calculated using the following formula:
ROI = (Benefits
Costs) / Costs
For example, if an ERP system costs $1 million to implement and provides benefits of $2 million, the ROI would be 100%.It is important to note that the ROI of an ERP system can vary depending on the size and complexity of the business, the industry, and the specific ERP system implemented.
Case Studies of ERP System Pricing

ERP system implementations can vary significantly in terms of pricing and ROI. Here are a few case studies of companies that have successfully implemented ERP systems:
Microsoft Dynamics AX Implementation at Harley-Davidson
Harley-Davidson implemented Microsoft Dynamics AX to streamline its operations and improve efficiency. The company invested $100 million in the project and achieved an ROI of 200% within three years. The ERP system helped Harley-Davidson to reduce its inventory costs by 15%, improve its customer service by 20%, and increase its sales by 10%.
SAP ERP Implementation at Unilever
Unilever implemented SAP ERP to consolidate its global operations and improve its financial reporting. The company invested $1 billion in the project and achieved an ROI of 150% within five years. The ERP system helped Unilever to reduce its operating costs by 10%, improve its inventory management by 20%, and increase its sales by 5%.
Oracle NetSuite Implementation at Netflix
Netflix implemented Oracle NetSuite to manage its rapidly growing business. The company invested $50 million in the project and achieved an ROI of 300% within two years. The ERP system helped Netflix to reduce its operating costs by 15%, improve its customer service by 25%, and increase its sales by 20%.These case studies demonstrate that ERP systems can provide a significant ROI for companies of all sizes.
The key to success is to choose the right ERP system for your business and to implement it properly.
Trends in ERP System Pricing
ERP system pricing is evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing customer needs. Emerging trends include:
- Subscription-based pricing:ERP vendors are increasingly offering subscription-based models, allowing customers to pay for access to the software on a monthly or annual basis. This provides greater flexibility and reduces upfront costs.
- Cloud-based pricing:Cloud-based ERP systems are becoming more popular, and their pricing models often differ from on-premise systems. Cloud-based pricing is typically subscription-based and may include additional fees for usage, storage, or support.
- Tiered pricing:ERP vendors often offer tiered pricing models, with different tiers offering different levels of functionality and support. This allows customers to choose the package that best fits their needs and budget.
- Value-based pricing:Some ERP vendors are moving towards value-based pricing models, where the price is based on the value that the ERP system delivers to the customer. This can be a more flexible and customer-centric approach to pricing.
These trends are impacting the cost of ERP implementation and ownership in several ways:
- Lower upfront costs:Subscription-based and cloud-based pricing models can reduce upfront costs, making ERP systems more accessible to small and medium-sized businesses.
- Increased flexibility:Subscription-based pricing allows customers to scale their ERP usage up or down as needed, providing greater flexibility in managing costs.
- Improved cost predictability:Subscription-based and tiered pricing models provide greater cost predictability, making it easier for businesses to budget for ERP costs.
Future of ERP System Pricing
The future of ERP system pricing is likely to be shaped by a number of factors, including the increasing adoption of cloud computing, the growing use of artificial intelligence (AI), and the emergence of new technologies such as blockchain.
Cloud computing is already having a major impact on the way that businesses purchase and use ERP systems. In the past, businesses had to purchase and install ERP systems on their own servers. This was a costly and time-consuming process.
Cloud computing allows businesses to rent ERP systems from a provider, which can save them a significant amount of money and time. As cloud computing becomes more popular, it is likely that ERP system pricing will become more flexible and affordable.
AI is also having a major impact on the way that businesses use ERP systems. AI can be used to automate many of the tasks that are traditionally performed by humans. This can free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
AI can also be used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of ERP systems. As AI becomes more sophisticated, it is likely that ERP system pricing will become more competitive.
New technologies such as blockchain are also likely to have a major impact on the future of ERP system pricing. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that can be used to create secure and transparent records of transactions. This could make it possible for businesses to share ERP data with each other in a more secure and efficient way.
As blockchain becomes more widely adopted, it is likely that ERP system pricing will become more flexible and affordable.
Impact of Cloud Computing on ERP System Pricing
- Cloud computing can save businesses a significant amount of money on ERP system costs.
- Cloud computing can make ERP systems more accessible to small businesses.
- Cloud computing can make it easier for businesses to upgrade their ERP systems.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on ERP System Pricing
- AI can automate many of the tasks that are traditionally performed by humans, which can save businesses money.
- AI can improve the accuracy and efficiency of ERP systems, which can lead to increased profits.
- AI can make ERP systems more user-friendly, which can make them more valuable to businesses.
Impact of New Technologies on ERP System Pricing
- New technologies such as blockchain could make it possible for businesses to share ERP data with each other in a more secure and efficient way.
- New technologies could make ERP systems more flexible and affordable.
- New technologies could make ERP systems more valuable to businesses.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, ERP system pricing is a multifaceted topic that requires careful consideration. By understanding the different pricing models, influencing factors, and potential hidden costs, businesses can make informed decisions and negotiate the best possible terms. Remember, the true value of an ERP system lies not only in its features and functionality but also in its ability to drive tangible benefits and intangible value for the organization.
Embracing a strategic approach to ERP system pricing can empower businesses to unlock the full potential of these transformative technologies and achieve lasting success.
Questions Often Asked
What are the different pricing models for ERP systems?
ERP systems are typically priced using one of three models: perpetual license, subscription, or cloud-based pricing. Perpetual license involves a one-time payment for the software, while subscription pricing involves regular payments for ongoing access and support. Cloud-based pricing is based on a monthly or annual subscription fee.
What factors influence ERP system pricing?
ERP system pricing can vary depending on several factors, including the number of users, the complexity of the implementation, the industry, and the size of the business. Additional factors such as customization, integration, and ongoing support can also impact the overall cost.
What are the potential hidden costs of ERP systems?
Hidden costs of ERP systems can include customization, integration, data migration, training, and ongoing maintenance and support. It is important to consider these costs when budgeting for an ERP implementation.